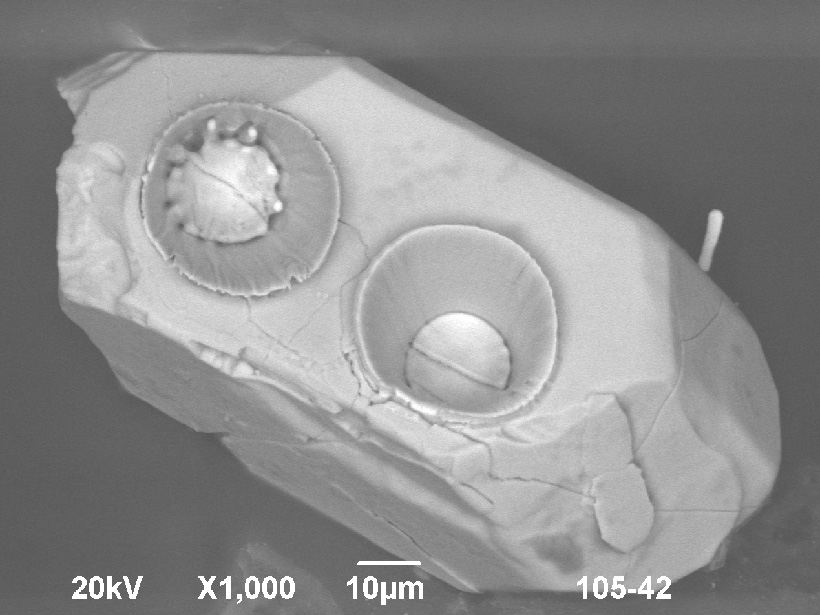
Volcanic eruptions spread harmful metals in the environment. Now the biggest study to date details exactly where they end up.
volcanoes
Modeling Volcanic Debris Clouds
How does a large volcanic cloud get into the stratosphere? Scientists model how volcanic debris injected into the lower stratosphere can be lofted high into the middle stratosphere.
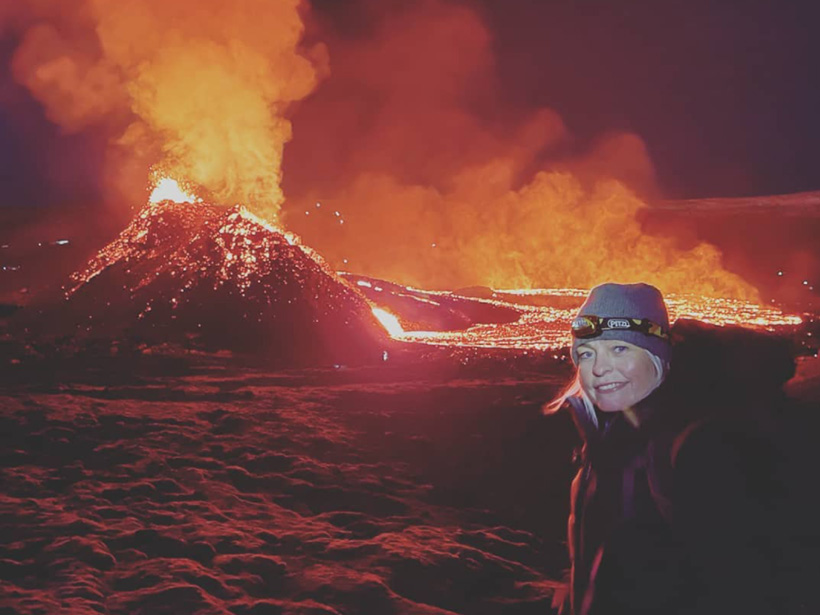
Persiguiendo magma por la península de Reykjanes en Islandia
La Oficina Meteorológica de Islandia ha estado rastreando la agitación cerca de la erupción de Fagradalsfjall desde diciembre de 2019, mientras que investigadores en otros lugares exploran nuevos métodos para ver los enjambres sísmicos de Islandia.
Vestiges of a Volcanic Arc Hidden Within Chicxulub Crater
Scientists discovered magmatic remnants of a volcanic arc by dating granitic rocks of the middle crust excavated by, and hidden within, the Chicxulub impact crater.
Seafloor Seismometers Look for Clues to North Atlantic Volcanism
Did the mantle plume that fuels Iceland’s volcanoes today cause eruptions in Ireland and Great Britain long ago? A new project investigates, while also inspiring students and recording whale songs.
Chasing Magma Around Iceland’s Reykjanes Peninsula
The Icelandic Meteorological Office has been tracking unrest near erupting Fagradalsfjall since December 2019, while researchers elsewhere explore new methods to see Iceland’s seismic swarms.
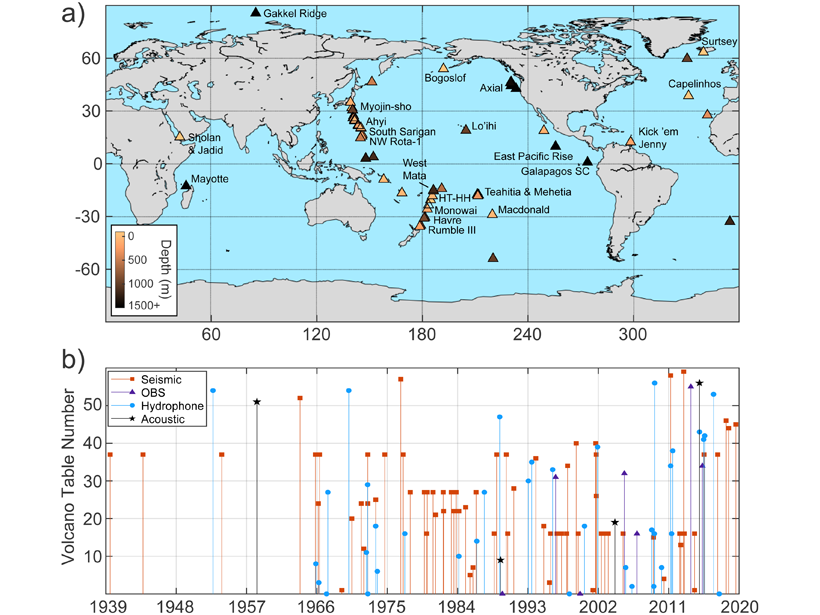
A Comprehensive Review of Submarine Volcano Seismoacoustics
Although most of Earth’s lava erupts beneath the oceans, submarine volcanoes are comparatively understudied, but a new review of submarine volcano seismoacoustics provides a framework for future work.
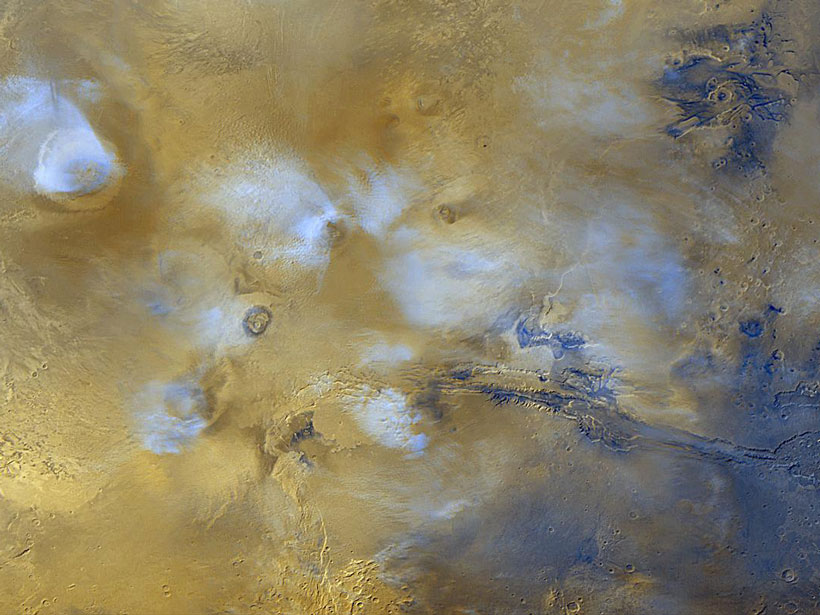
Tiny Volcanoes Are a Big Deal on Mars
Cinder cones and fissure vents provide clues about the evolution of the Red Planet’s mantle and crust.
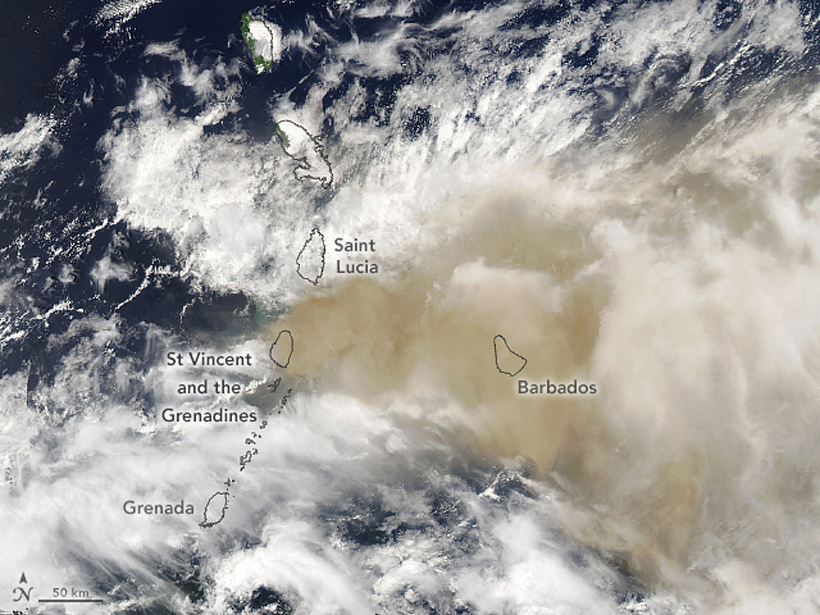
Eyeing Explosive Ash Clouds from Above and Below
Satellites in the sky combined with computers on the ground detect and track volcanic ash clouds, like those produced by Soufrière St. Vincent in April, in near-real time.
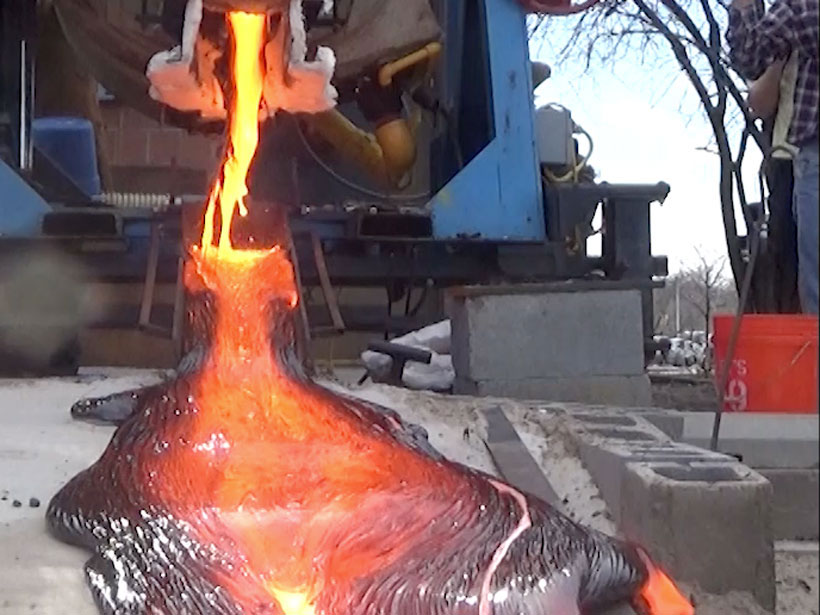
Imagining What a Metal Volcano Would Look Like
Large-scale lava experiments are helping scientists imagine how metallic lava would flow across and shape a landscape, either on Earth or on a distant asteroid.