A multidisciplinary team studying lake sediments and climate change found evidence that the archipelago was inhabited 700 years earlier than historical sources claim.
sediments
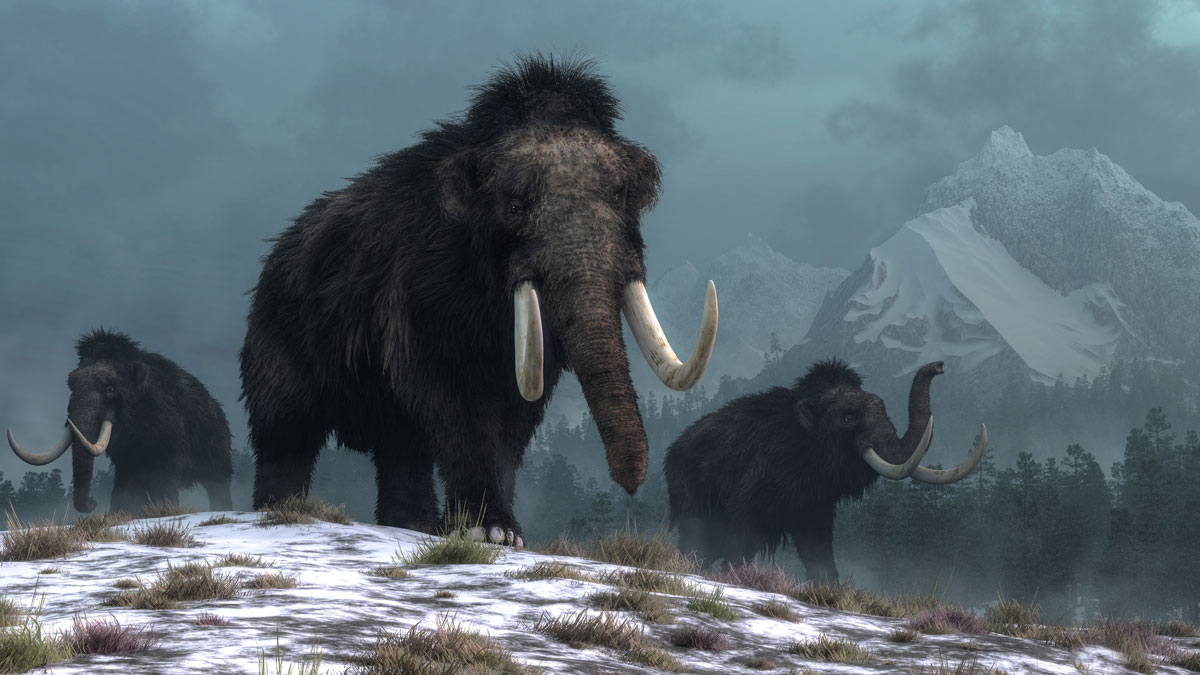
Mammoths Lost Their Steppe Habitat to Climate Change
Ancient plant and animal DNA buried in Arctic sediments preserve a 50,000-year history of Arctic ecosystems, suggesting that climate change contributed to mammoth extinction.
New Theory Connects Tree Uprooting and Sediment Movement
Tree throw from extreme wind events plays an important role in the movement of sediment and erosion on forested hillslopes. A new theory offers a novel way to measure its impact.
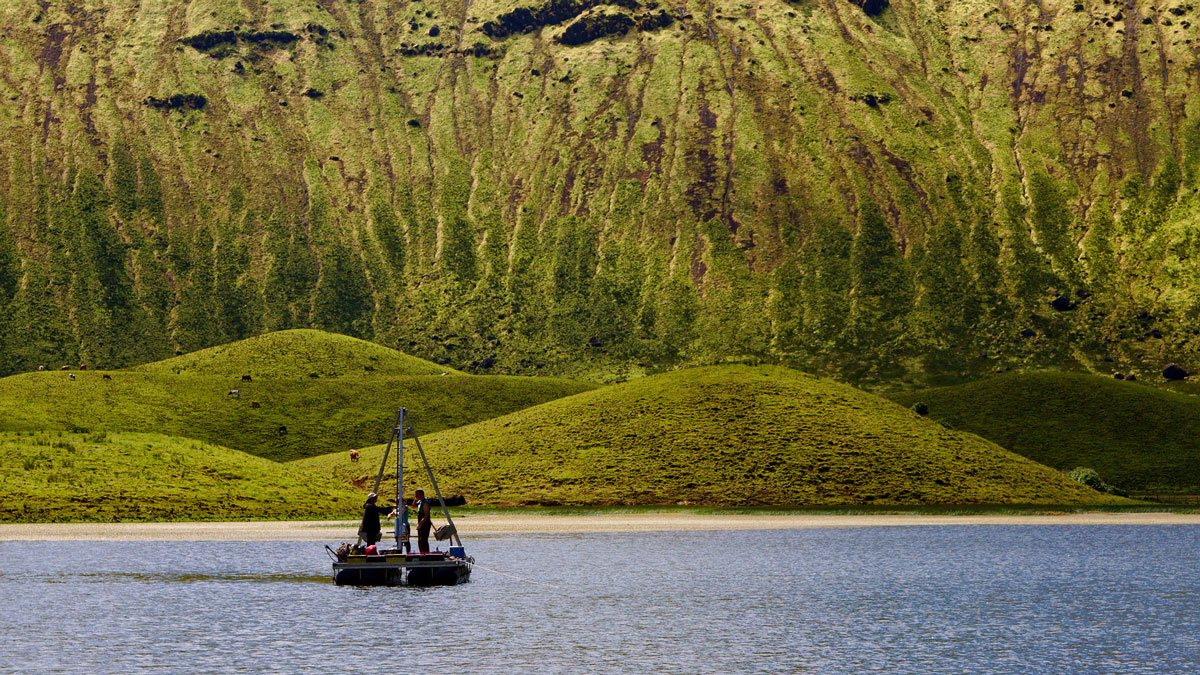
Māori Arrival in New Zealand Revealed in Antarctic Ice Cores
A new study shows smoke from fires set by the first inhabitants of Aotearoa from around 1300 left a mark in the ice 6,000 kilometers away, on an island off the Antarctic Peninsula.
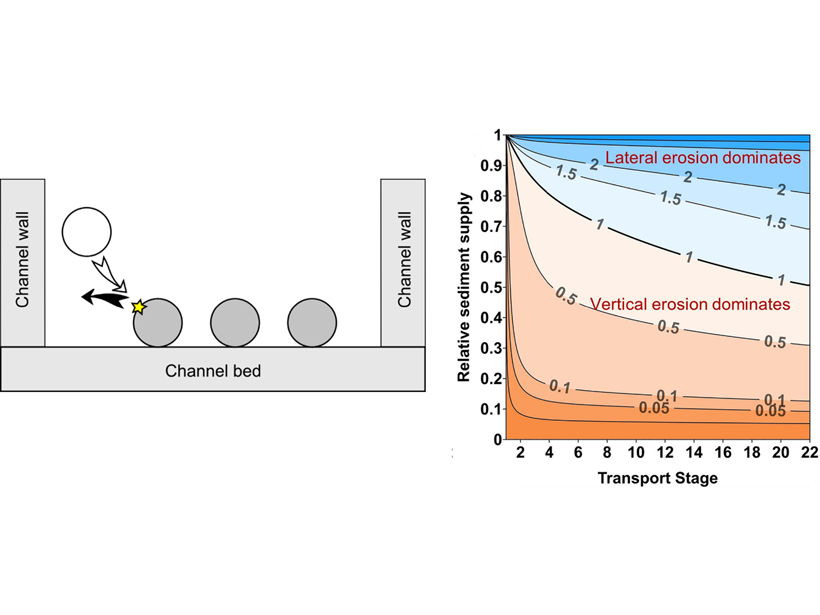
Impacts by Moving Gravel Cause River Channels to Widen or Narrow
A new analytical model describes how the amount and grain size of sediment transported by rivers influences bedrock channel width, which can be used to predict where rivers will widen or narrow.
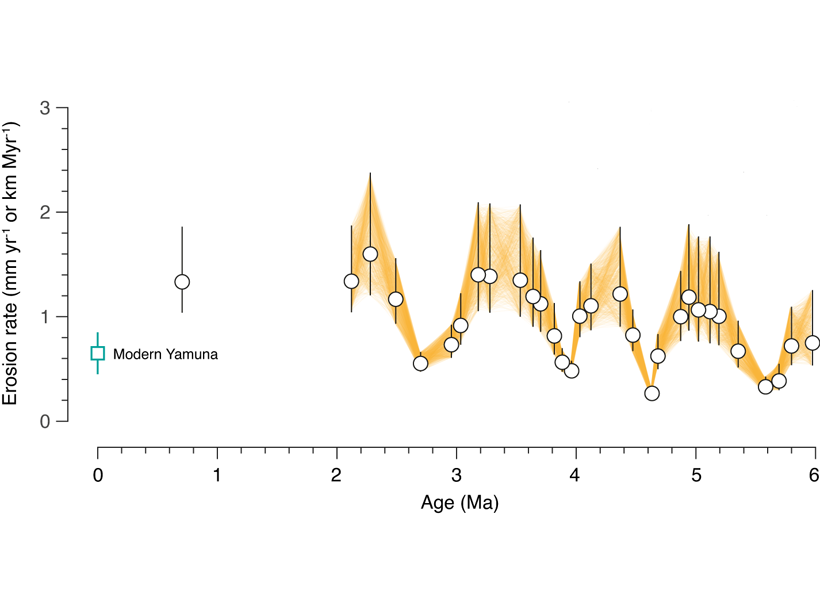
Himalayan Tectonics in the Driver’s Seat, Not Climate?
Earth’s oscillating climate is a natural guess to explain cyclic patterns in erosion, but new sediment data suggests that cyclicity may emerge from tectonic processes adding material to the Himalaya.
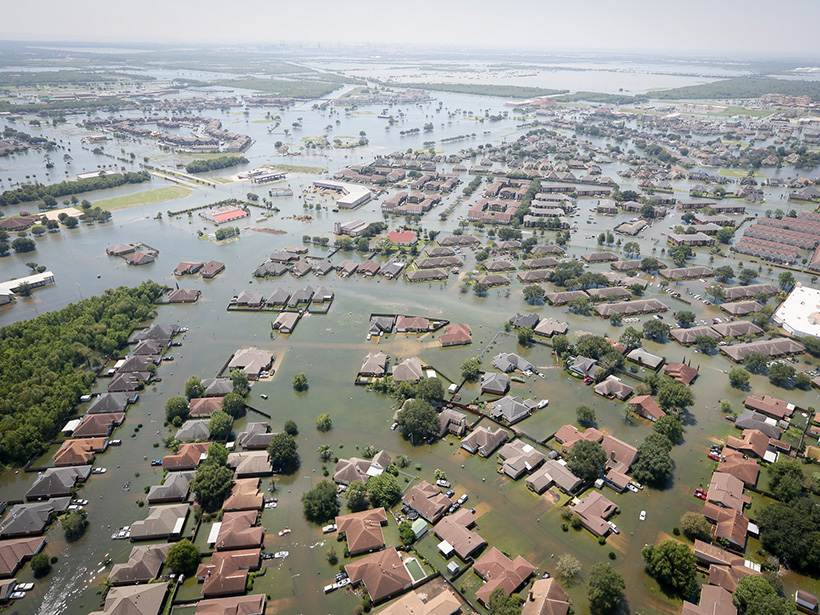
When Rivers Are Contaminated, Floods Are Only the First Problem
As floods increase in frequency and intensity, chemicals buried in river sediments become “ticking time bombs” waiting to activate.
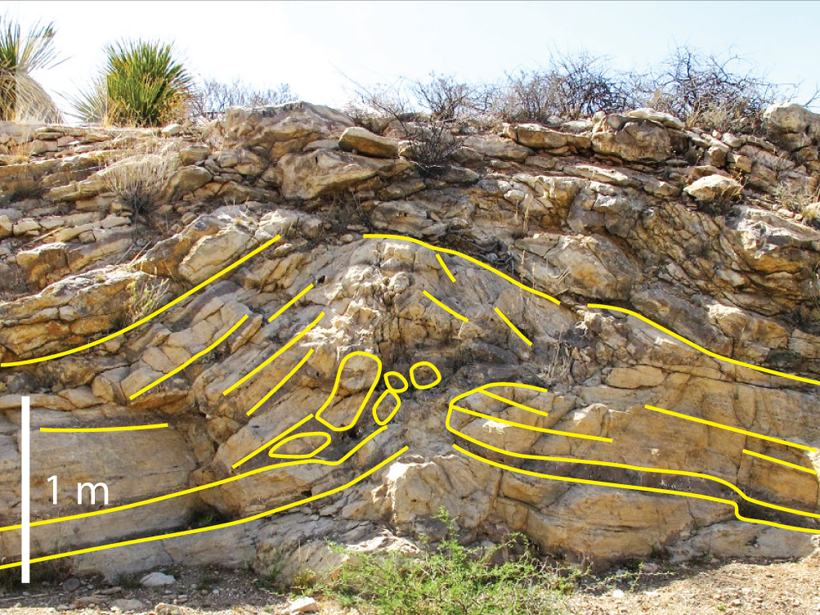
Sedimentary Tepees Record Ocean Chemistry
Sedimentary structures from evaporative coastal environments indicate carbonate saturation, offer insight in mid-Mesozoic ocean chemistry and potentially even earlier times.
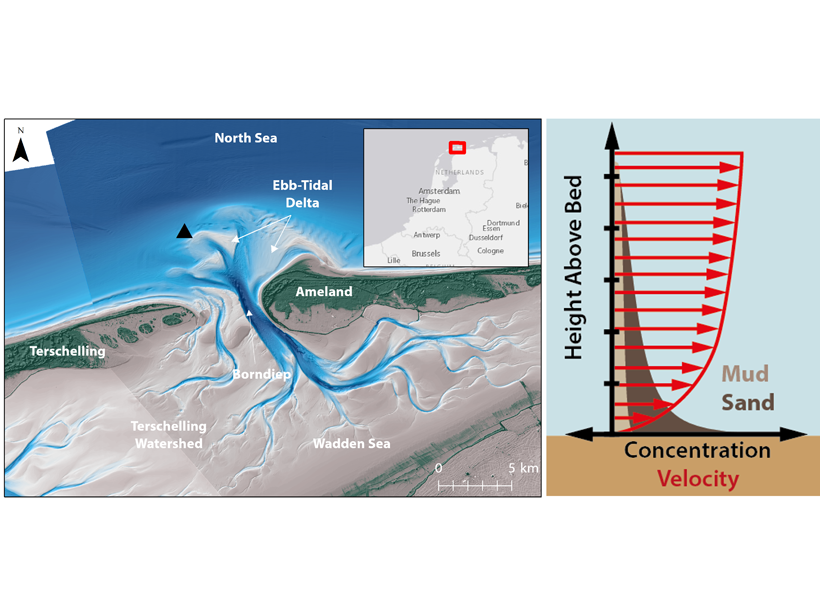
Unravelling Sands and Muds Suspended in Coastal Environments
A new study uses the response of optical and acoustic measurements to derive a sediment composition index for prediction of the relative fractions of mixed sediments in suspension.
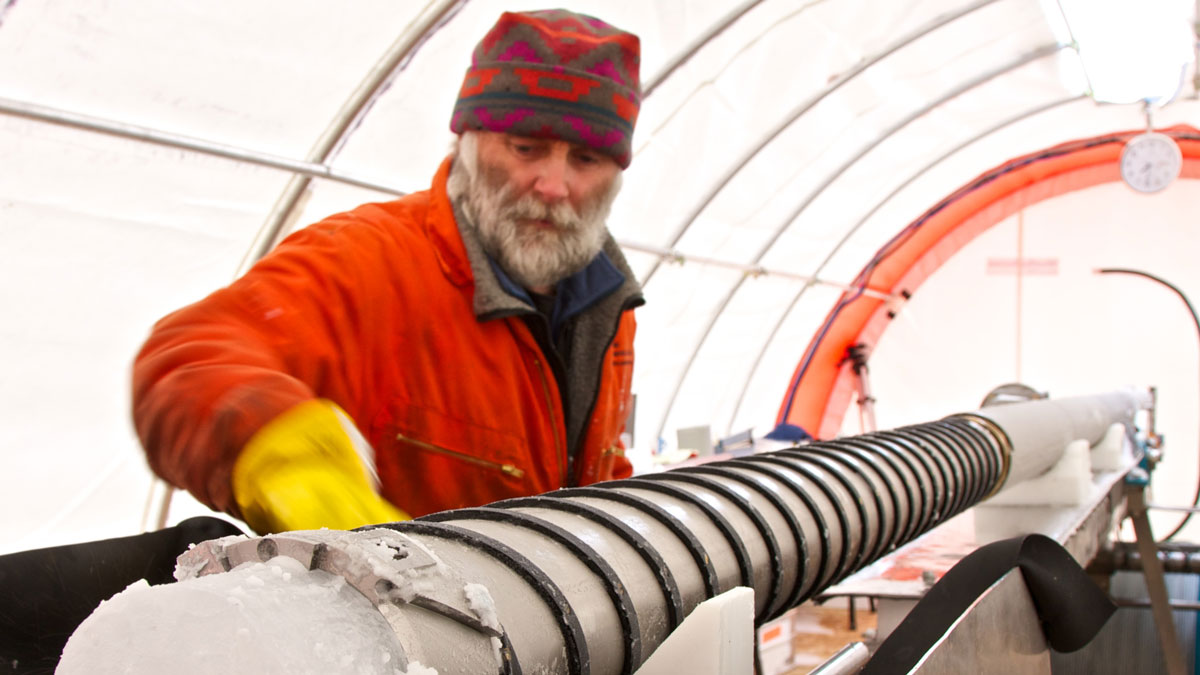
Cutting to the Core
In our July issue, Eos looks at the collection, study, and storage of cores—from sediment drilled up from the age of the dinosaurs to tree rings as big as a house.