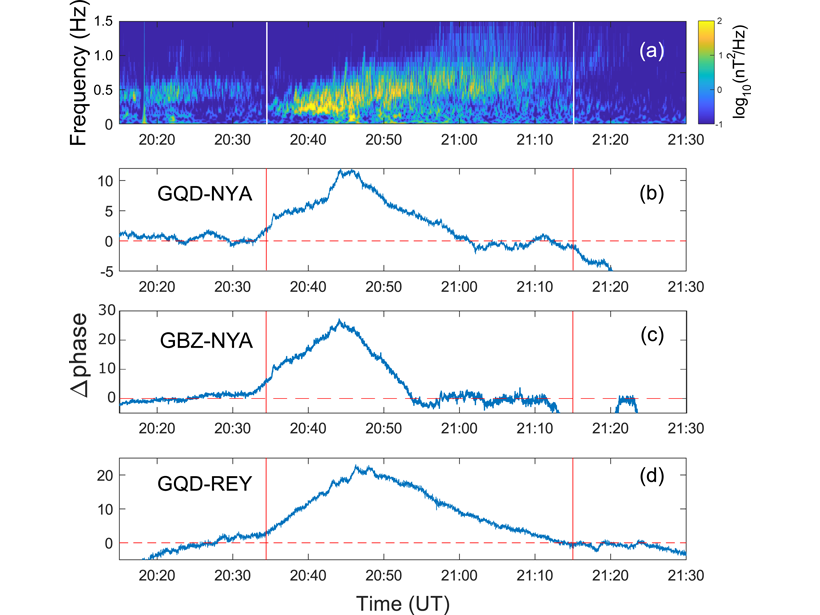
An international armada of orbiting satellites and ground VLF network join forces to form a “magnetosphere-ionosphere observatory” to size up electromagnetic ion cyclotron waves in the magnetosphere.
Editors’ Highlights
A New Perspective on a Classic Climate Conundrum
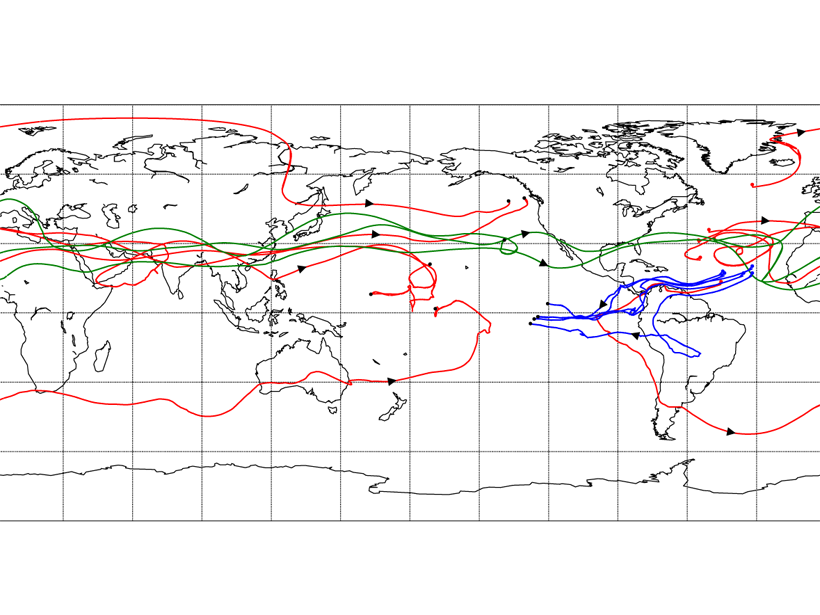
The Lagrangian method applied to tracking water transport between the Atlantic and Pacific basins reveals a larger contribution by mid-latitude westerly winds across Eurasia than previously thought.
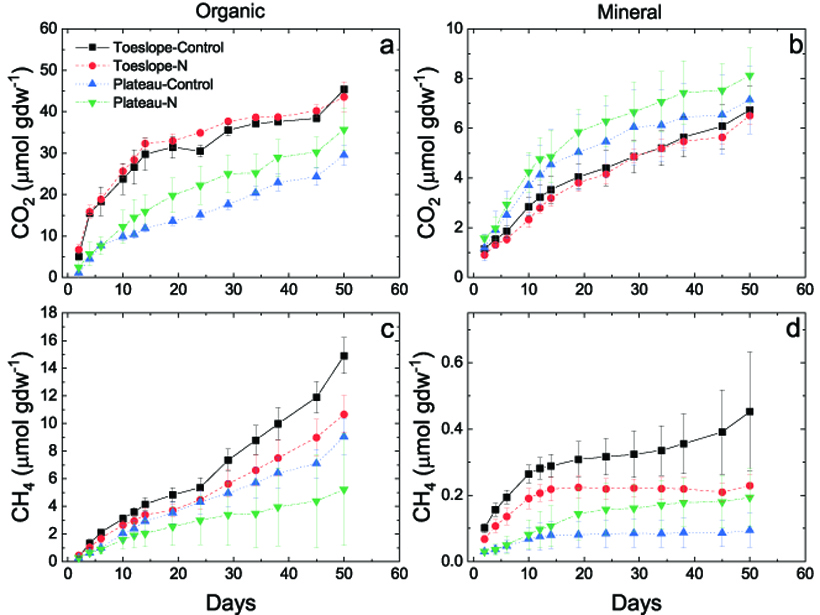
Downhill from Here: Landscape Positions and Greenhouse Emissions
In comparing soils from two tundra wetland landscape positions, landscape position is found to matter, and toeslopes are associated with higher greenhouse gas production.
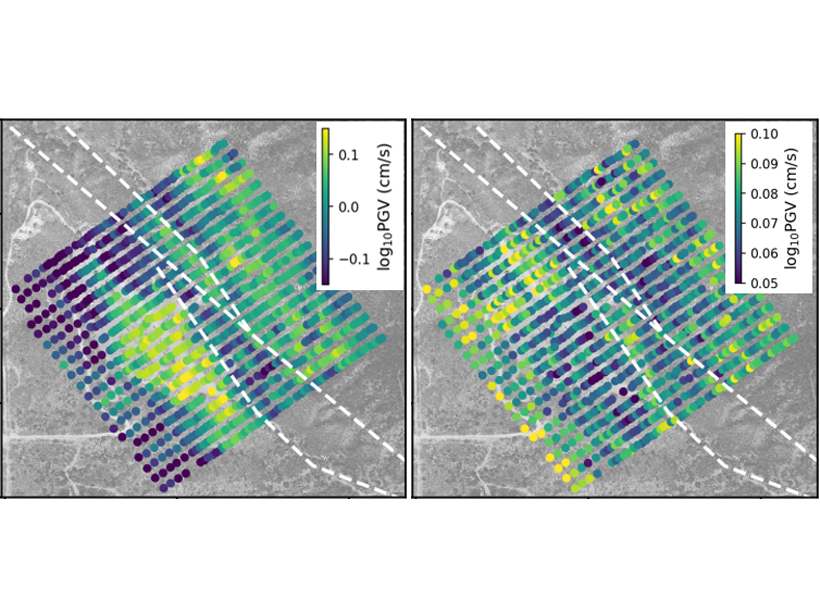
Super Dense Array Measurement Magnifies Seismic Wavefields
An investigation of small-scale spatial variability in earthquake ground motions helps to quantify the uncertainty of ground motions in probabilistic seismic hazard analysis.
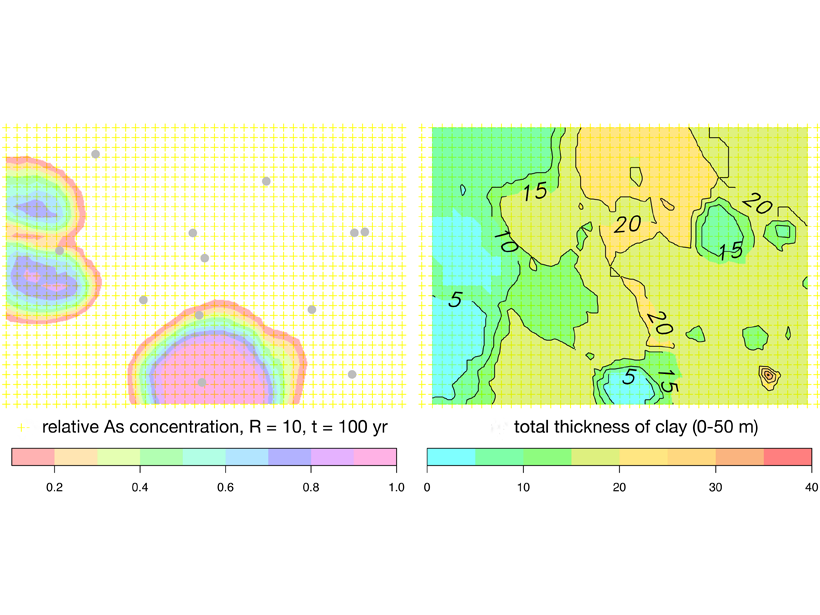
Arsenic Pollution in Bangladesh is Catching Up with Deeper Wells
Inhabitants of Bangladesh have deepened drinking water wells to avoid extracting arsenic-rich groundwater from shallow aquifers, but these may not be free from pollution either.
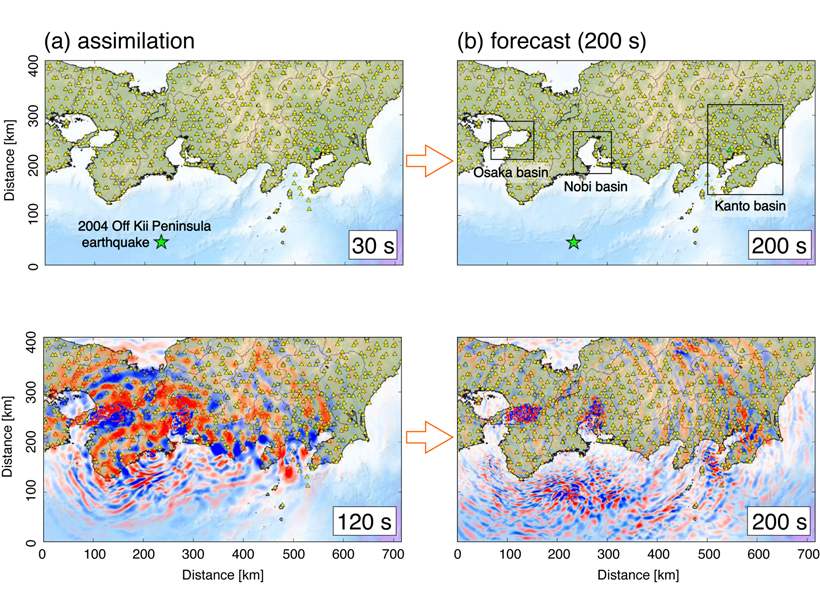
Real-time Ground Motion Estimation for Large Earthquakes
Advanced computing technology can be used to forecast ground shaking from earthquakes and provide an early warning in real time.
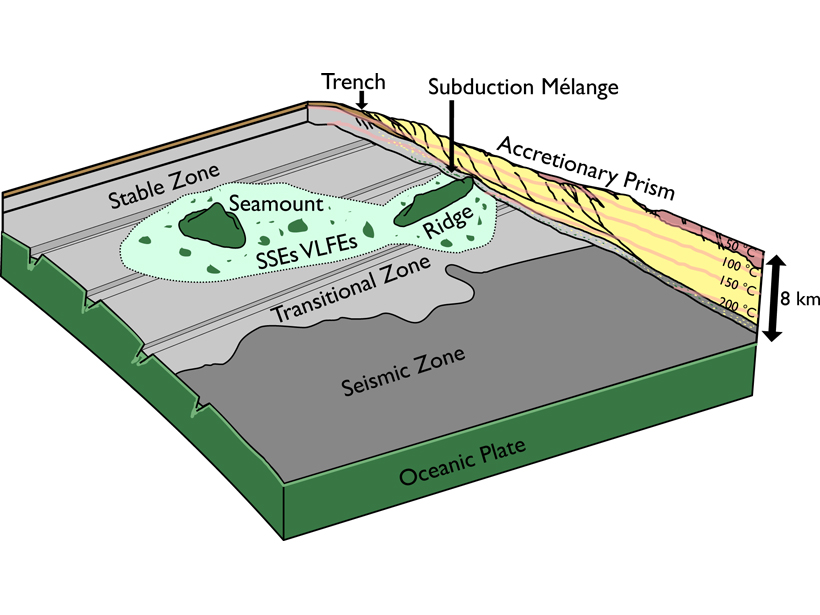
A Mechanism for Shallow, Slow Earthquakes in Subduction Zones
Slow earthquakes beneath the accretionary prism updip from the locked portion of a subduction zone can be caused by basaltic blocks embedded in a shale matrix.
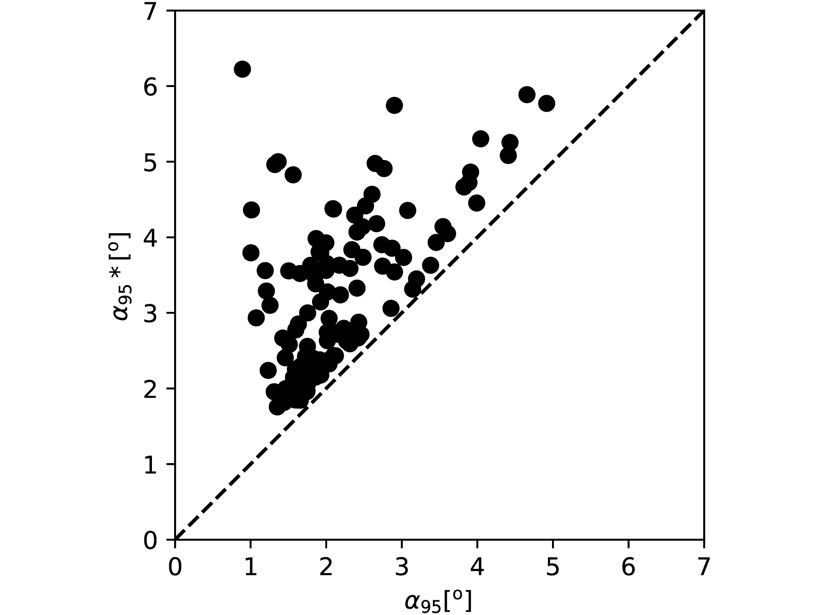
Uncertainty Propagation in Paleomagnetic Data Quantified
In classic paleomagnetic data processing uncertainties are calculated at a single level only, but there is now a more lucid way to include error propagation.
Upstream Propagating Magnetic Dips in the Magnetosheath
The previous consensus that magnetic dips in the magnetosheath can be attributed to non-propagating mirror waves is now shown to be oversimplified.
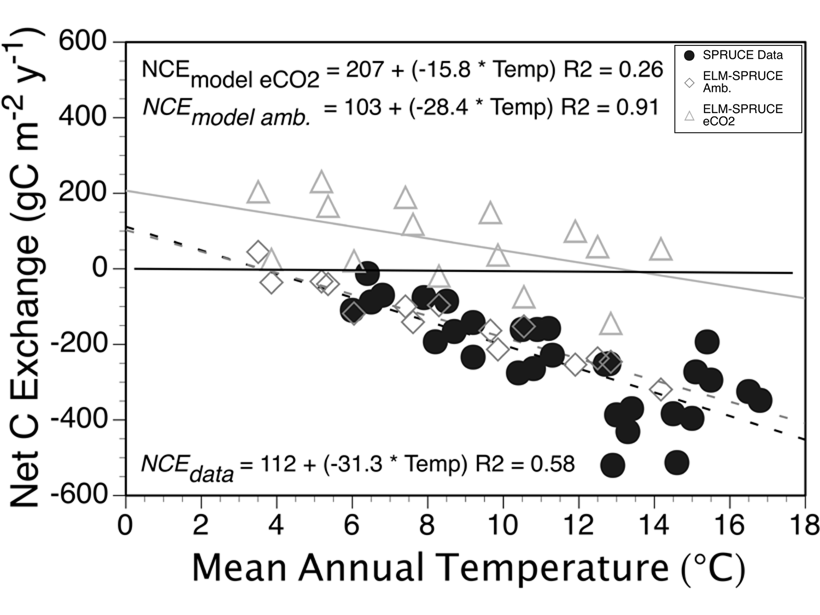
Soil Carbon May Not Remain Bogged Down in a Warmer World
Carbon was lost from an experimentally warmed boreal peatland much faster than it took to accumulate. Elevated CO2 had little effect on stored carbon, requiring re-evaluation of model assumptions.