MAGPRIME is a library of magnetic interference removal algorithms, including benchmarks, that can aid in the design of spacecraft by providing simulations to determine optimal magnetometer placement.
Editors’ Highlights
A Seismogenic Shear Zone Diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts
Scientists document active seismic shear along a major lineament of Sikkim Himalaya diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts.
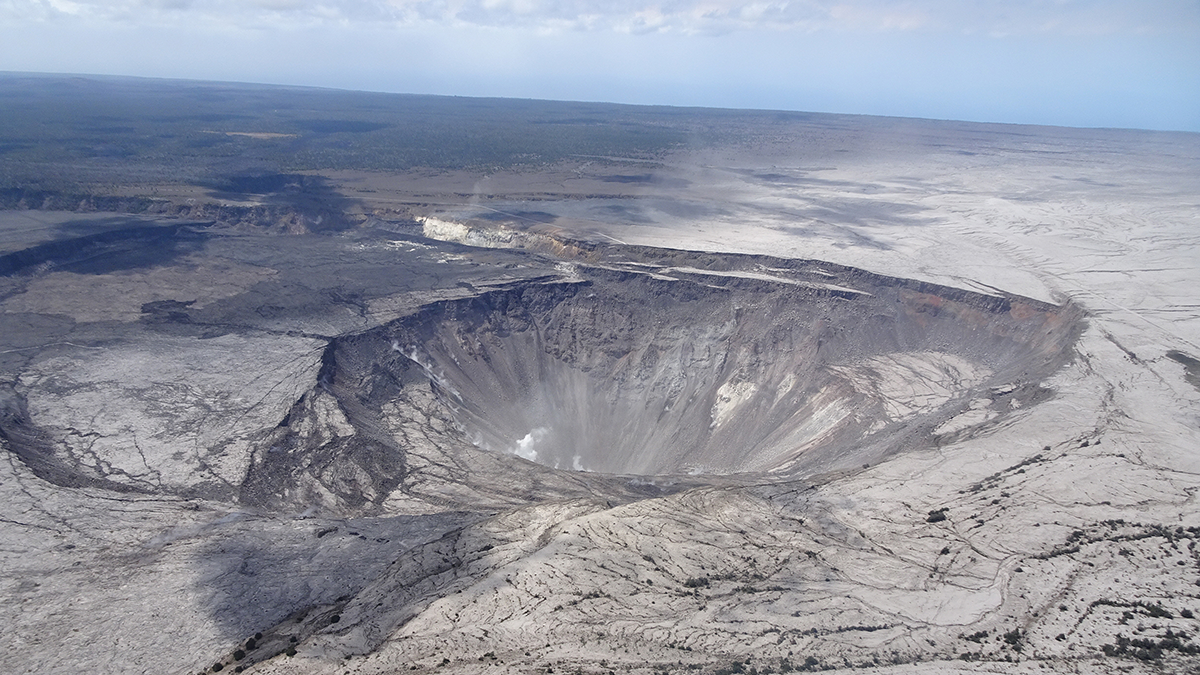
Caldera Collapse as a Natural Example of Rock Friction
Recurrent slips on the caldera wall of the Kīlauea Volcano are a natural experiment not only to understand the mechanics of caldera formation but also to gain more insights into fault friction.
Dual Tsunami Generation from Atmospheric and Oceanic Sources
The 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption generated waves that propagated across the Pacific Ocean. A new analysis of sea level measurements is used to dissect the difference in wave components from two sources.
Biogenic Sources Still Dominate Organic Carbon Aerosol in Europe
Scientists use radiocarbon measurements from Alpine ice to quantify present and past anthropogenic versus biogenic sources of organic carbon aerosols in the European atmosphere.
A Fast and Accurate Open-Source Atmospheric Transport Model
A new zonally-averaged atmospheric transport model will be useful for estimating emissions of ozone-depleting substances and greenhouse gases.
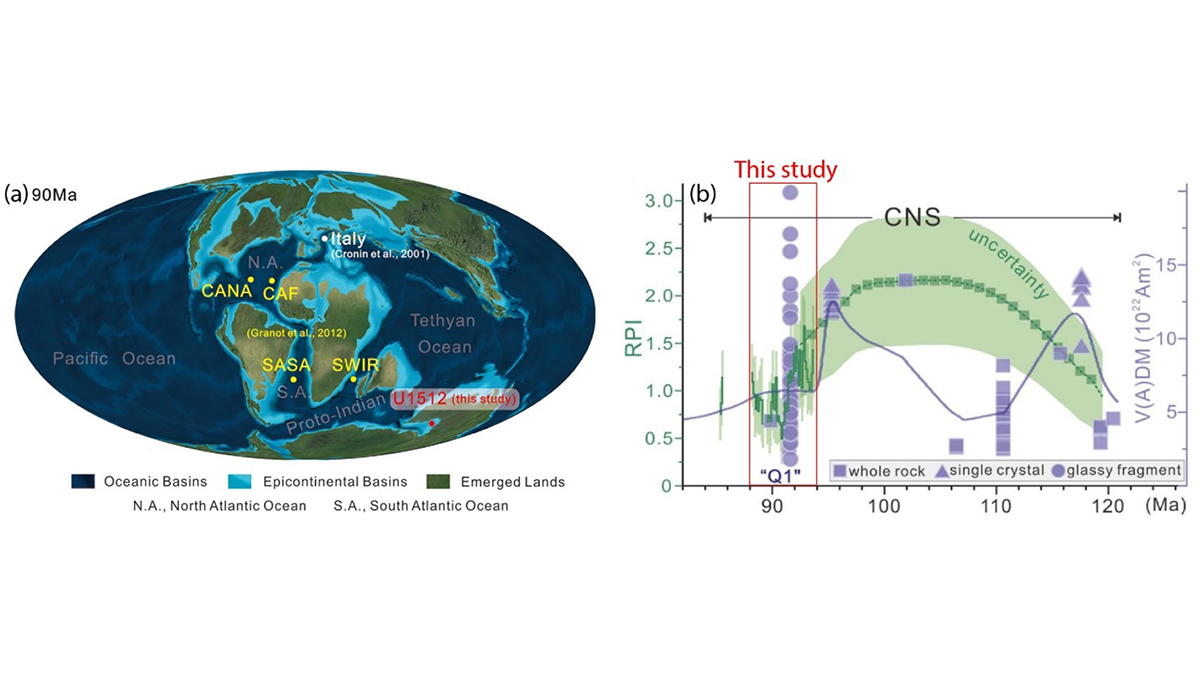
The Not-So-Quiet Cretaceous Quiet Zone
A new study finds that Earth’s magnetic field intensity varied significantly during the Cretaceous Normal Superchron, providing insights into the operation of the geodynamo during superchrons.
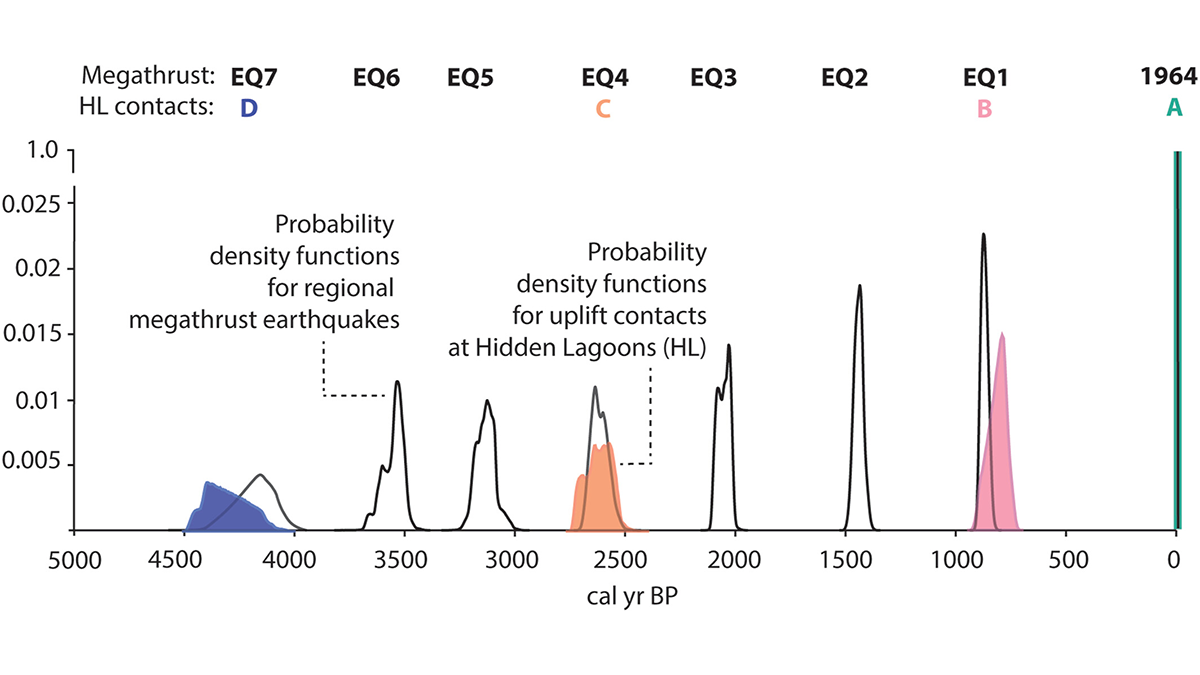
Repeated Coseismic Uplift Above the Patton Bay Splay Fault, Alaska
Stratigraphic and diatom analyses suggest ruptures of the Patton Bay splay fault occurred together with half of the documented great Alaskan megathrust earthquakes during the past 4,200 years.
Are the Geosciences Failing Their Qualifying Exam Goals?
Scientists favor data-driven reasoning but administer graduate student qualifying exams with surprisingly little guiding data. Re-examining these exams may advance educational equity and quality.
A Powerful New Model for U.S. Climate–Air Quality Interactions
NOAA’s Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory has developed a new variable-resolution global chemistry-climate model for research at the nexus of U.S. climate and air quality extremes.