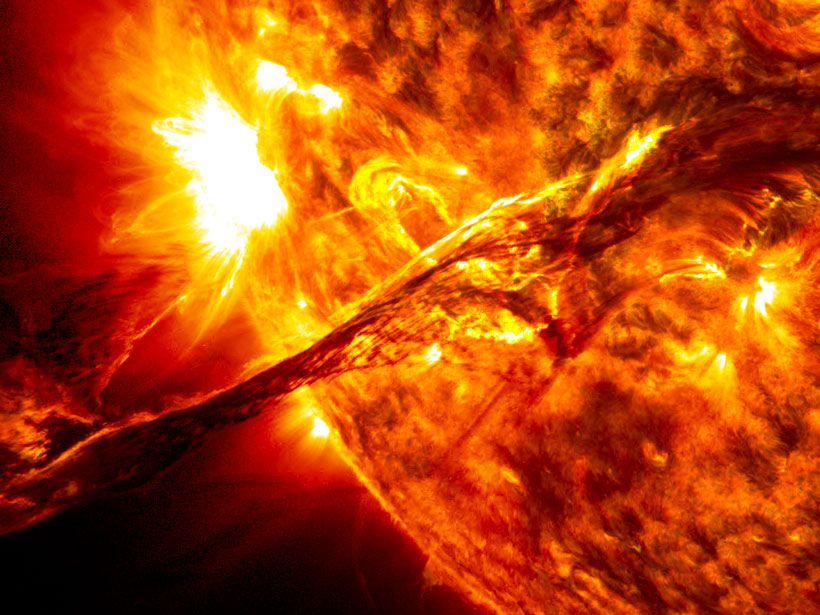
In the latest episode of its Centennial series, AGU’s Third Pod from the Sun talks space weather and its influence on global policy with Delores Knipp.
solar activity
Moon Sheds Light on Early Solar Spin
Lunar samples reveal that the Sun spun relatively slowly in its first billion years and blasted the Earth and Moon with coronal mass ejections.
Planetary Low Tide May Force Regular Sunspot Sync Ups
A regular alignment of the planets—no, it’s not pseudoscience—makes a strong enough tug to regulate the Sun’s 11- and 22-year cycles.
Solar Flares Increase Radiation Risk on Commercial Aircraft
A new study quantifies how space weather may affect polar transcontinental flight.
The Thermosphere Responds to a Weaker Than Normal Solar Cycle
Infrared emissions from nitric oxide and carbon dioxide in Earth’s upper atmosphere, which are closely tied to incoming solar radiation, are drastically lower than in the previous solar cycle.
First Multi-Decade Simulation of the Earth’s Radiation Belt
A new simulation of the Earth’s electron radiation belts captures large-scale variations over nearly three solar cycles, and replicates primary cyclical features and extreme behaviors.
Plasma Activity Around Sunspots May Foreshadow Solar Storms
A new study identifies possible precursors to space weather in the regions encircling sunspots.
John T. “Jack” Gosling (1938–2018)
This prolific researcher helped us understand the interactions of the solar wind and coronal mass ejections with Earth’s magnetic field.
Better Data for Modeling the Sun’s Influence on Climate
Several international initiatives are working to stitch together data describing solar forcing of Earth’s climate. Their objective is to improve understanding of climate response to solar variability.
Edward L. Chupp (1927–2017)
This pioneer in high-energy solar physics devised instruments for observing solar and cosmic ray emissions with which he detected, for the first time, nuclear gamma rays from solar flares.