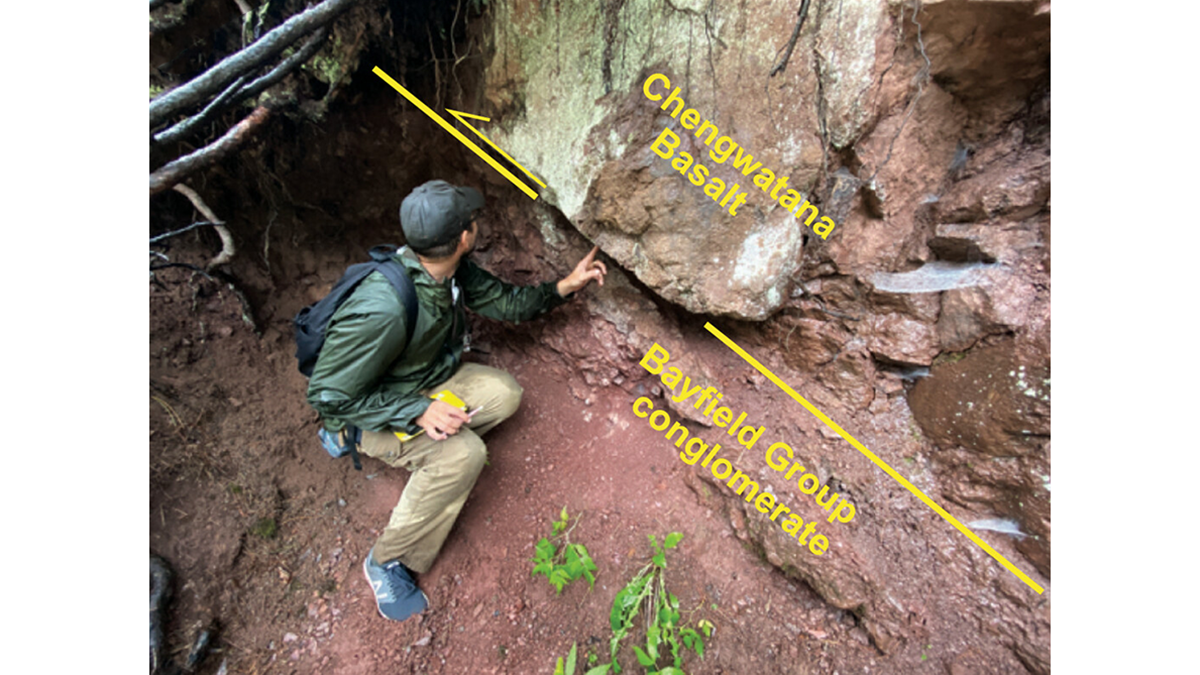
A new study reconstructs how an ancient North American rift system was uplifted in space and time due to subsequent continent-continent collision.
Editors’ Highlights
Clumped CO Isotopes – New Tracers for Atmospheric Chemistry
A new study reports the first measurements of 13C18O in atmospheric carbon monoxide (CO) and show their variations reflect chemical ‘aging’ consistent with predicted kinetic isotope effects.
Timing the Global Expansion on the Moon
A new analysis of the relation between randomly oriented linear gravity anomalies and two large craters on the Moon implies that the gravity anomalies formed over a long period of time.
Seismotectonic Update of the Philippines-Taiwan Region
Using more than two decades of data, scientists find that the Philippine and Taiwan subduction region is controlled mainly by shallow seismicity and low magnitude earthquakes.
The Delicate Balance of Permafrost in Arctic River Floodplains
To evaluate the vulnerability of permafrost in Arctic floodplain landscapes to warming, scientists explore dynamics of its loss and reformation.
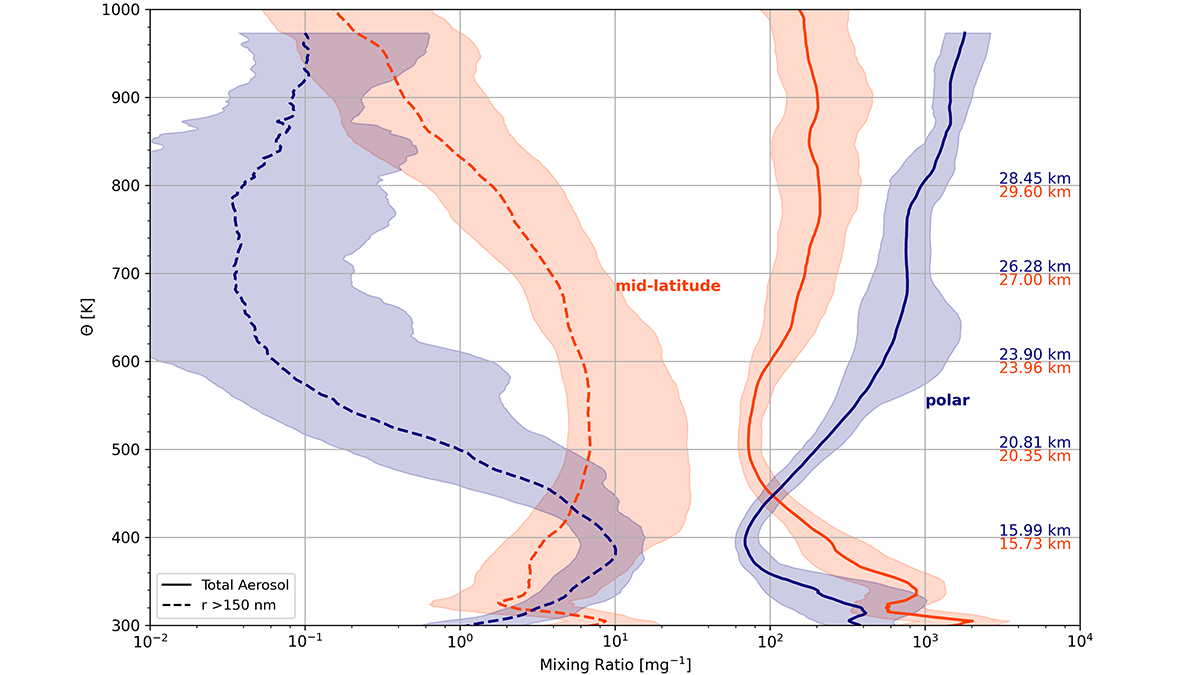
Five Decades of Stratospheric Aerosols from Balloon Measurements
Long-term global measurements of stratospheric aerosols reveal climatological structures and processes controlling new particle formation.
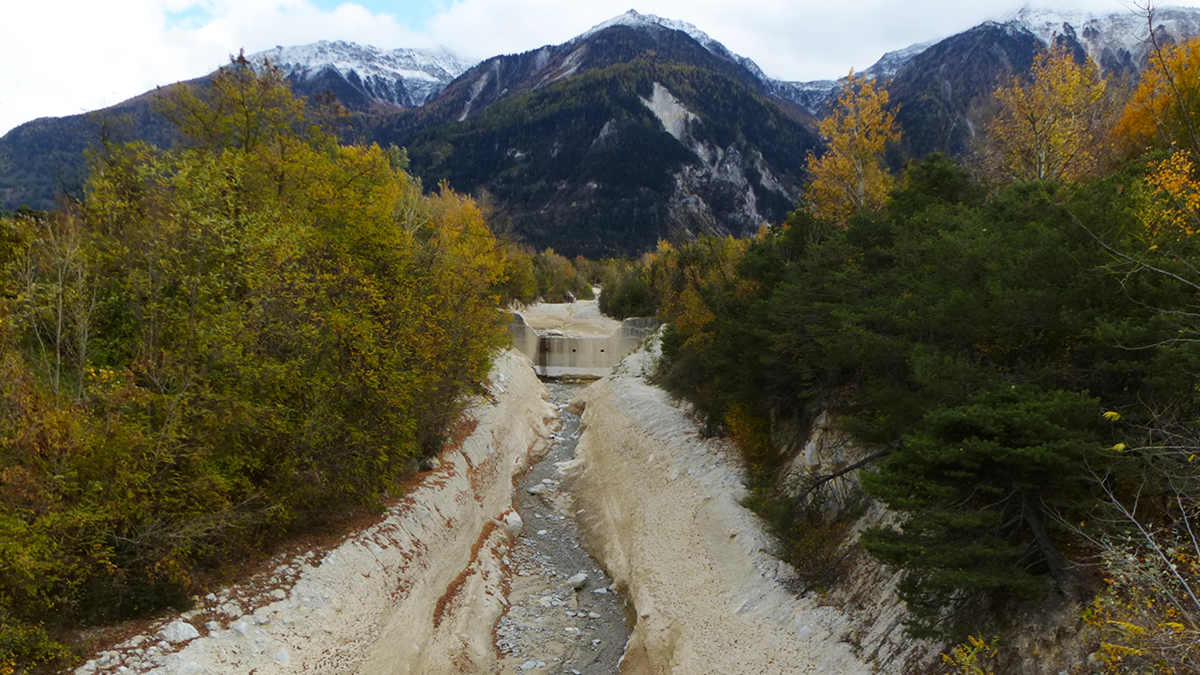
Counting from One to Nine to Detect Debris Flows
A groundbreaking method using Benford’s law allows the detection of debris flows from seismic signals.
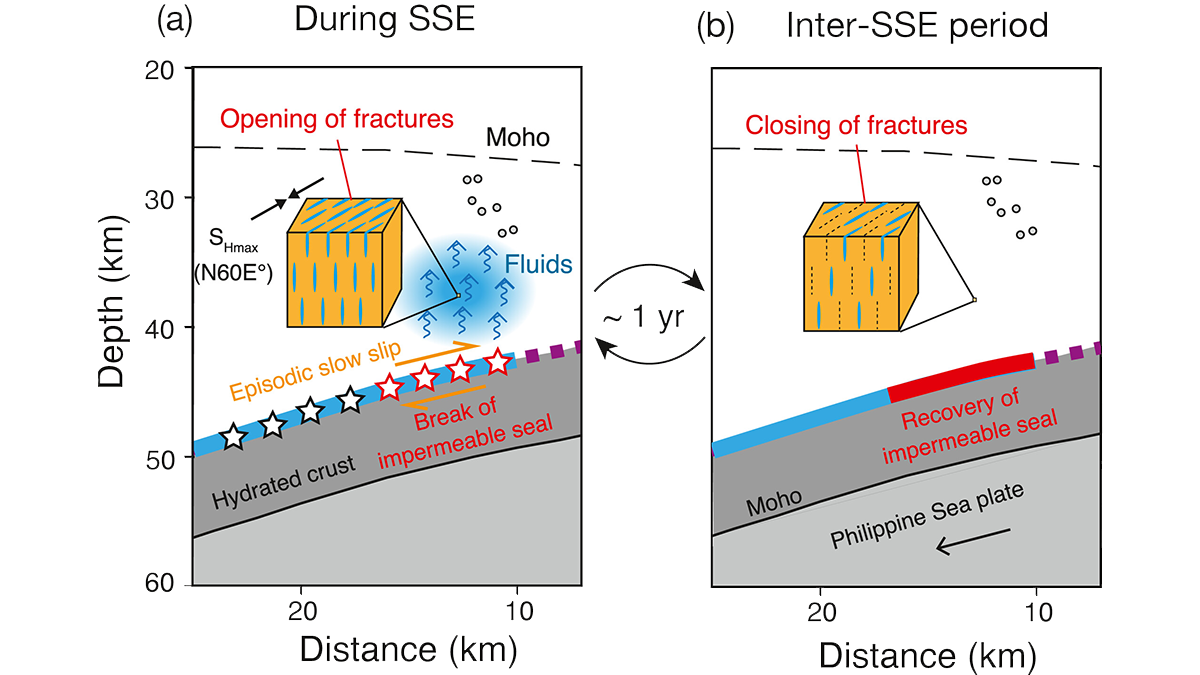
Cyclic Opening of Deep Fractures Regulates Plate Boundary Slip
Seismic anisotropy changes through time suggest that cyclical opening of fluid-filled fractures is synchronized with subduction zone slow slip events.
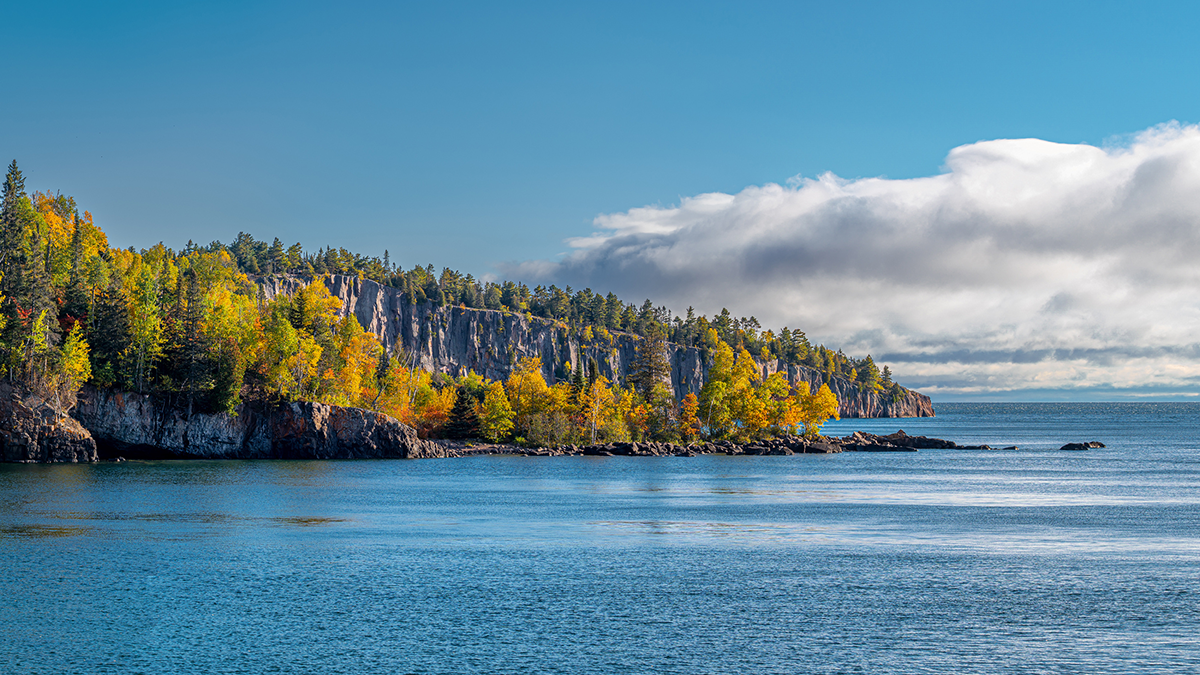
New Insights into a Blind Spot in Aquatic Carbon Dioxide Exchange
Multi-annual measurements across Lake Superior indicate remarkable similarities between large lakes and ocean CO2 exchange during the ice-free season.