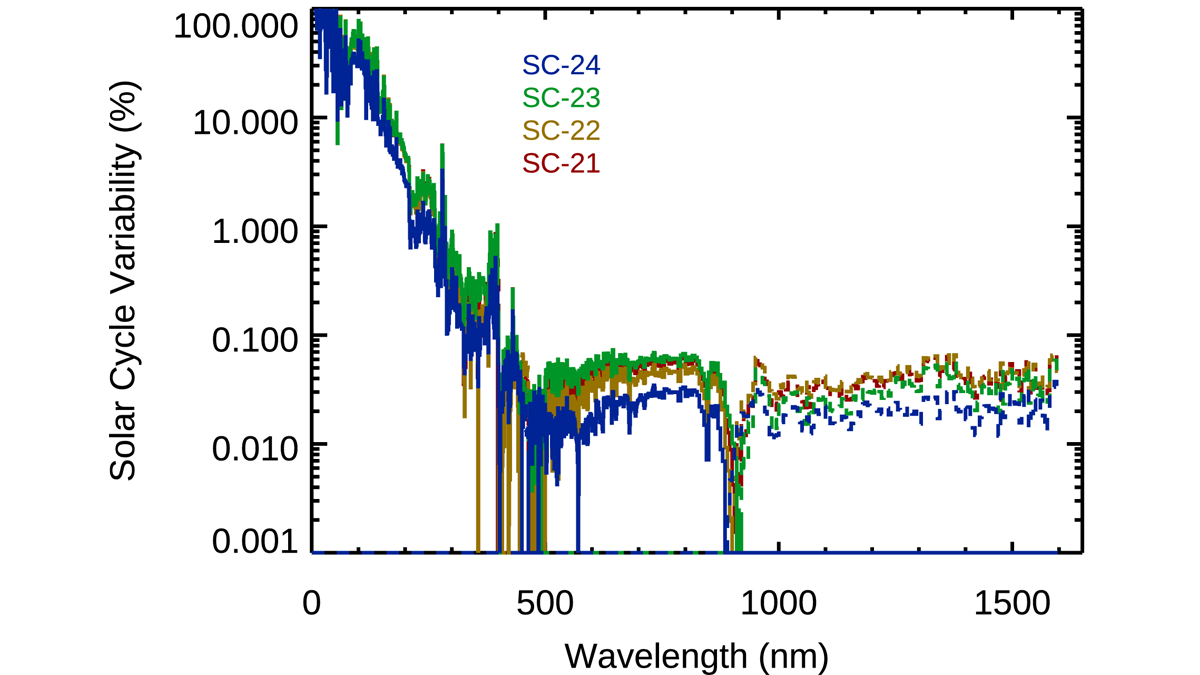
Each solar cycle might seem like the same old story, but one thing has changed significantly since the previous solar maximum–our technology.
the Sun
Why Did Sunspots Disappear for 70 Years? Nearby Star Holds Clues
Five decades of data revealed a star undergoing a pause in magnetic activity similar to what the Sun experienced almost 400 years ago.
A “Dam” in the Corona May Make the Solar Wind Gain Its Unusual Speeds
A new study supports the idea of a “helicity barrier” influencing the fluctuating stream of interplanetary plasma.
Chinese-Led Solar Research Is Looking Bright
With new missions underway and planned, China is stepping up to observe our nearest stellar neighbor.
A New Journey Around (and Around) the Sun
The Solar Orbiter just completed its commissioning phase while en route to the Sun. It has already provided valuable looks at solar campfires and Venus’s magnetic fields, and it promises much more.
The Young Earth Under the Cool Sun
How did our planet avoid being frozen solid during the early days of our solar system?
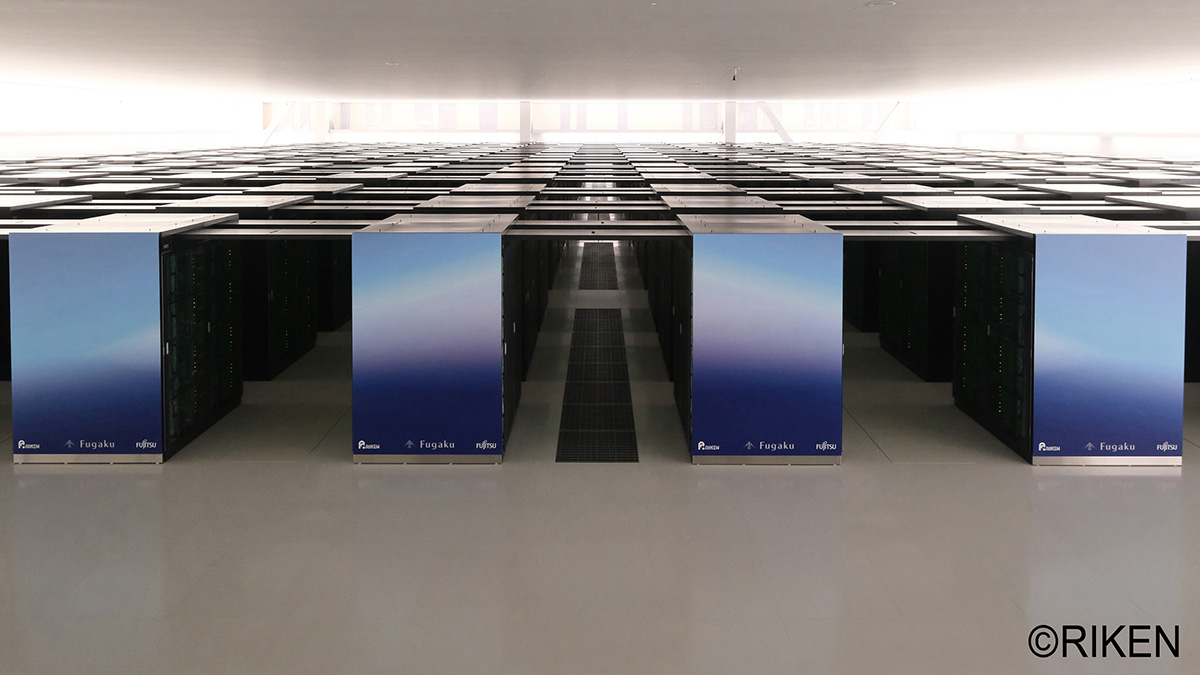
Accurate Simulation of Sun’s Rotation Might Illuminate Solar Cycle
Scientists have known for 400 years about a particularity in the way the Sun rotates. It took the world’s most powerful supercomputer to accurately simulate it.
Newly Improved Solar Spectral Irradiance Composite Record
A new study accurately captures solar irradiance, which is crucial to understand the energetics and radiation balance of Earth and its influences on the cryosphere, atmosphere, and ocean currents.
Wind: Discoveries and Impacts of a Venerable Spacecraft
Wind has been one of the most robust, diverse, long-lasting, and impactful heliophysics missions ever to have been carried out.
New Book Collection Presents Latest in Heliophysics Research
A new set of five books presents the latest science on the Sun and the solar wind, magnetospheres in the solar system, Earth’s ionosphere, Earth’s upper atmosphere, and the effects of space weather.