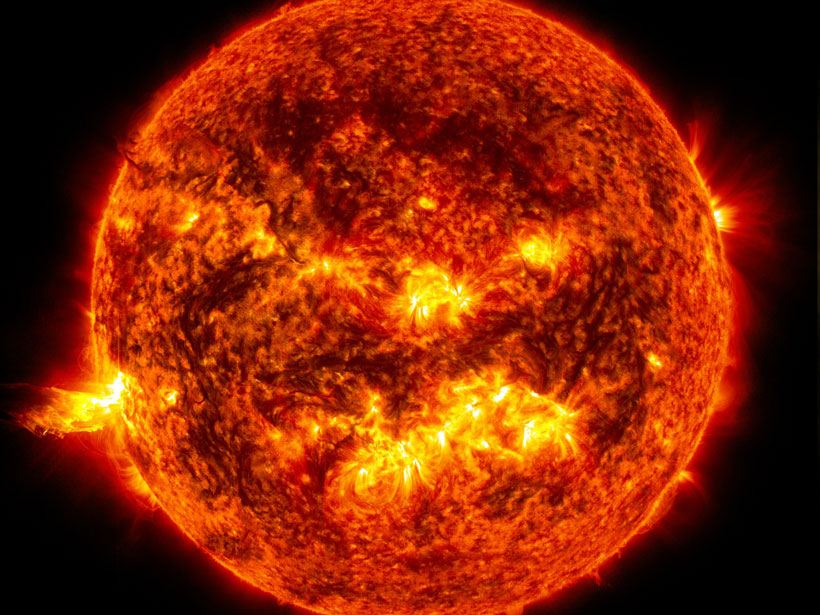
Solar radio bursts are background noise for satellite-based radio observations that monitor soil moisture, so, with appropriate processing, those observations can provide data on radio bursts.
the Sun
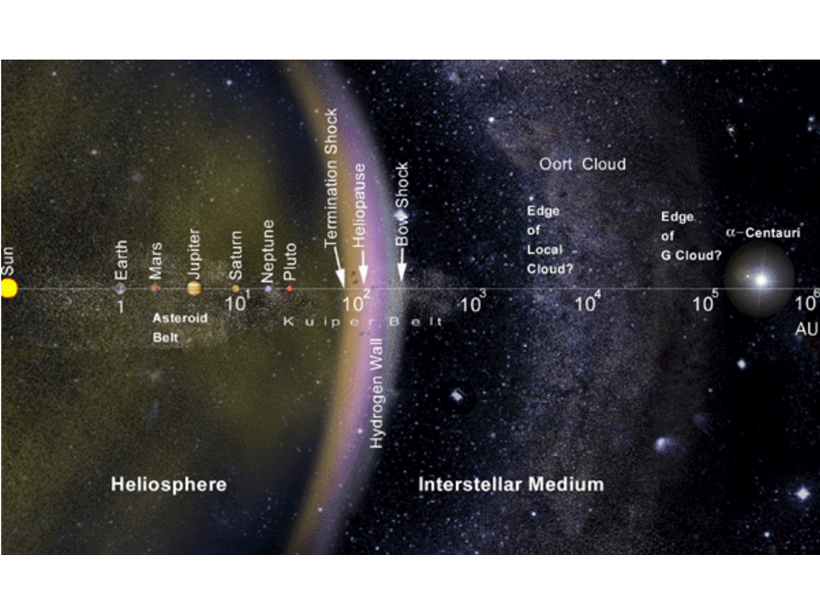
The Cosmic Timeline of Heliophysics
Thom Moore began his career after the start of the space age. This is the story of how he converted his interests in evolution, philosophy, and psychology and writing into the study of heliophysics.
A Better Understanding of How the Sun Bends Light
Incorporating the refractive index of the Sun into models of gravitational lensing effects improves agreement with measurements of the phenomenon.
Altitude Matters for Solar Eclipse Observations
The path of a solar eclipse through Earth’s ionosphere, which can be quite different than it is at ground level, appears to explain patterns of ionized particle depletions.
Ghostly Particles from the Sun Confirm Nuclear Fusion
Using the Borexino particle detector—located deep underground in Italy—researchers spot elusive neutrinos from the Sun’s CNO cycle.
How Accurate Are Our Measurements of the Sun’s Energy?
As instruments collecting solar data degrade, researchers must correct for errors. A new study compares several methods to correct solar spectral irradiance measurements.
Using Earth’s Atmosphere as a Solar Flare Monitor
Measurements of very-low frequency radio signal phase and amplitude can detect upper atmosphere changes caused by solar flares, enabling us to monitor flare occurrence and intensity.
Virtual Super Instrument Enhances Solar Spacecraft
The same algorithms that help control self-driving cars and speech-to-text functionality have helped build a virtual instrument to study the Sun.
Hearing the Sun Tock
The appearance of sunspots—their number, duration, and location—suggests that the dynamics of the Sun’s outer layer is synchronized with an internal clock.
Million-Degree Experiment Complicates Solar Science
Experiments at Sun-like temperatures show that certain elements absorb more light than solar models predict, creating uncertainties for stellar science.