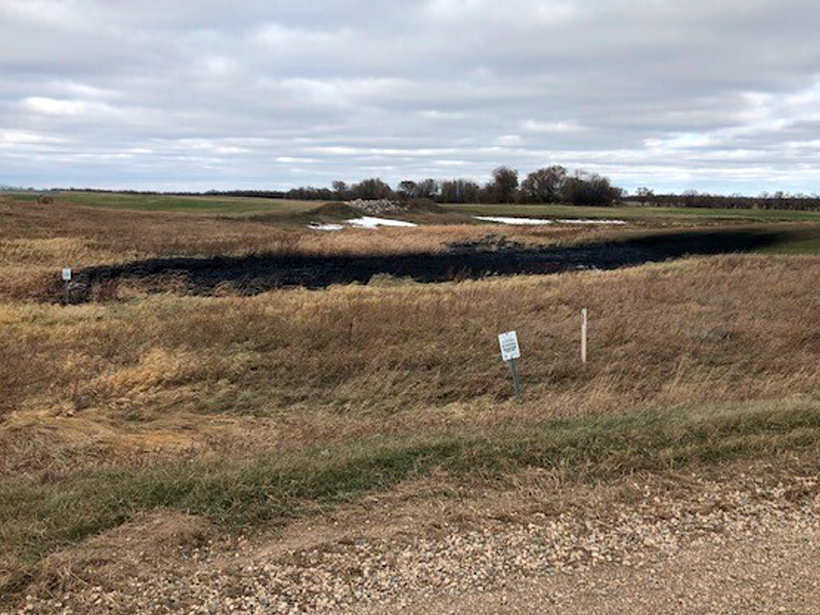
The leak took place along a preexisting section of the Keystone Pipeline. This is the pipeline’s fourth spill in 9 years.
wetlands
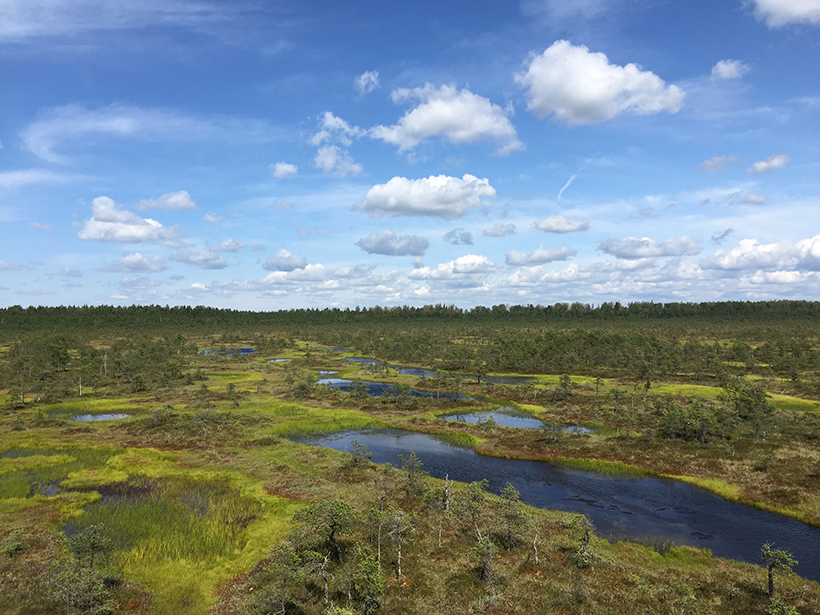
Resilient Peatlands Keep Carbon Bogged Down
Boreal peatlands contain some of the world’s largest reservoirs of soil carbon, and new research suggests some peatlands may hold on to that carbon even as the climate changes.
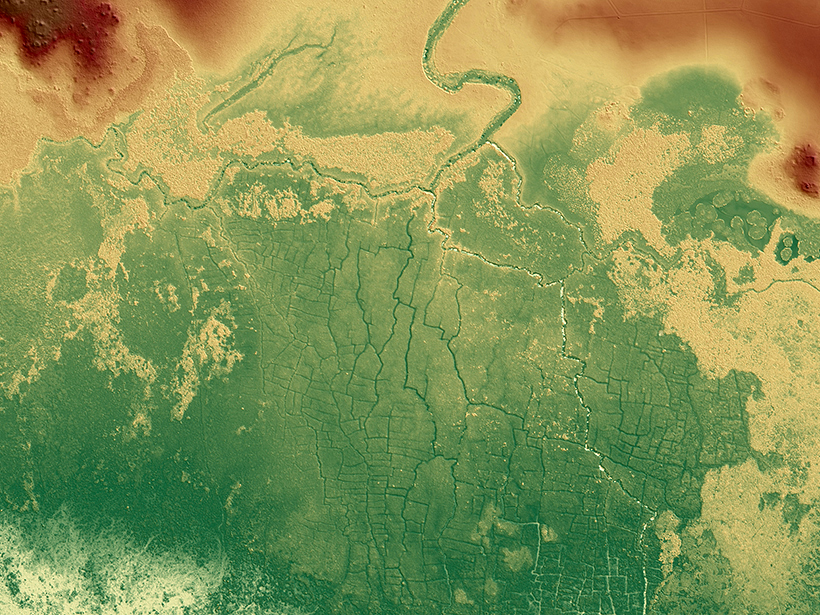
Ancient Maya Farms Revealed by Laser Scanning
One agricultural network was 5 times larger than earlier estimates, and the fields may be an early source of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions.
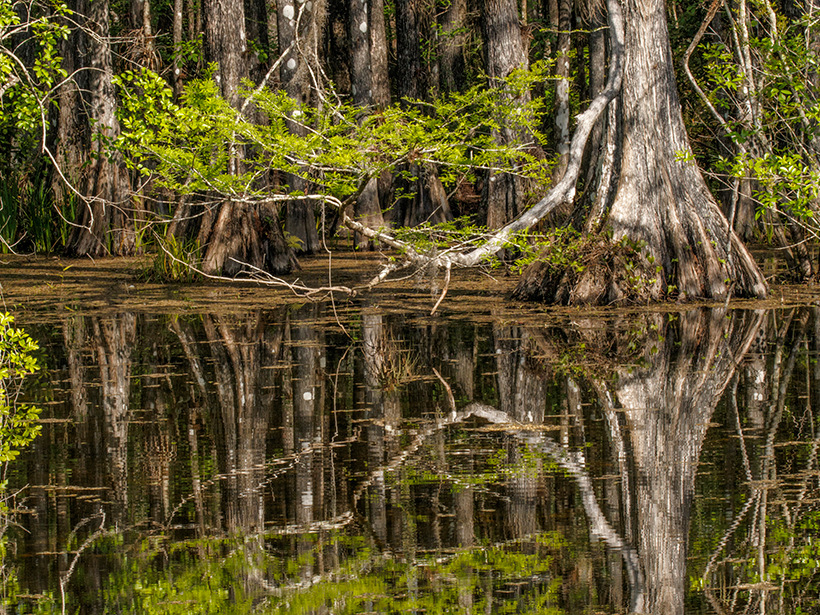
North Carolina Bald Cypress Tree Is at Least 2,674 Years Old
Researchers say it’s the oldest-known living tree in eastern North America. If it hadn’t been protected, it could have ended up as garden mulch.
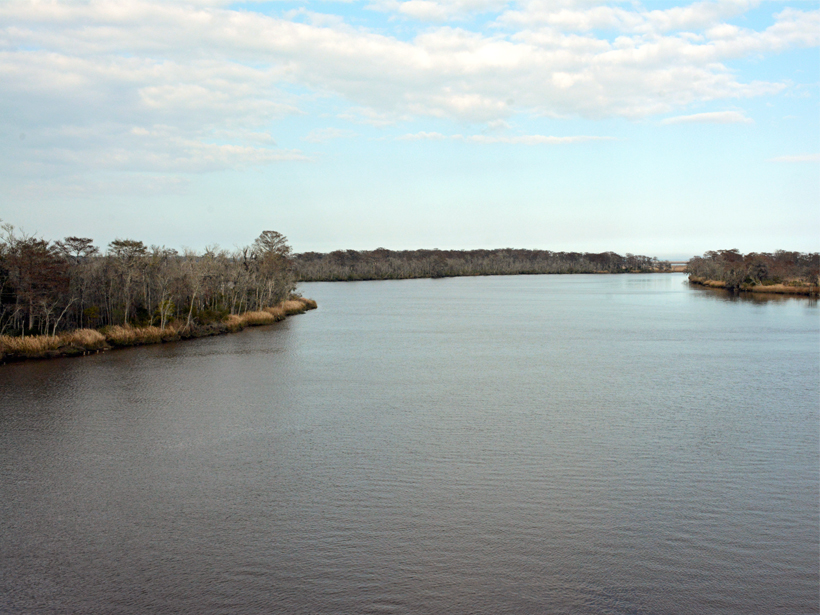
Tracking Dissolved Organic Matter in Coastal Ecosystems
Dissolved organic matter supports aquatic food webs and holds as much carbon as the atmosphere. A new study tracks which sources and processes play the biggest role in coastal systems.
New Study Shifts Paradigm of Coastal Sediment Modeling
A new model improves predictions for sediment movement in vegetated shoreline zones and reveals a universal predictor that could change the understanding of coastal landscape evolution.
Formation of Sedimentary Deposits: Bypass Versus Mass Extraction
Grain size and sediment delivery pathways from the Ganges delta have been used to model downstream facies changes.
The Urban Dry Island Effect
A study of the Yangtze River Delta shows how urbanization dries out the atmosphere.
Budgeting Ozone-Depleting Emissions from Coastal Tidal Marshes
Brackish wetlands and their salt-tolerant vegetation are significant methyl halide emitters. The natural emissions add chlorine and bromine to the stratosphere, which break down ozone.
Human Activities Create Corridors of Change in Aquatic Zones
Canals, dammed reservoirs, irrigation ditches, and pollution are changing species diversity, microbial communities, and nutrient levels in aquatic zones across the planet.