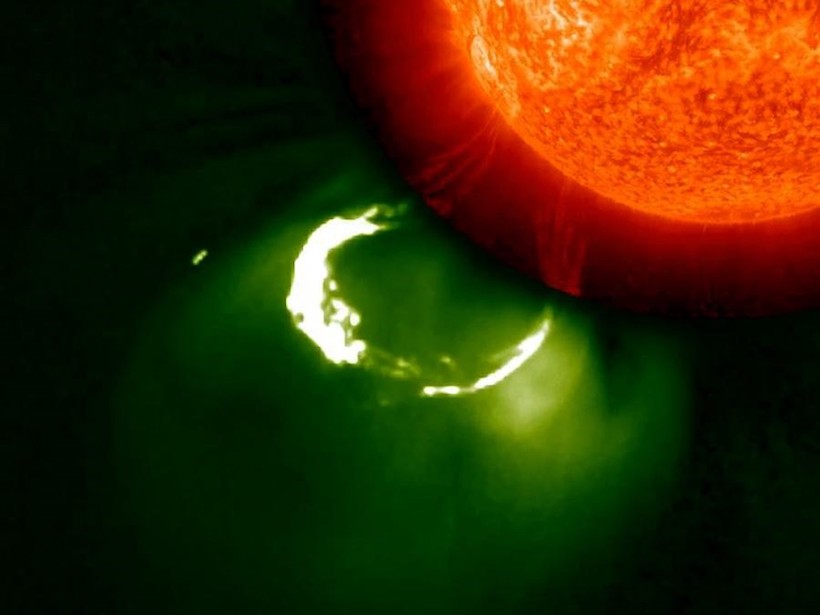
Researchers turned to crowdsourced science to identify patterns in coronal mass ejections.
solar activity
Scientists Claim a More Accurate Method of Predicting Solar Flares
Supercomputer 3D modeling of magnetic fields could help mitigate damage from geomagnetic storms.
The Importance of Solar Lyman-alpha Emissions for Space Weather
Lyman-alpha emissions convey a major part of the solar-flare photon energy reaching Earth and play a significant role in flare-driven enhancements of ionospheric conductivity.
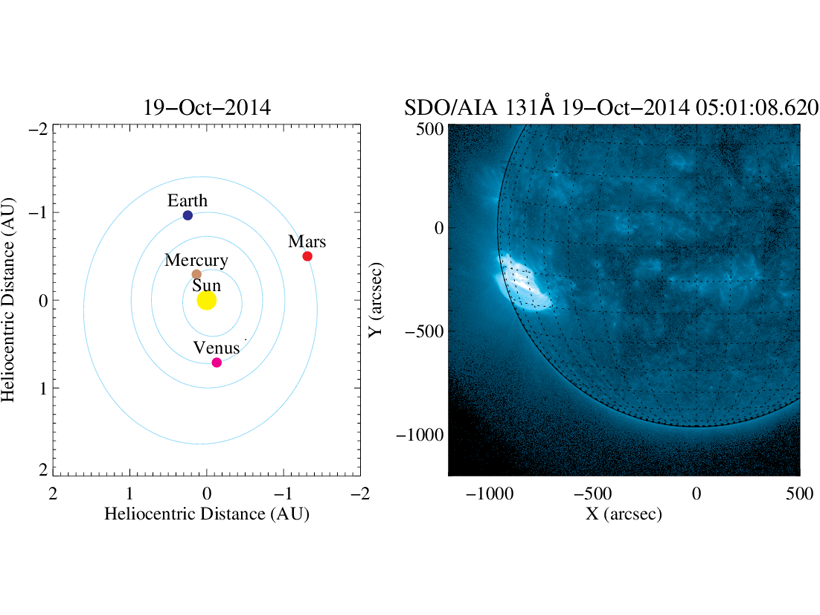
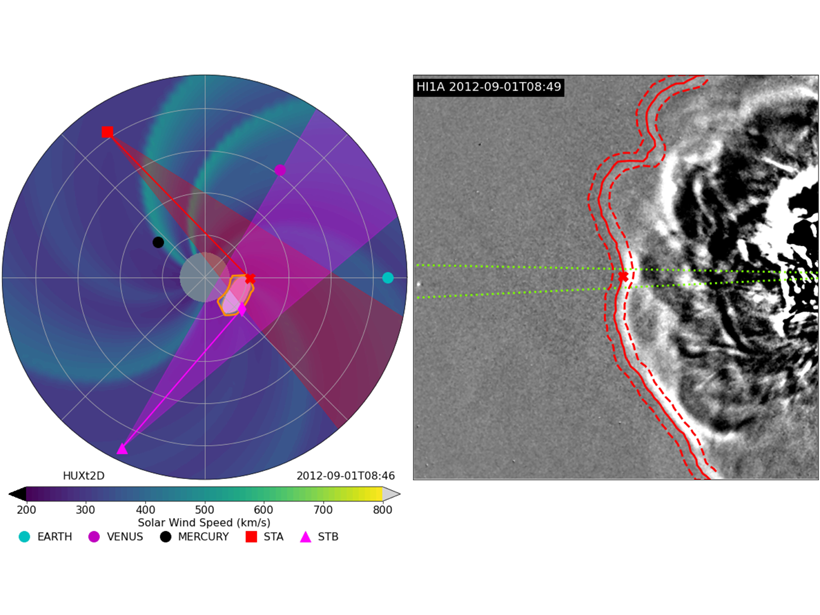
Ensemble Modeling of Coronal Mass Ejection Arrival at 1 AU
Heliospheric imaging data can be used in ensemble modeling of CME arrival time at Earth to improve space weather forecasts, treating the solar wind as a 1-D incompressible hydrodynamic flow.
Liu Receives 2019 Fred L. Scarf Award
Terry Zixu Liu received the 2019 Fred L. Scarf Award at AGU’s Fall Meeting 2019, held 9–13 December in San Francisco, Calif. The award is given annually to “one honoree in recognition of an outstanding dissertation that contributes directly to solar–planetary science.”
Ghostly Particles from the Sun Confirm Nuclear Fusion
Using the Borexino particle detector—located deep underground in Italy—researchers spot elusive neutrinos from the Sun’s CNO cycle.
How to Improve Space Weather Forecasting
The field of space weather forecasting could take cues from its Earthly counterpart to increase the reliability of models as well as warning times ahead of inbound solar storms.
Using Earth’s Atmosphere as a Solar Flare Monitor
Measurements of very-low frequency radio signal phase and amplitude can detect upper atmosphere changes caused by solar flares, enabling us to monitor flare occurrence and intensity.
Ancient Assyrian Aurorae Help Astronomers Understand Solar Activity
Records of aurorae in Mesopotamia from 2,600 years ago are helping astronomers understand and predict solar activity today.
Hearing the Sun Tock
The appearance of sunspots—their number, duration, and location—suggests that the dynamics of the Sun’s outer layer is synchronized with an internal clock.