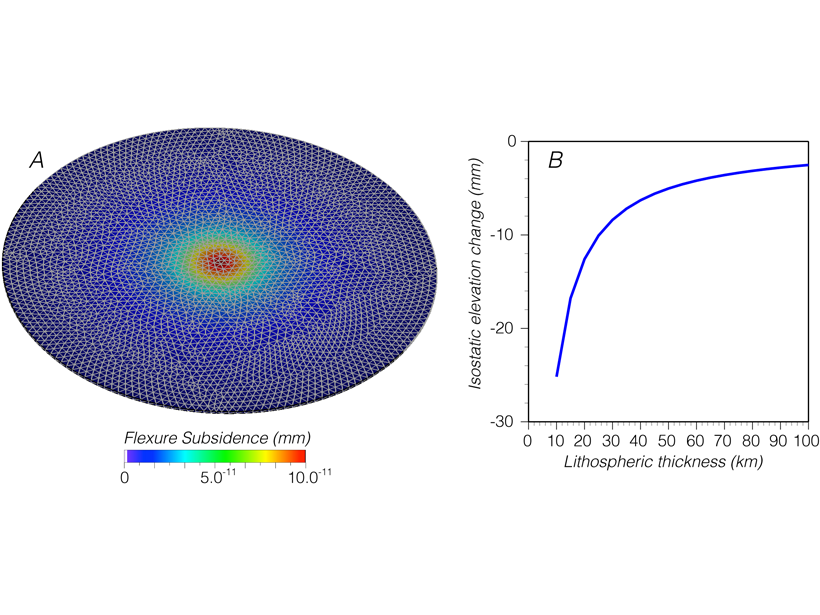
Calculations show that the added weight of growing cities can lead to tens of millimeters of subsidence, an effect that needs to be considered for coastal cities under threat by sea-level rise.
2021 CC BY-NC-ND
Deep Decarbonization? Yes We Can!
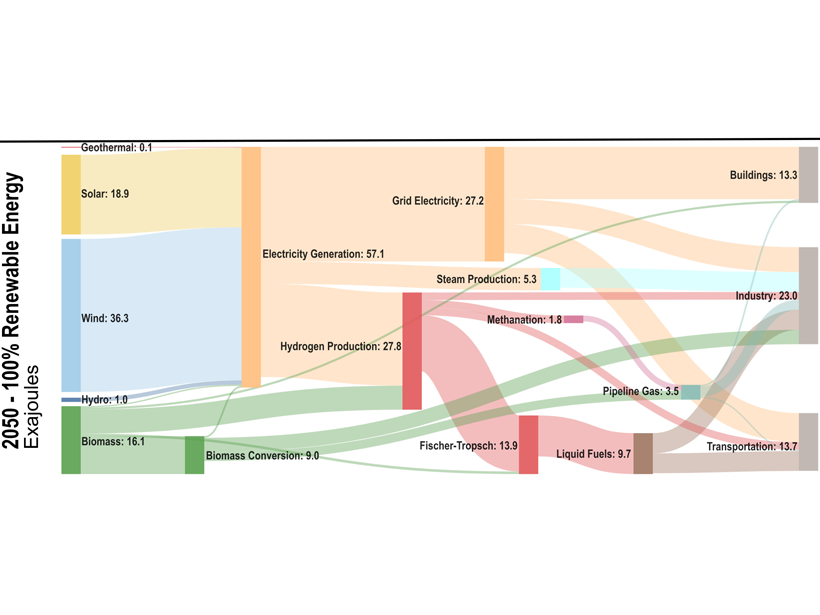
Modeling the U.S. energy system demonstrates several pathways to net-zero CO2 emissions by 2050. The pathway with the lowest cost, 0.2–1.2% of GDP, relies on >80% contribution of renewables.
Modeling Earth’s Ever-Shifting Magnetism
The World Magnetic Model, updated every 5 years through an international collaboration, supports numerous technologies that help us find our way.
A Culinary Silver Lining of Climate Change: More Truffles
The cultivation potential of a popular truffle species will increase in central Europe by 2050, global climate models predict.
Fault Related Anisotropy in the Hikurangi Subduction Zone
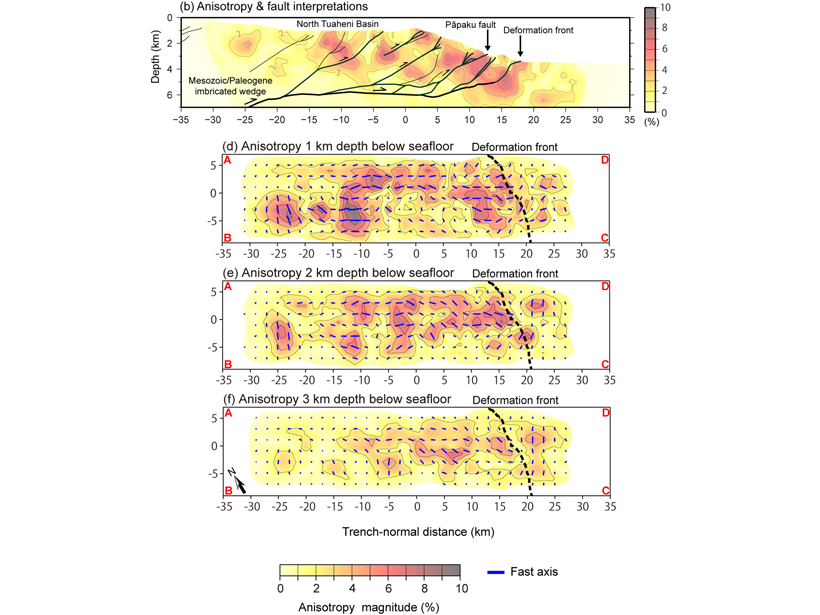
A new study provides the first high-resolution three-dimensional anisotropic P-wave velocity model of the shallow part of the Northern Hikurangi subduction zone offshore New Zealand.
Modeling the Creation of Cratons, Earth’s Secret Keepers
Geoscientists have long been trying to answer the complicated questions of how and why Earth’s continents formed. New research suggests a solution that surprised even the investigators themselves.
Freshened Groundwater in the Sub-seafloor
Scientists are using a variety of geochemical, geophysical, and numerical methods to study offshore freshened groundwater and better understand its role in the global water cycle.
European Colonists Dramatically Increased North American Erosion Rates
Around 200 years ago, when conversion of land for agriculture became more widespread, the amount of sediment accumulating in riverbeds across the continent jumped tenfold.
A Tried-and-True Medium to Broaden the Reach of Science
Television programming reaches broad, diverse audiences, but scientists must help tell their own stories and speak to the communities in which they live.
What Causes Centennial Changes in the Indonesian Throughflow?
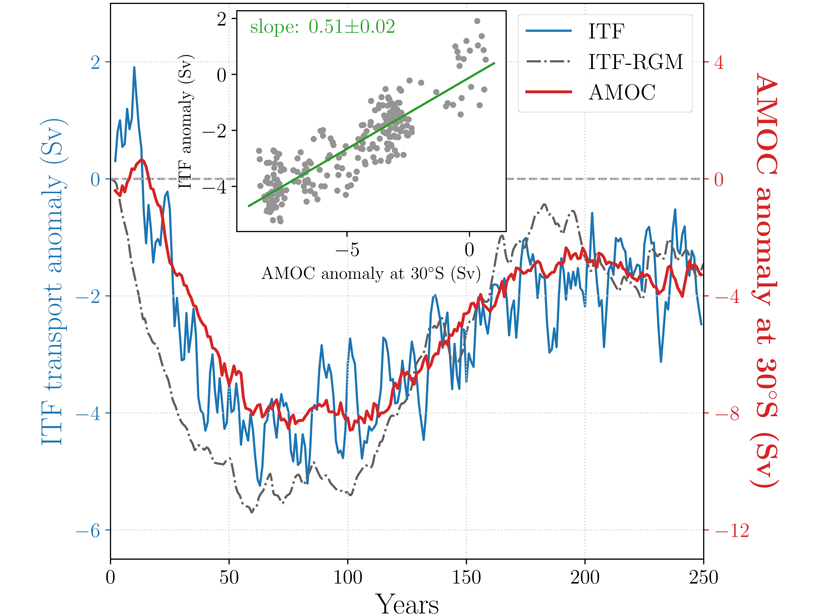
Transient long-term changes in the strength of the Indonesian Throughflow are unexpectedly linked to circulation changes in the remote high-latitude North Atlantic.