A statistically robust approach applied to long-term flux measurements quantifies forest ecosystem response to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide, providing a valuable benchmark for climate models.
Editors’ Highlights
Machine Learning Masters Weather Prediction
Community datasets and evaluation standards are needed to further advance machine learning for weather prediction.
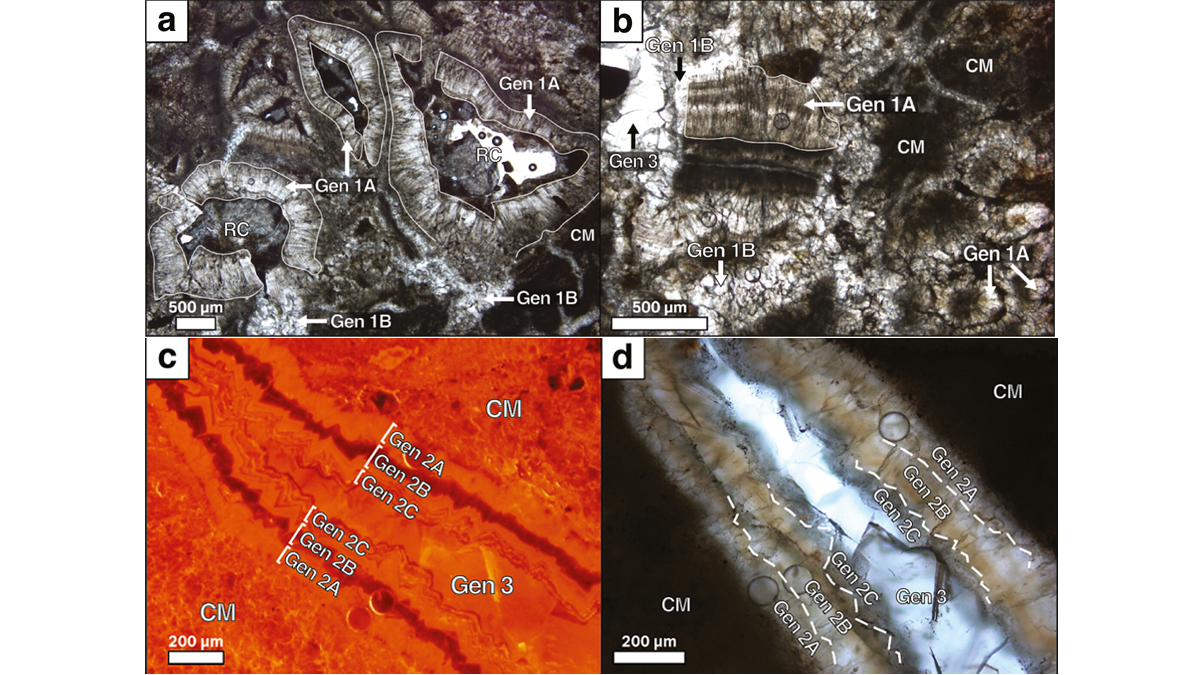
Unlocking Earth’s Terrestrial Sedimentary Record with Paleosols
Harnessing the micro-stratigraphy of pedogenic carbonates, scientists have demonstrated that age determination of fossil soils is possible via uranium-lead dating.
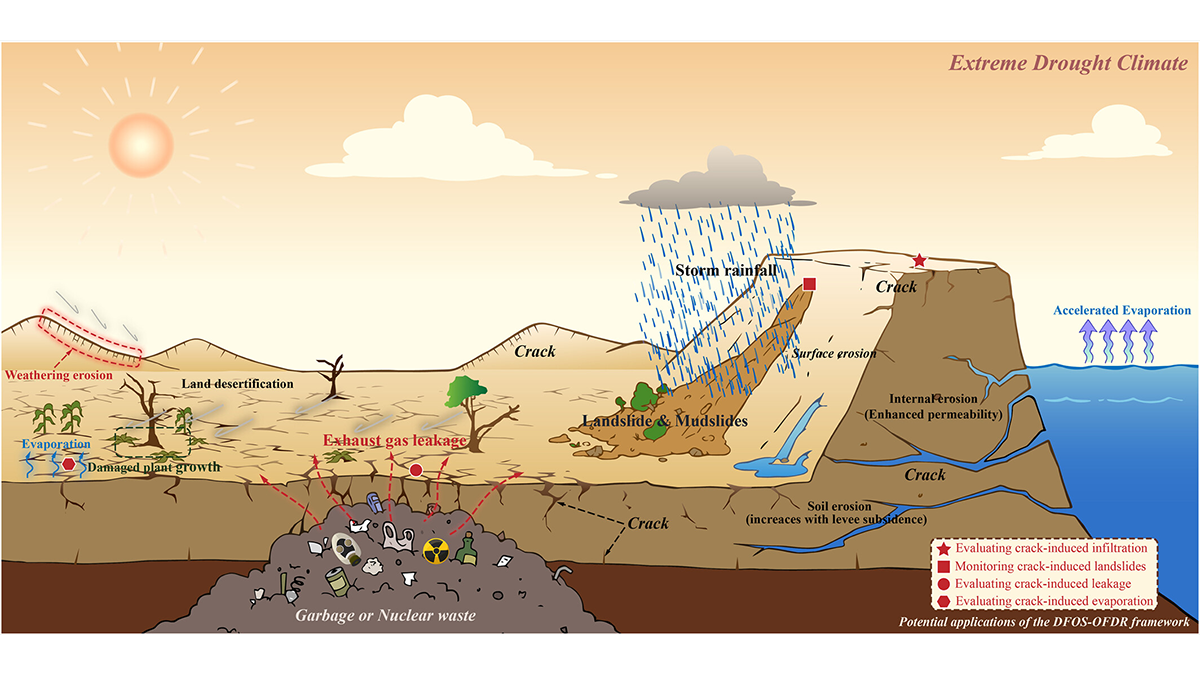
New Observations Provide Insight into Soil Desiccation Cracking
A new application of distributed fiber optic sensing provides early detection of soil desiccation cracking behavior and illustrates, for the first time, the phenomenon of soil crack breathing.
Open-Source MAGPRIME Supports Space Magnetism in the Heliosphere
MAGPRIME is a library of magnetic interference removal algorithms, including benchmarks, that can aid in the design of spacecraft by providing simulations to determine optimal magnetometer placement.
A Seismogenic Shear Zone Diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts
Scientists document active seismic shear along a major lineament of Sikkim Himalaya diagonal to the Main Himalayan Thrusts.
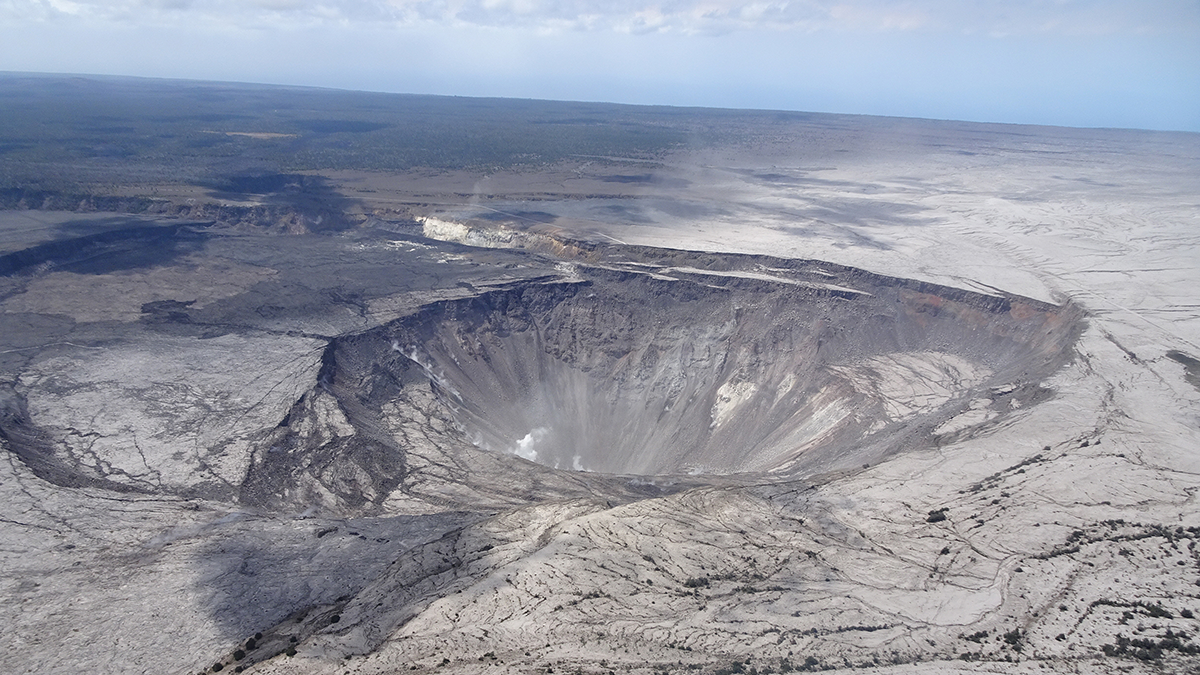
Caldera Collapse as a Natural Example of Rock Friction
Recurrent slips on the caldera wall of the Kīlauea Volcano are a natural experiment not only to understand the mechanics of caldera formation but also to gain more insights into fault friction.
Dual Tsunami Generation from Atmospheric and Oceanic Sources
The 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption generated waves that propagated across the Pacific Ocean. A new analysis of sea level measurements is used to dissect the difference in wave components from two sources.
Biogenic Sources Still Dominate Organic Carbon Aerosol in Europe
Scientists use radiocarbon measurements from Alpine ice to quantify present and past anthropogenic versus biogenic sources of organic carbon aerosols in the European atmosphere.
A Fast and Accurate Open-Source Atmospheric Transport Model
A new zonally-averaged atmospheric transport model will be useful for estimating emissions of ozone-depleting substances and greenhouse gases.