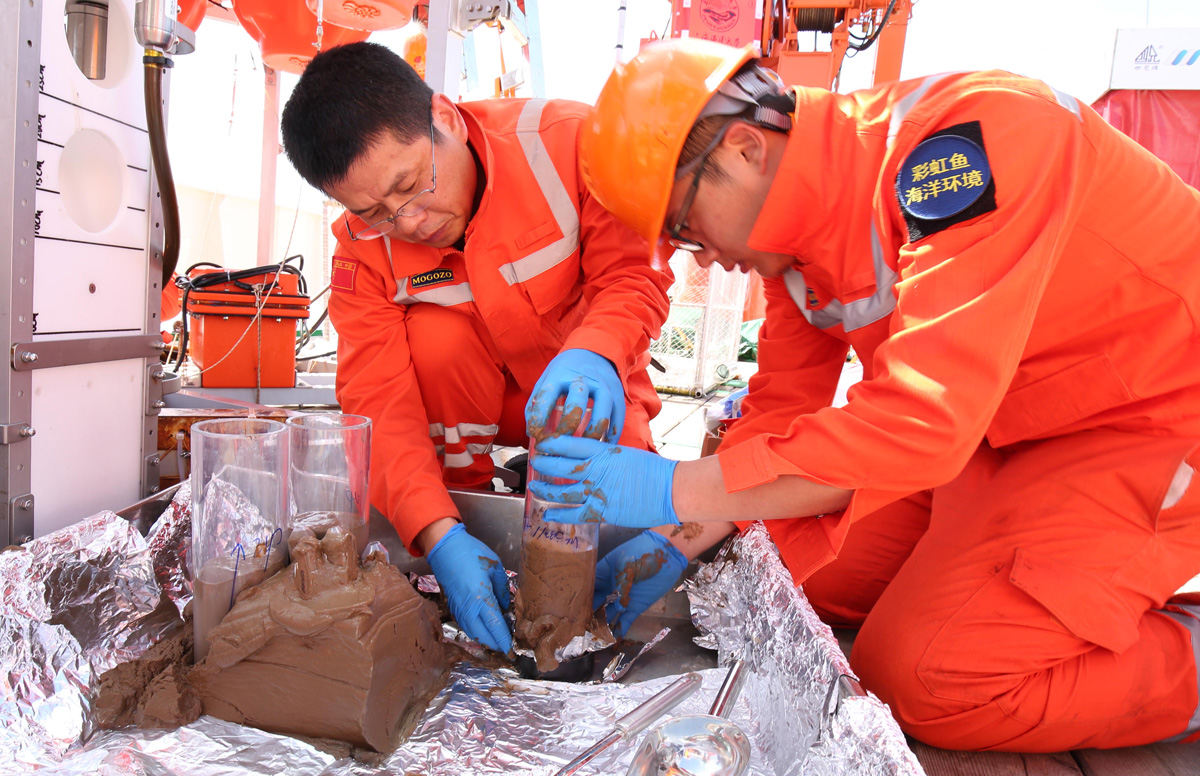
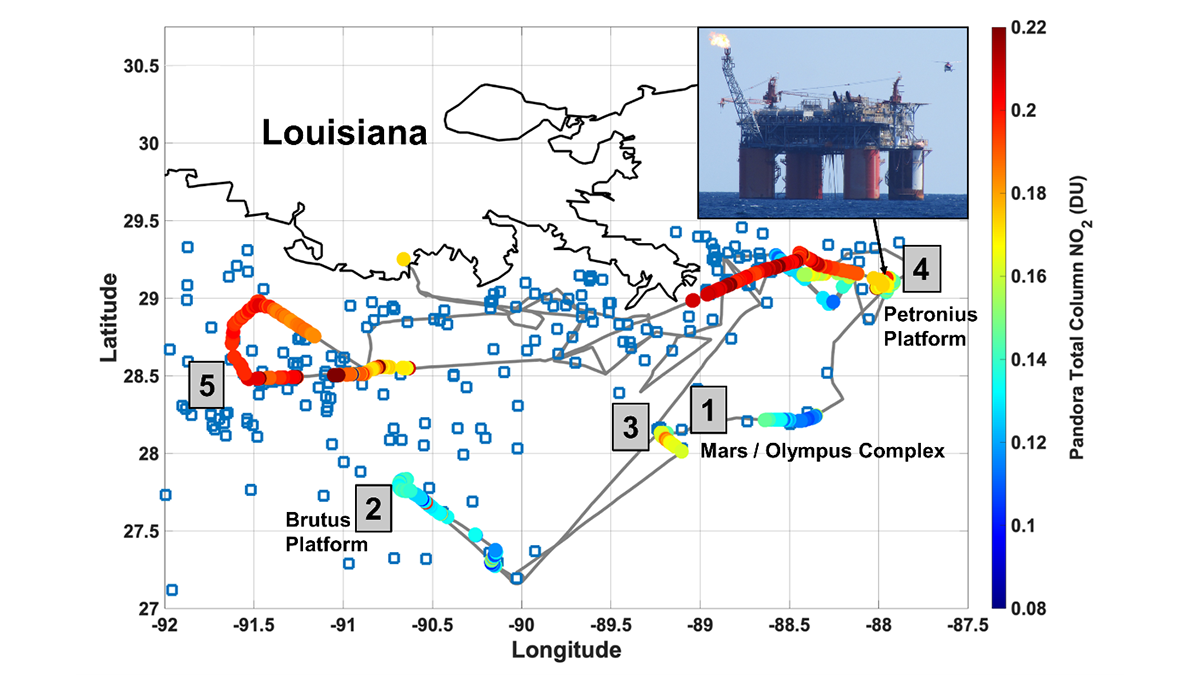
Satellites can see NO2 pollution from space, but can they detect individual oil and natural gas operations, and are the measurements accurate?
pollution
Seafloor Plastic Pollution Is Not Going Anywhere
The amount of microplastics at the bottom of the Mediterranean is growing as global production increases and plastic breakdown is halted.
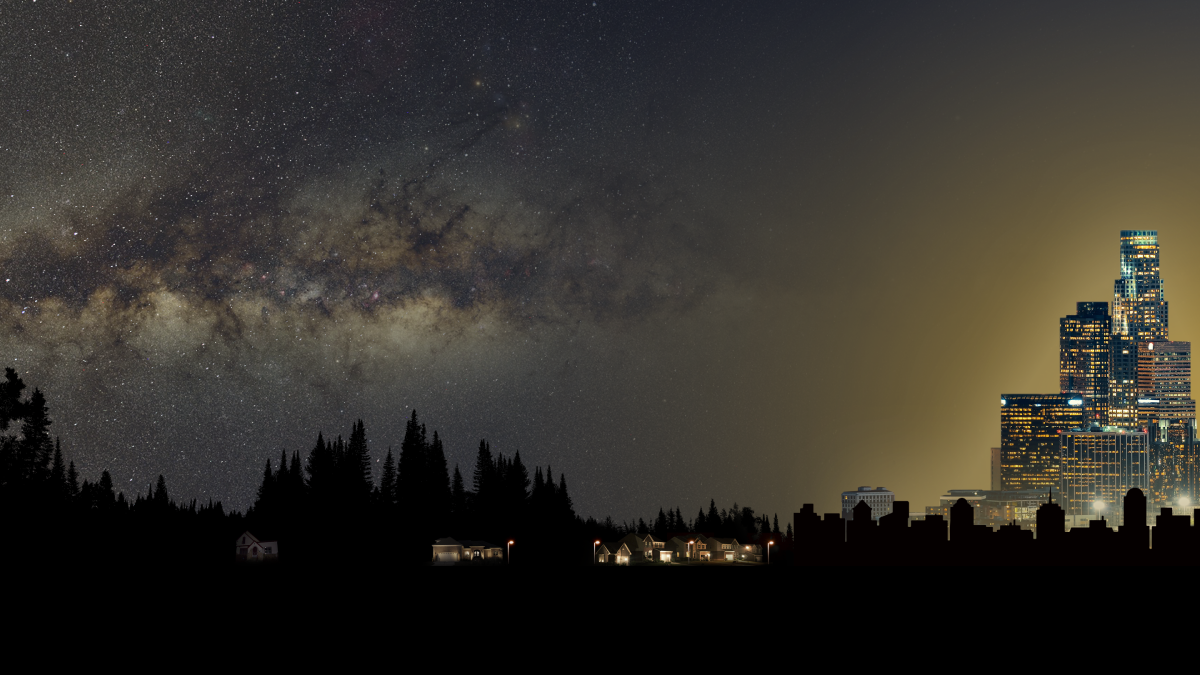
Starry Nights Are Disappearing
Stars dim as the sky gets brighter, a result of expanding cities and bright LEDs. Simple low-tech changes can help preserve dark night skies.
Sedimentos lacustres registran el legado del carbón de Carolina del Norte
Los lagos contaminados con cenizas de carbón se encuentran en áreas residenciales y recreativas, provocando preocupaciones por la salud de los residentes locales y los ecosistemas.
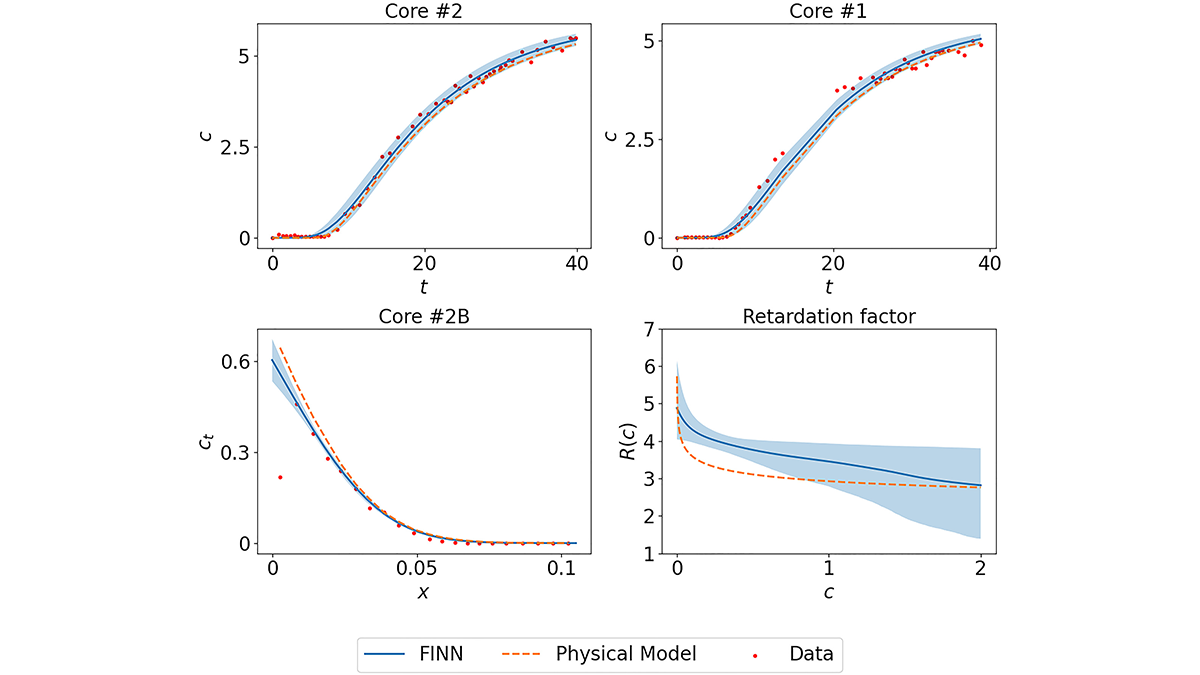
Playing Bricks with Neural Networks to Learn Sorption Processes
Designated neural network modules are combined to mimic numerically-discretized diffusion-sorption equations, which allows learning “missing pieces” in system understanding and their uncertainties.
Even at the Bottom of the World, the Ocean Is Belching Plastic
Plastic fills the air above Auckland, New Zealand.
Mapeando estimaciones de la contaminación a nivel de calle para encontrar rutas más seguras
Un nuevo enfoque de alta resolución que combina múltiples tipos de datos detección remota de la contaminación permitió a investigadores desarrollar una aplicación que mapea las rutas más saludables para los transeúntes urbanos.
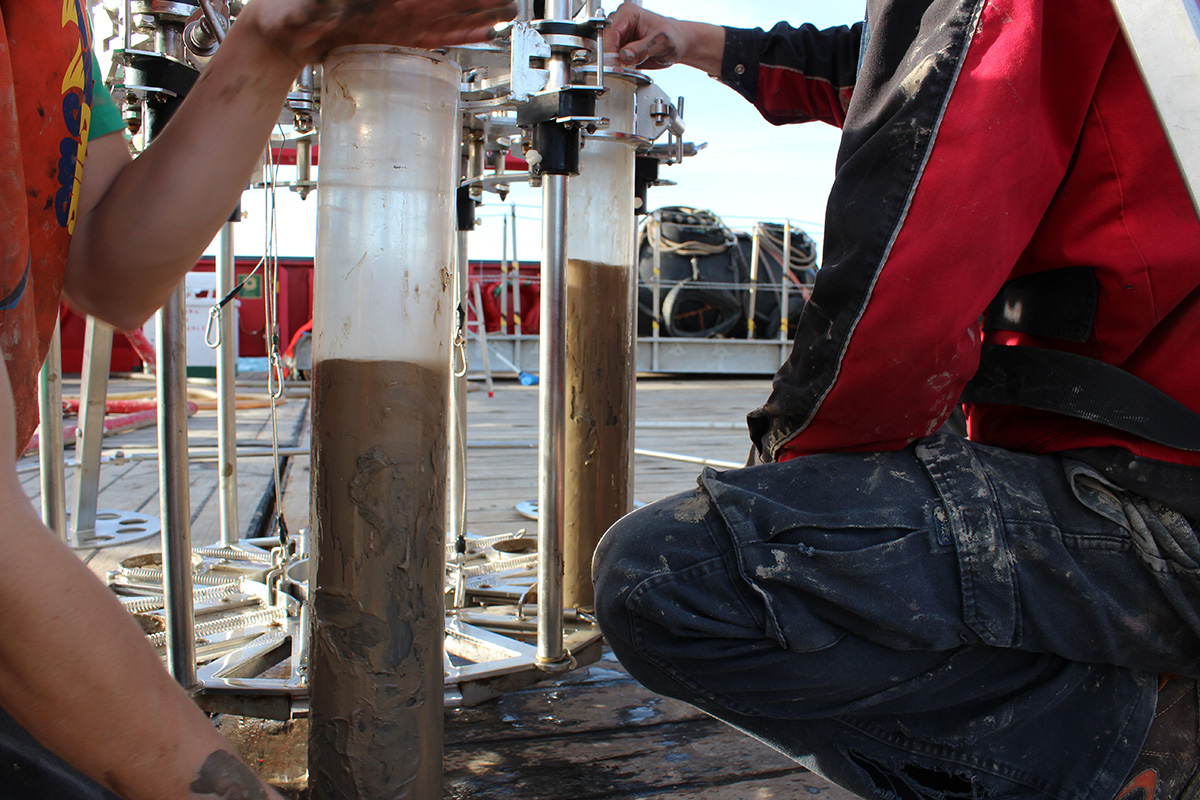
In the Deepest Ocean Reaches, a Potent Pollutant Comes to Rest
Surprising amounts of mercury settling into deep-sea trenches may provide a fuller picture of the metal’s path through the environment, but pulling it to the surface is no easy feat.
通过街道污染估计图选择更健康的通行路线
研究人员采用一种新的高分辨率方法结合多种类型的遥感污染数据,开发出一款应用程序,可为城市通勤者绘制最健康的路线。
Mapping Street-Level Pollution Estimates to Reveal Safer Routes
A new high-resolution approach combining multiple types of remotely sensed pollution data allowed researchers to develop an app that maps the healthiest routes for urban commuters.