Human-made substances hold dangers for the environment, but they also give scientists a view into recent history.
water
The State of the Science 1 Year On: Environment
Administration policies have eliminated funding sources, review processes, and pollution limits designed to protect the nation’s land, water, and air.
Los microplásticos tienen efectos muy variados en el suelo
Un nuevo estudio revela que una concentración de microplásticos de tan solo el 0,4 % altera el drenaje del suelo, lo que podría afectar al crecimiento de los cultivos y otras plantas.
Microbial Genes Could Improve Our Understanding of Water Pollution
New research in Germany’s Ammer floodplain examines microbial biomarkers to help improve modeling of denitrification.
After Sackett, a Wisconsin-Sized Wetland Area Is Vulnerable
An analysis of wetland legal frameworks shows how water rules could leave millions of hectares without meaningful protections.
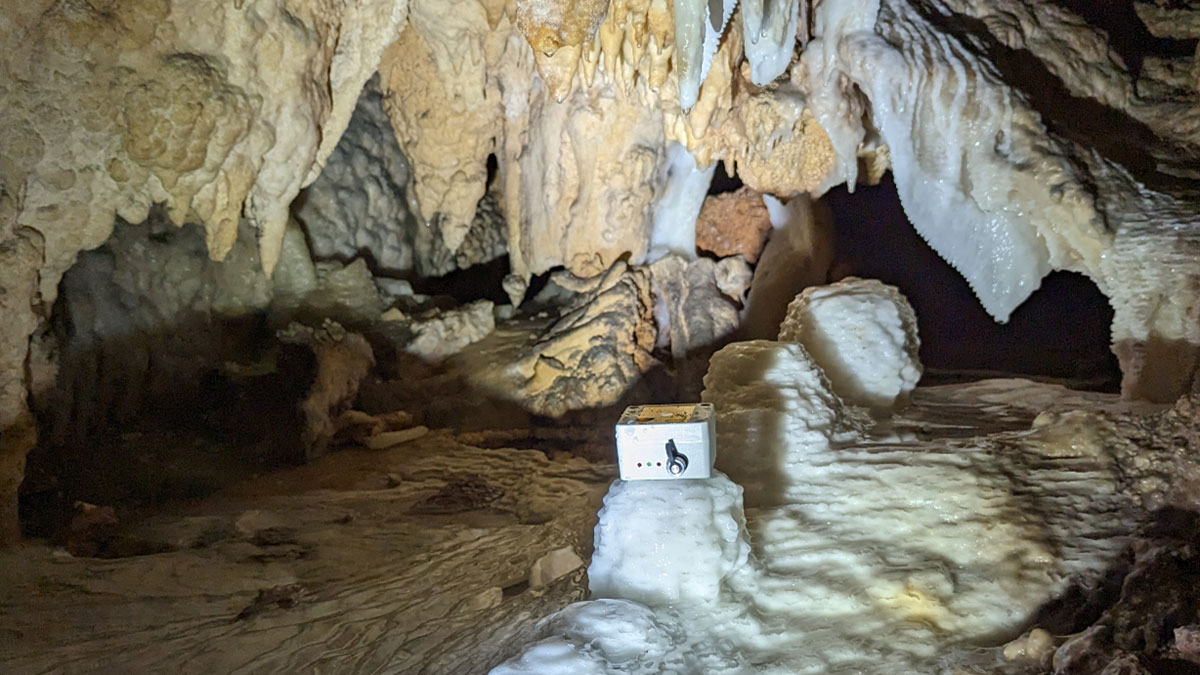
When Does Rainfall Become Recharge?
Counting drips in caves is helping to reveal how much precipitation is needed to start refilling underground aquifers.
Maybe That’s Not Liquid Water on Mars After All
A “very large roll” of a radar instrument offers new insight into a highly reflective area near the Martian south pole.
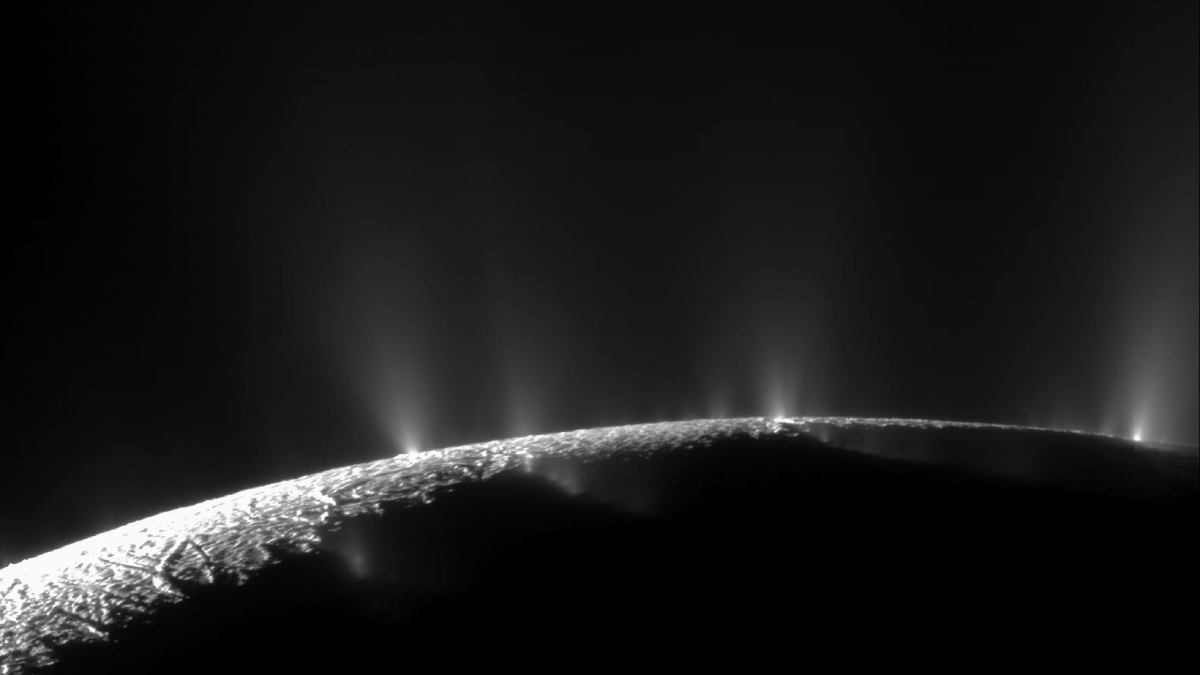
Speedy Flyby Adds New Organics to Enceladus’s “Primordial Soup”
A new analysis of old Cassini data has also verified past detections of complex organics in Saturn’s E ring, strengthening the chemical ties between the ring and its progenitor.
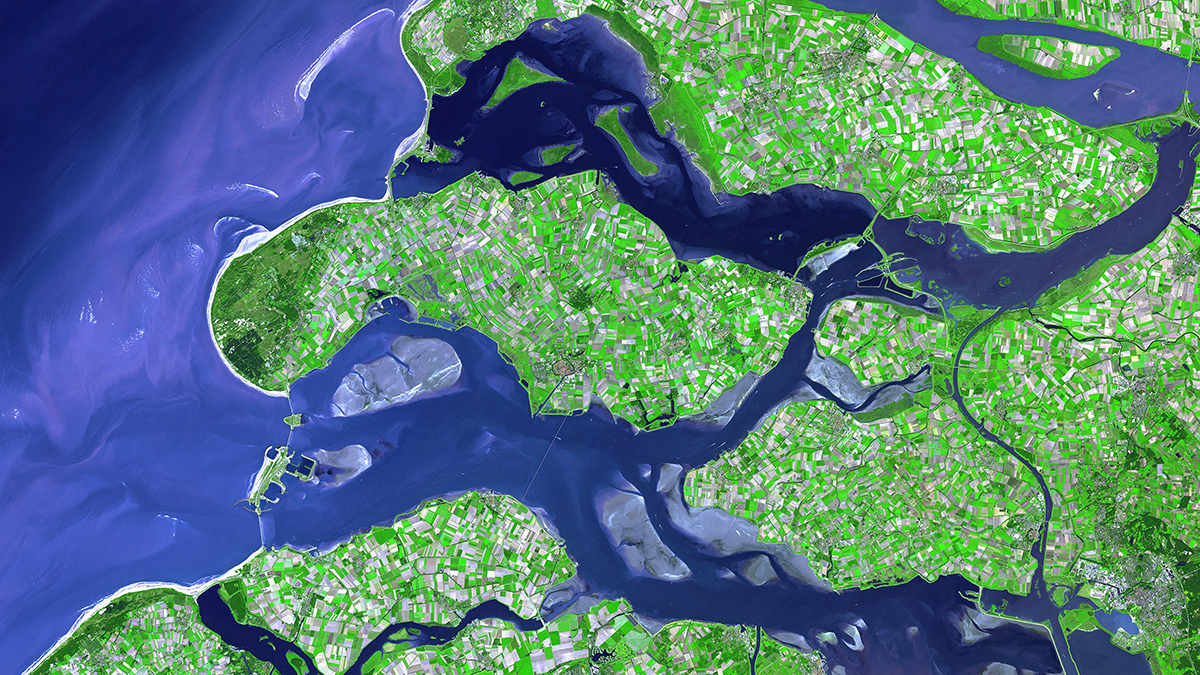
The Role of a Ditch in the Matrix
These constructed waterways are often a “no-man’s-land” between terrestrial scientists and limnologists. But ditches’ role in transport, agriculture, biodiversity, greenhouse gas emissions, and even archaeology means it’s time to take a closer look.
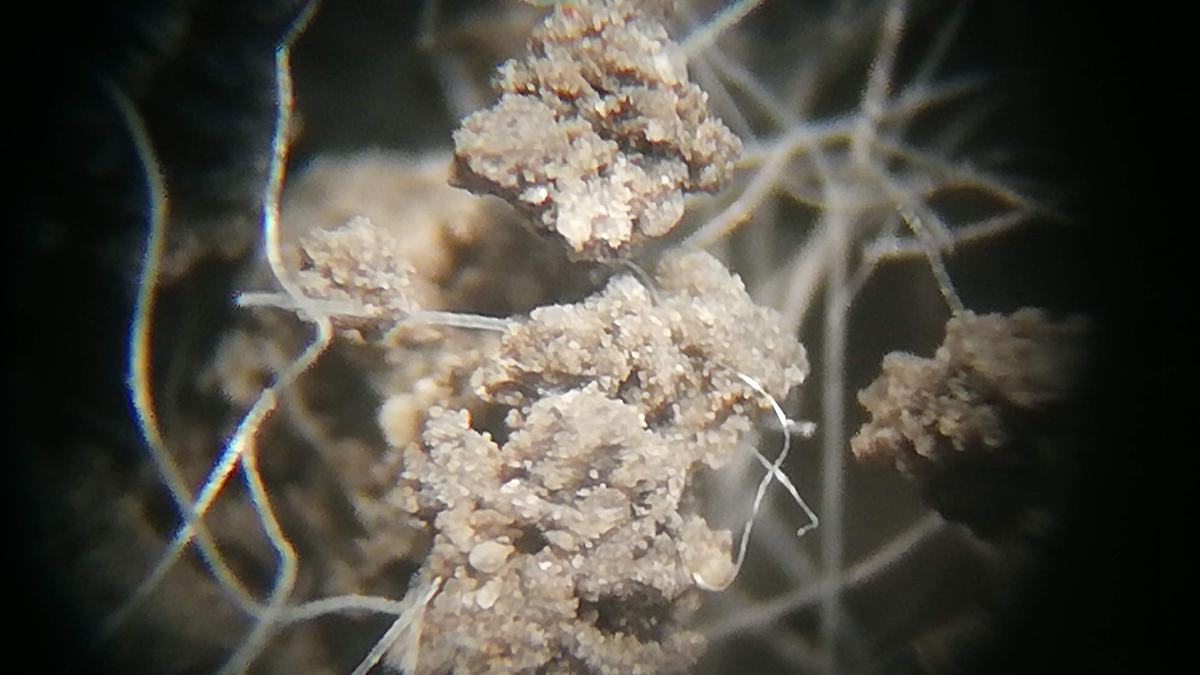
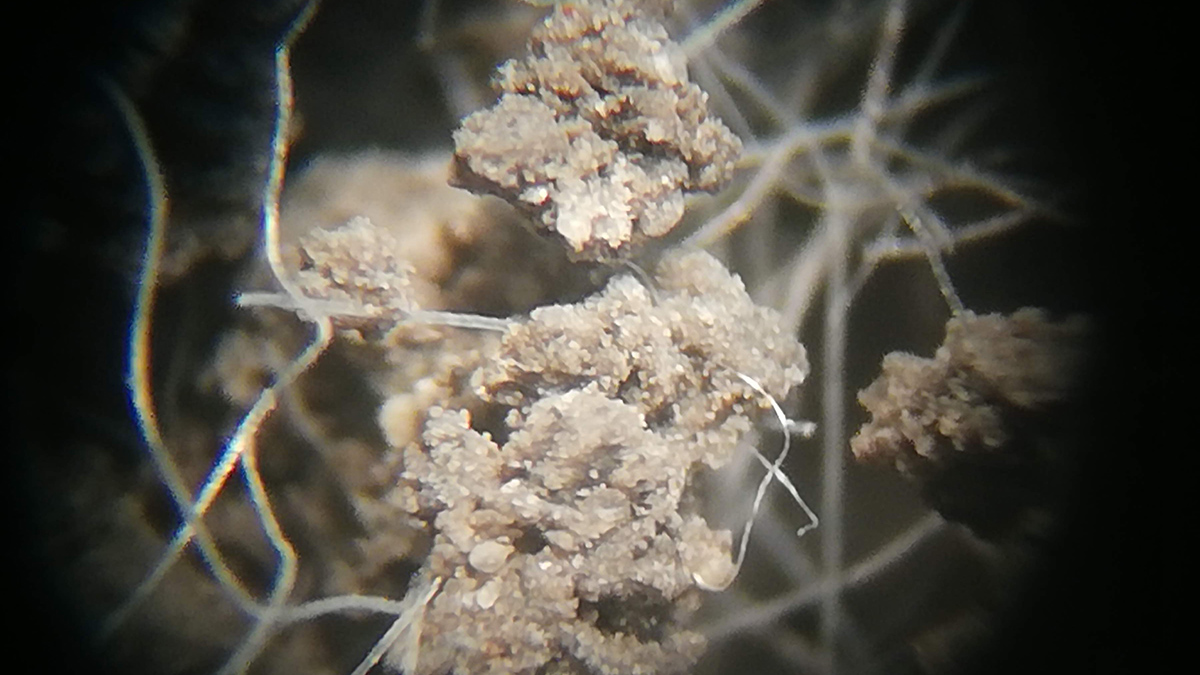
Microplastics Have Widely Varying Effects on Soil
A new study finds that a microplastic concentration of just 0.4% alters the drainage of soil, which could affect the growth of crops and other plants.