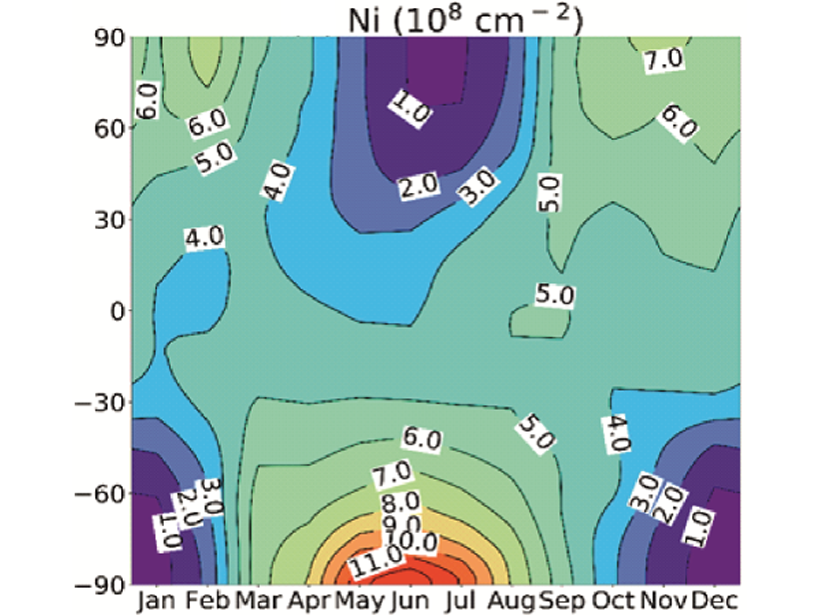
A layer of nickel of cosmic origin, which exists between 80 and 110 km high in Earth’s atmosphere, has been modeled for the first time, including dynamics and complex neutral and ion chemistry.
Editors’ Highlights
Saharan Dust Reaching the Americas Comes from El Djouf
The Saharan dust that crosses the Atlantic and fertilizes the Amazon may be coming from the El Djouf region between Mauritania and Mali, which is farther west than previously thought.
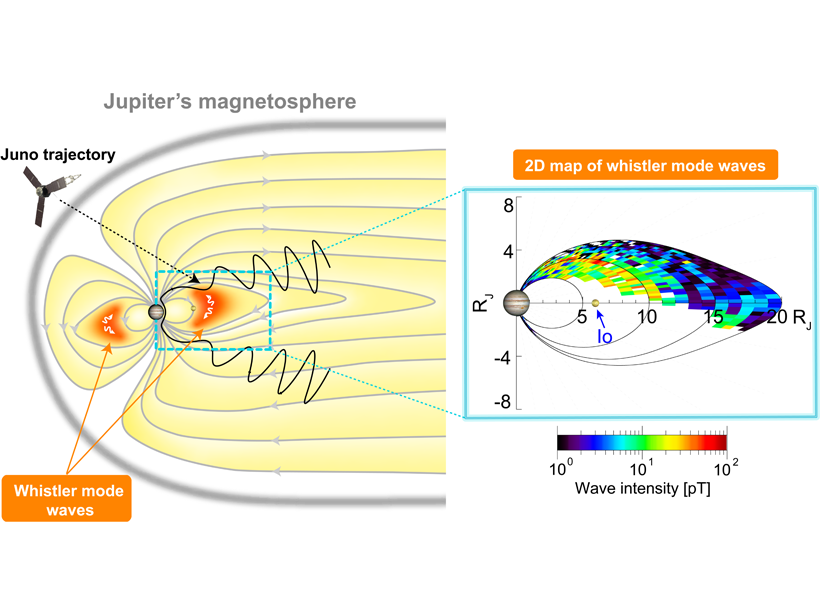
A Whistle Here, There, and Everywhere on the Giant Planet
NASA’s Juno spacecraft is “hearing whistles” all over the place on Jupiter, a type of natural plasma waves called whistlers that are sometimes associated with atmospheric lightning.
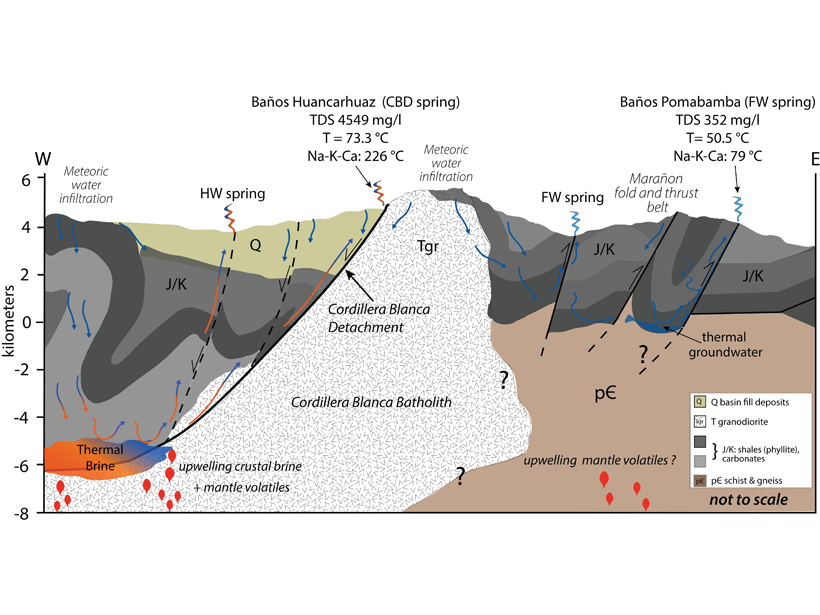
Structural Style Controls Crustal Fluid Circulation in Andes
Variations in hot spring geochemistry from adjacent mountain ranges with different styles of faulting highlight the influence of crustal-scale structures on circulating fluids in the Peruvian Andes.
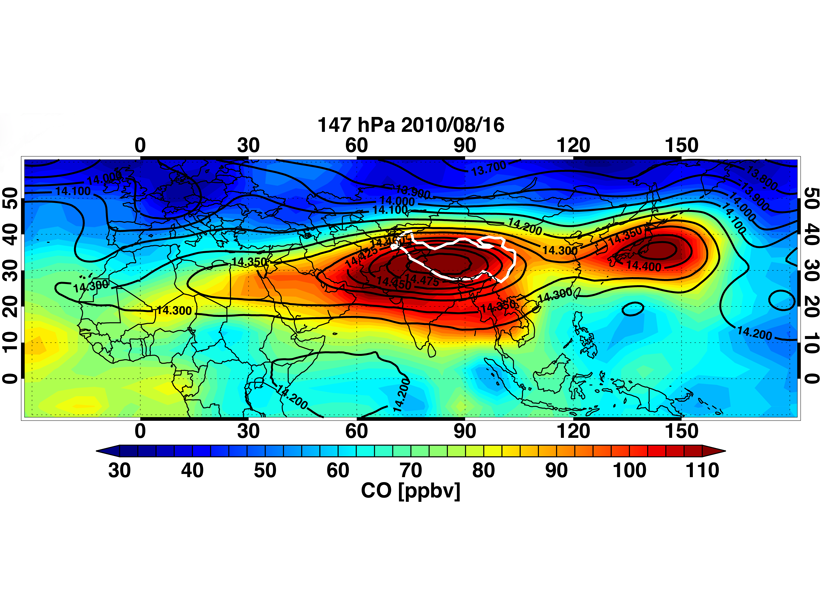
When Chemistry Lends a Hand to Dynamics
Chemical signature and chemical transport analyses help understand the dynamics of the Asian Summer Monsoon.
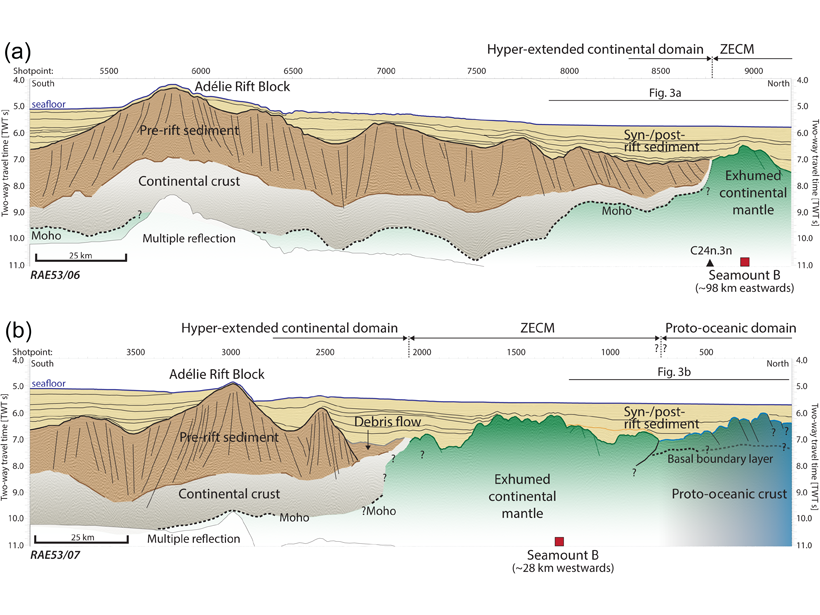
New Data from Earth’s Largest Non-Volcanic Rift Margin
Seismic reflection images combined with petrological data provide new constraints on the nature of the basement in the enigmatic Australia-Antarctic oceanic-continent transition zone.
Characteristics of Polar Sea Ice in Latest Climate Models
Sea ice area in CMIP6 is similar to previous versions while its sensitivity to external forcing is subtly different and closer to observations, but still not in step with global surface temperature.
Can We Observe How Cloud Clustering Affects the Radiation Budget?
Satellite observational analysis confirms that lower-atmospheric stability and cloud clustering are major factors modulating the tropical radiation budget that had been suggested by modeling studies.
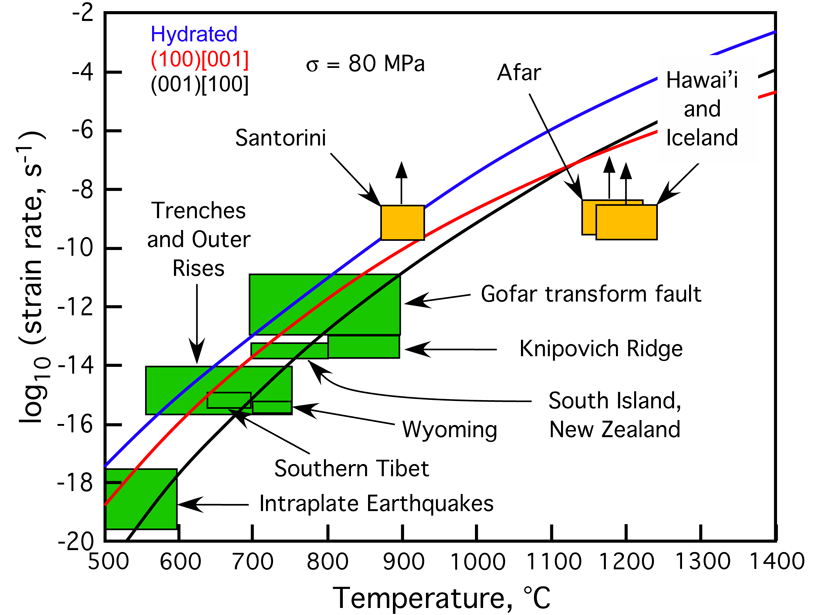
Strain Rate: The Overlooked Control on Earthquake Depth
Regional strain rate may play as significant a role as temperature in governing the depth distribution of earthquakes in mantle lithosphere.
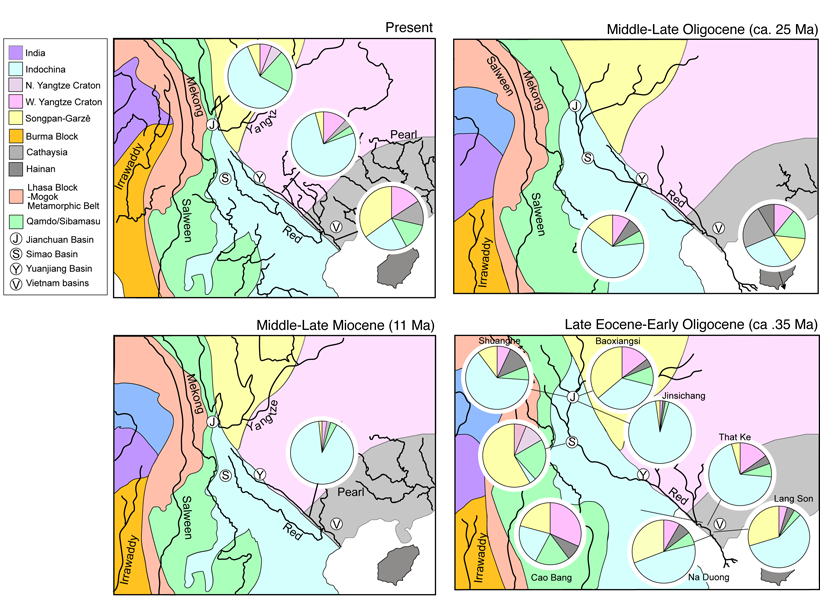
A River Ran Through It
The history of river system in southeast Tibet and Indochina reconstructed using the ages of thousands of zircon sand grains in modern and ancient river sediments.