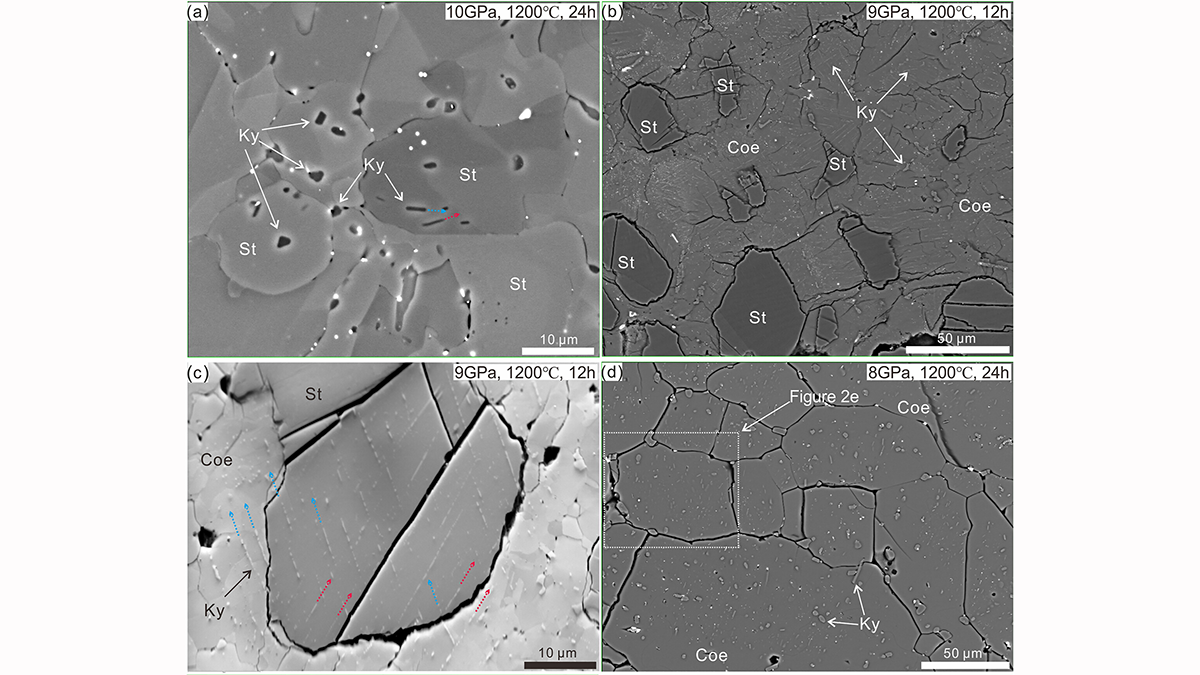
Laboratory experiments provide the first experimental evidence that continental rocks can be subducted to depths greater than 300 kilometers and return to the surface.
seismology
Where the Tianshan Will Break Next: Strain, Slip, and Seismic Hazard
Geodetic strain and slip deficits reveal where the Tianshan is storing stress and which faults may generate the next major earthquakes in the region.
Are We Really Seeing More Foreshocks with Enhanced Catalogs?
Different definitions and selection methods can lead to large differences in estimated foreshock rates; however, robust statistical method shows that foreshock rates are similar between standard and enhanced catalog.
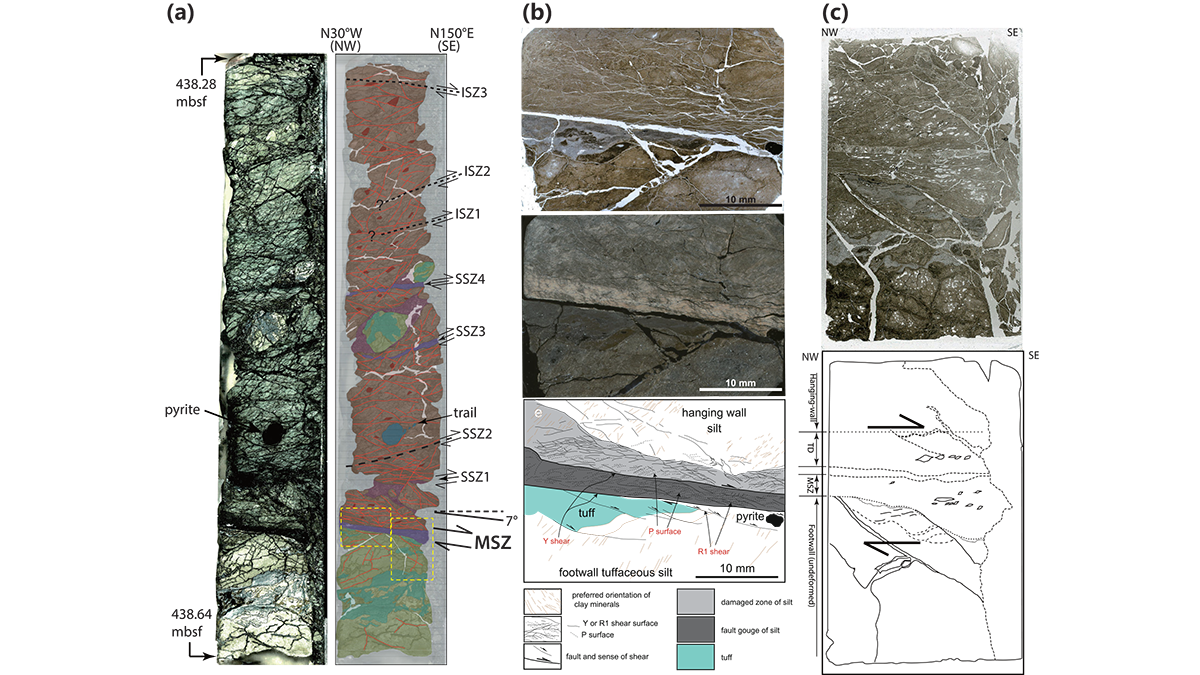
Frictional Properties of the Nankai Accretionary Prism
A database of frictional properties from IODP drilling materials explores the range of slip spectrum and the generation of slow to fast earthquakes in the Nankai subduction zone in light of mineralogy.
The Land Beneath Antarctica’s Ice Might Be Full of Water
Seismic surveys hint at the extent of a potential groundwater system in the White Continent.
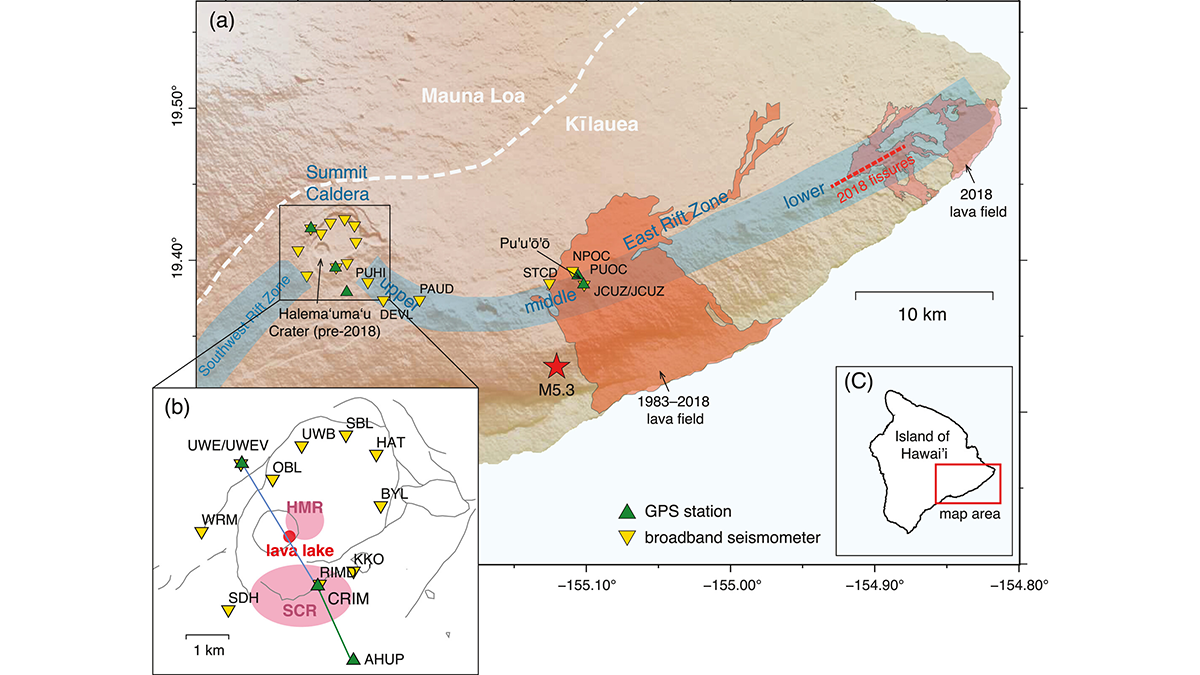
Complex Plumbing Dynamics for Kīlauea Volcano
A new analysis of subtle seismic velocity changes provides insights into the coupling of magma reservoirs of Hawaiian volcanoes.
The Ridgecrest Earthquake Left Enduring Damage in Earth’s Deep Crust
The shallow crust has recovered since California’s 2019 quake, but damage persists at depths greater than 10 kilometers.
AI is Changing our Understanding of Earthquakes
Machine learning is expanding scientists’ catalogs of quakes and refining maps of underground faults. It also promises to improve quake forecasts.
New Earthquake Model Goes Against the Grain
Subducting plates are stronger in certain directions than others, which may be a factor in how earthquakes occur and how seismic waves propagate.
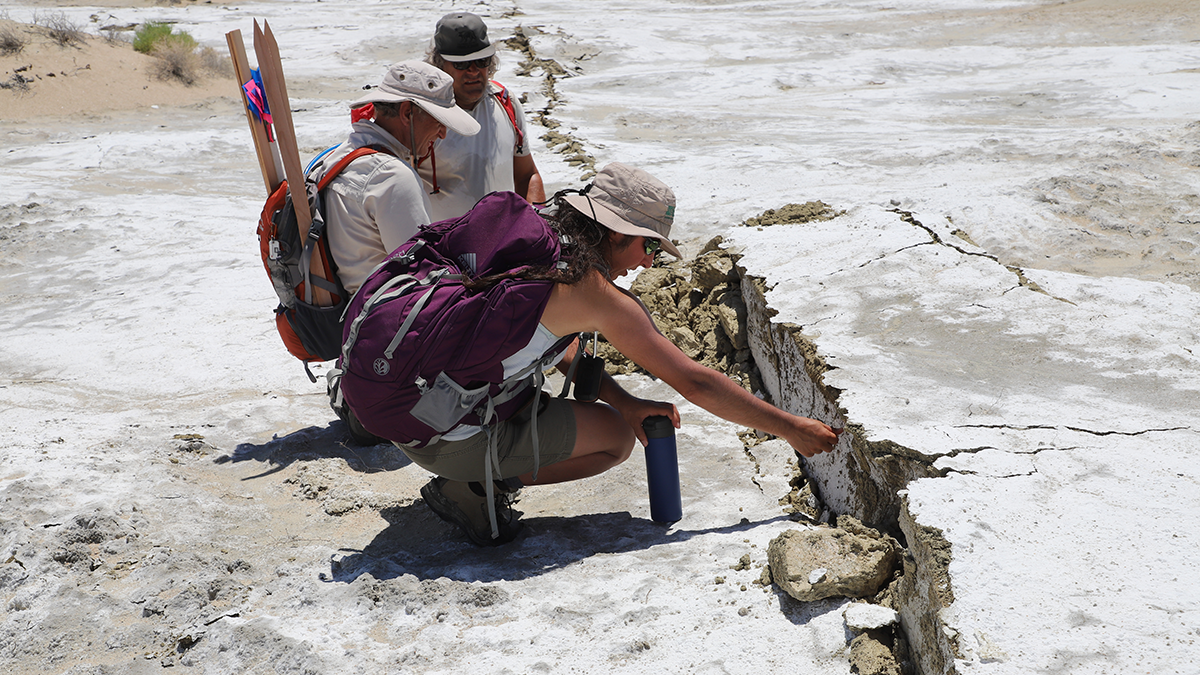
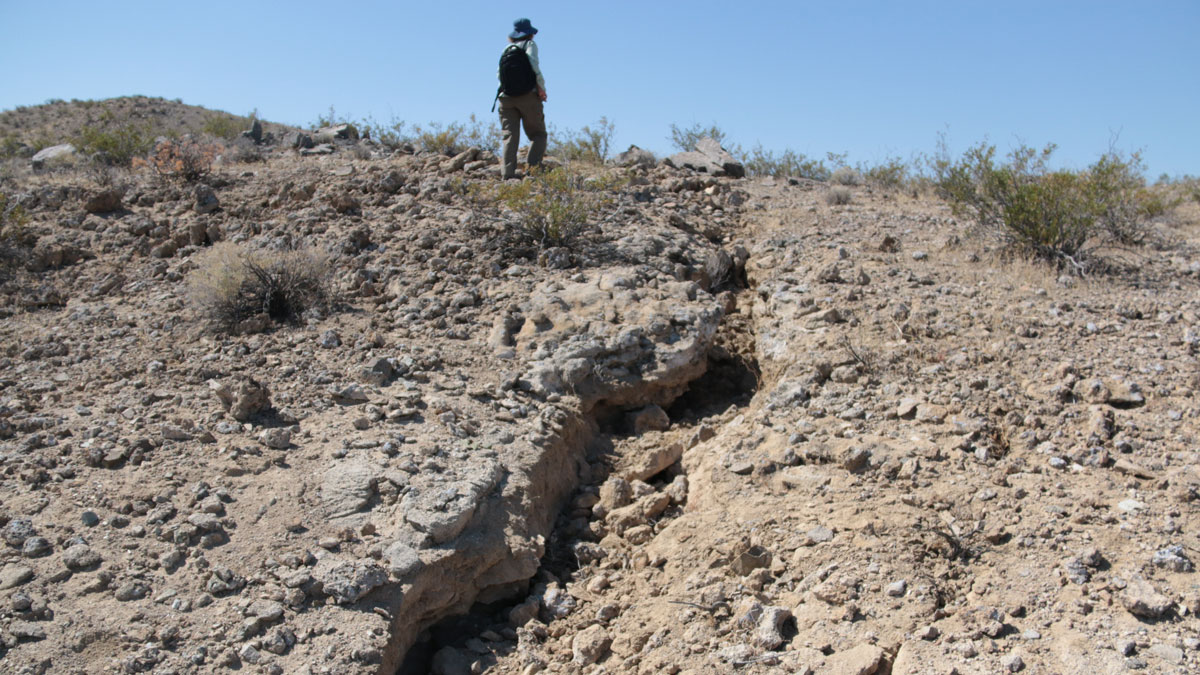
When the Earth Moves: 25 Years of Probabilistic Fault Displacement Hazards
Surface ruptures causing earthquakes pose risks to infrastructure and human lives, but advances in models and data in the last few decades have improved our ability to mitigate their effects.