Elevated copper isotope ratios in arc magmas from fluid-rich cold subduction zones support the role of oxidizing fluids from the subducted lithospheric serpentinite in the oxidization of arc magmas.
subduction
Old Igneous Rocks Hold the Key to Crustal Thickness Evolution
The chemical composition of orogenic igneous rocks and their zircons is sensitive to crustal thickness and can be used to quantify the evolution of Moho depths beneath continents back in time.
Months of Gravity Changes Preceded the Tōhoku Earthquake
Using GRACE satellite data, researchers discovered anomalous gravimetric signals that occurred before a seismic event that started deep within Earth.
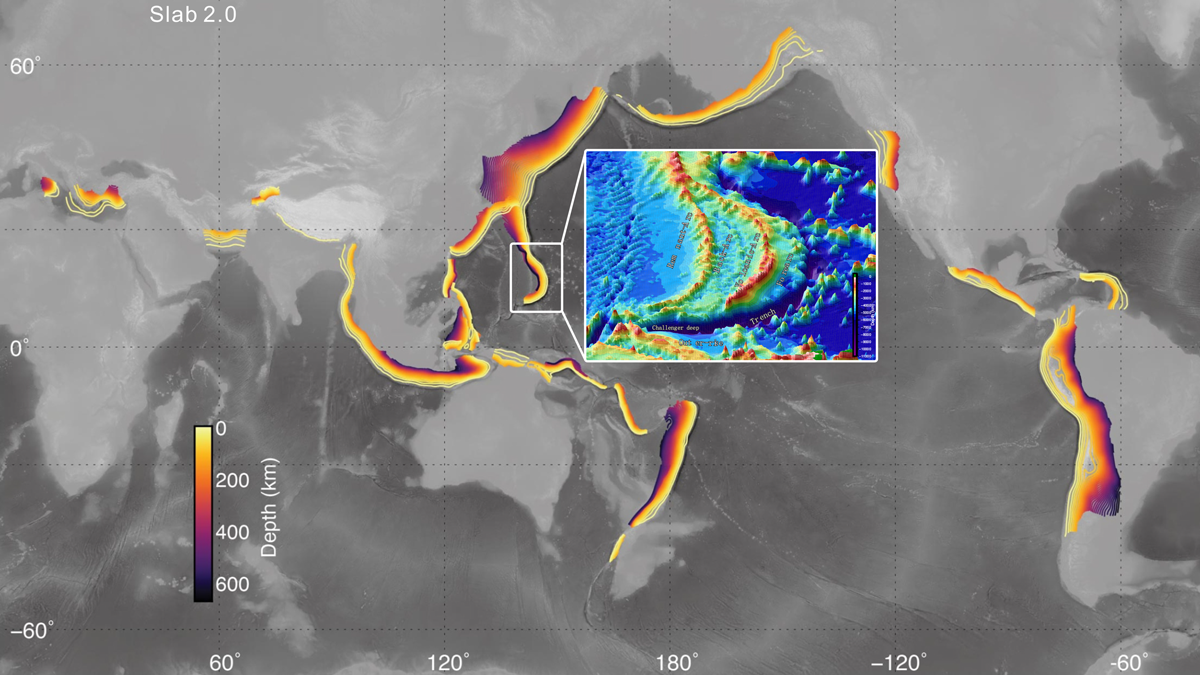
Deep Earthquakes Suggest Well-Hydrated Mariana Subduction Zone
Earthquakes as deep as 50 kilometers below the seafloor were detected by 12 ocean bottom seismometers placed around the Challenger Deep.
Aftershocks Reveal Coseismic Rupture of Megathrust Earthquakes
More accurate aftershock zones reveal that the rupture areas of megathrust Aleutian–Alaska earthquakes are larger than we thought and partly overlap, in contradiction with the seismic gap hypothesis.
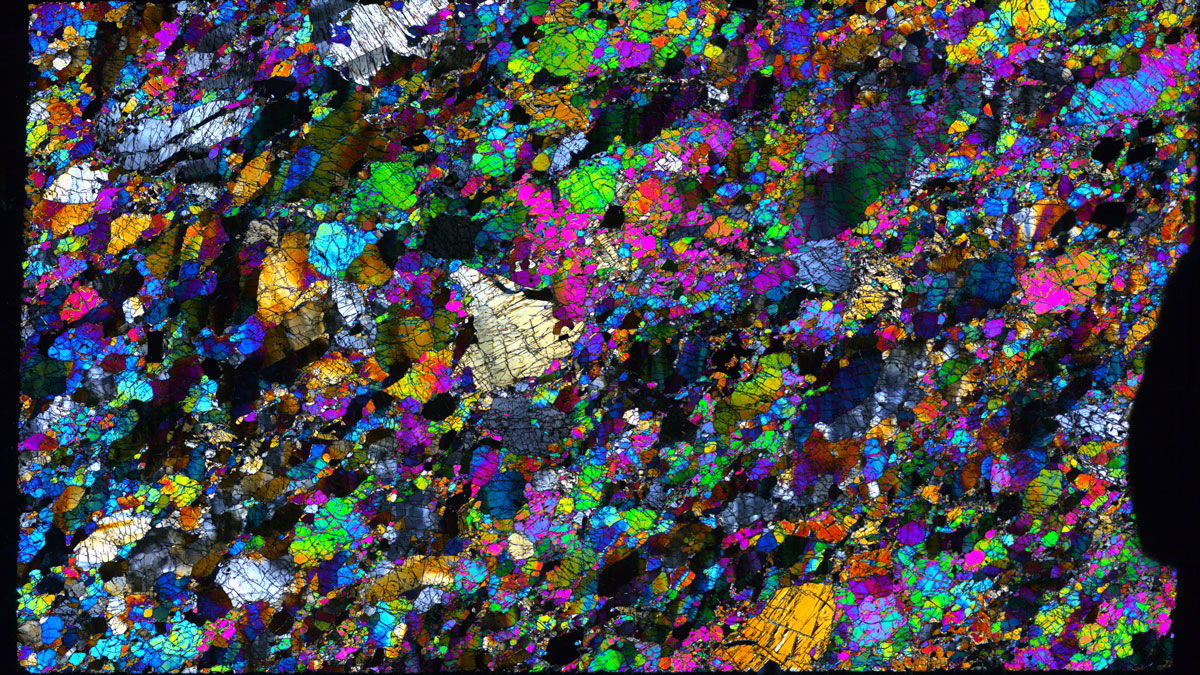
Holey Eclogite!
Scientists have found holes filled with minerals that indicate fluid-filled pores exist many tens of kilometers below Earth’s surface. But no, The Core fans, you still can’t get amethyst-laden geodes in the mantle.
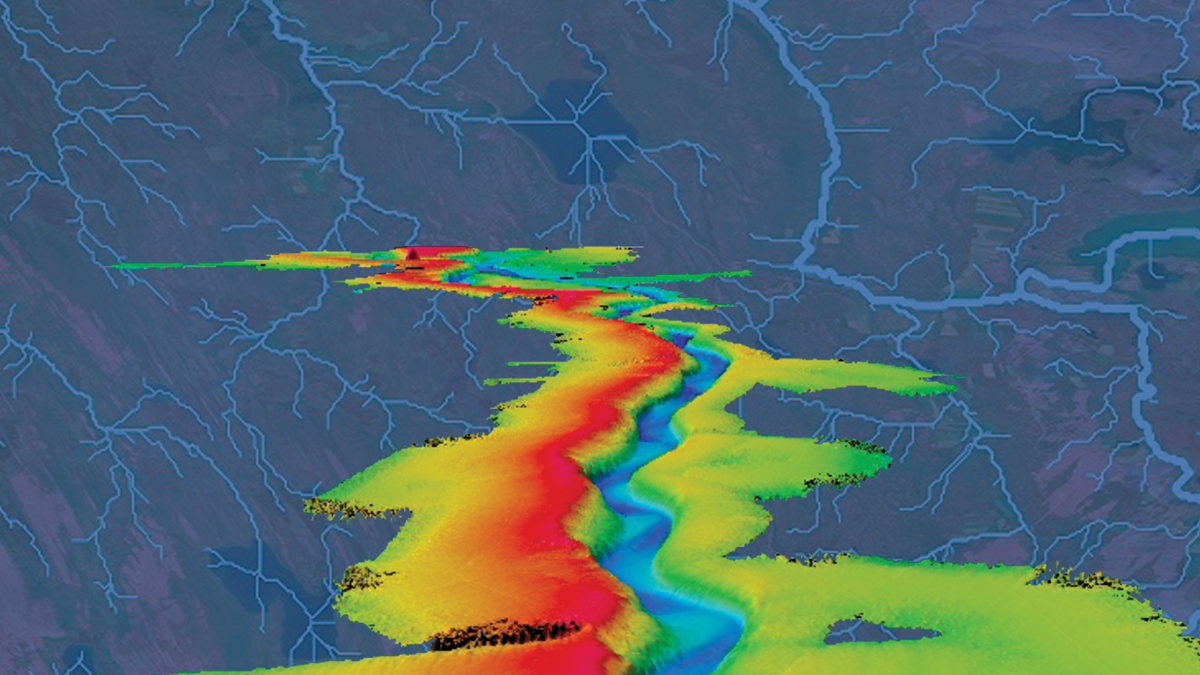
Charting Paths to New Knowledge
In our June issue of Eos, we home in on the unique ways researchers are using maps to better understand Earth and beyond.
Million or Billion? Narrowing Down the Age of Mantle Processes in New Guinea
Mantle rocks in Papua New Guinea contain curious geochemical signatures that scientists have traditionally interpreted as evidence of billions-year-old melting. New evidence suggests otherwise.
Is Earth’s Core Rusting?
If subduction carries hydrous minerals deep into Earth’s mantle, they may “rust” the iron outer core, forming vast sinks of oxygen that can later be returned to the atmosphere.