Analysis of nutrient concentrations in four streams that discharge to the Southern Ocean indicates they are important sources of iron and phosphorous for coastal phytoplankton communities.
Southern Ocean
Understanding Past Changes in Southern Ocean Sea Ice
C-SIDE Workshop; Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, 24–26 October 2018
Connecting the Southern Ocean with Clouds
ACE-DATA/Antarctic Sea-Atmosphere Interactions Data (ASAID) Workshop; 5–6 November 2018, Lausanne, Switzerland
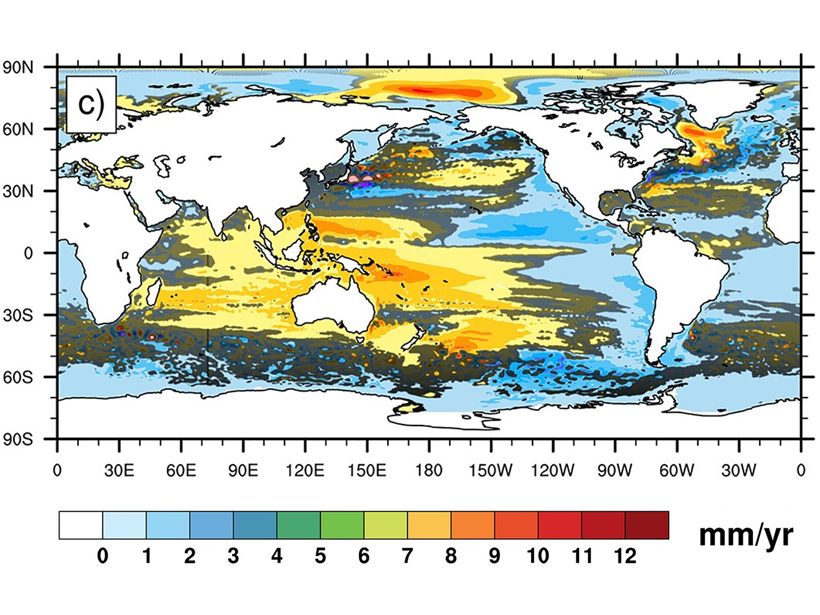
An Inherently Noisy Ocean Can Disguise Regional Sea Level Trends
Sea level trends in different regions of the ocean caused by both natural and man-made changes in the atmosphere can be partially hidden by internal random processes intrinsic to the ocean.
Exploring the Unknown of the Ross Sea in Sea Ice–Free Conditions
A team of polar scientists aboard the OGS Explora, cruising in rare ice-free conditions, discovered new evidence of ancient and modern-day ice sheet sensitivity to climatic fluctuations.
A Complete Picture of Southern Ocean Surface Circulation
For the first time, researchers combine estimates of sea surface height and circulation patterns in both ice-covered and ice-free regions of the Southern Ocean.
Shedding Light on the Southern Ocean Carbon Sink
One of the world’s largest carbon sinks is still poorly understood.
Understanding a Changing West Antarctic Peninsula
The 1st Workshop of the SOOS WAP Working Group; Cambridge, United Kingdom, 15–16 May 2017
In Icy Waters: The Future of Marine Biogeochemical Research off the West Antarctic Peninsula; Chicheley, United Kingdom, 17–18 May 2017
Warm Waters in West Antarctica
A recent paper in Reviews of Geophysics describes the atmospheric and oceanic processes that are causing ice loss in the Antarctic.
Elephant Seals' Dives Show Slowdown in Ocean Circulation
Data from instruments mounted on elephant seals reveal that melting ice flushes fresh water into the Southern Ocean, suppressing an important arm of the global ocean circulation belt.