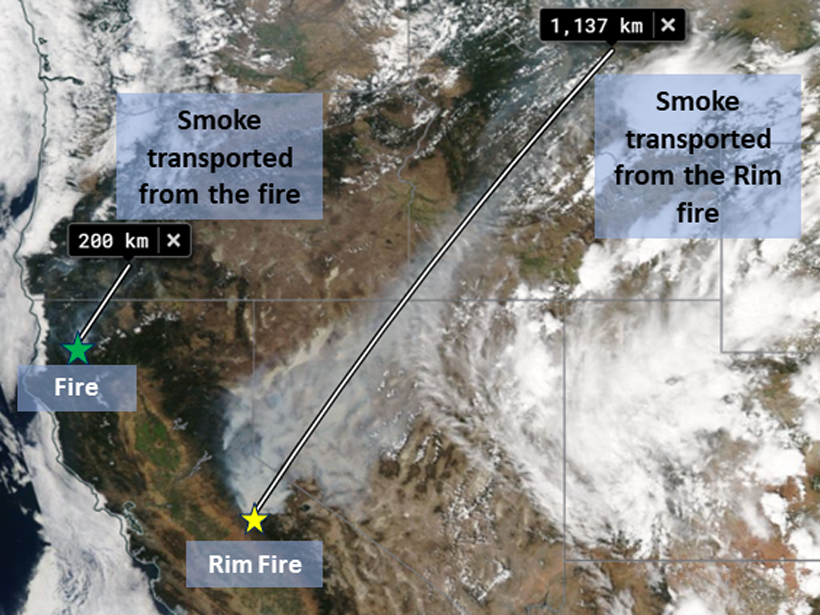
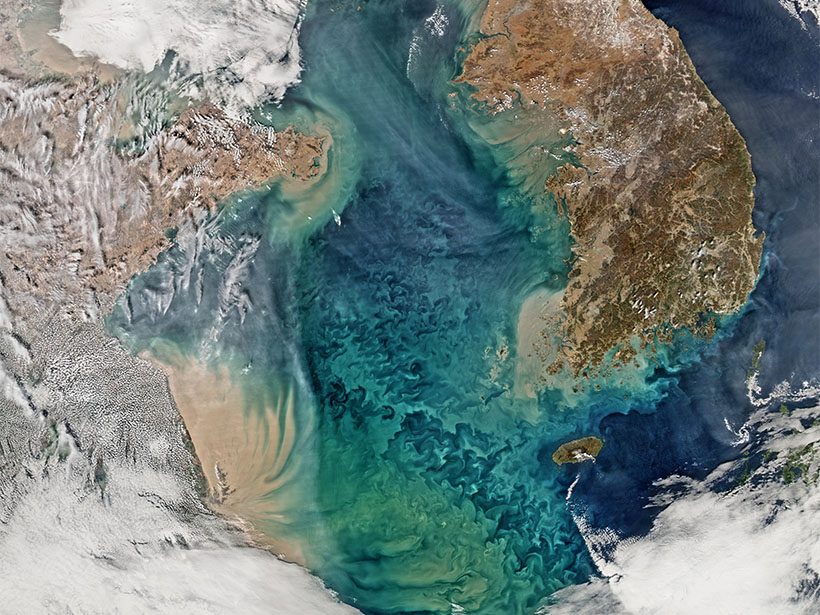
Aerosol observations from EPIC—a sensor aboard a satellite—align well with ground- and aircraft-based data, including measurements of smoke plumes produced by recent megafires.
remote sensing
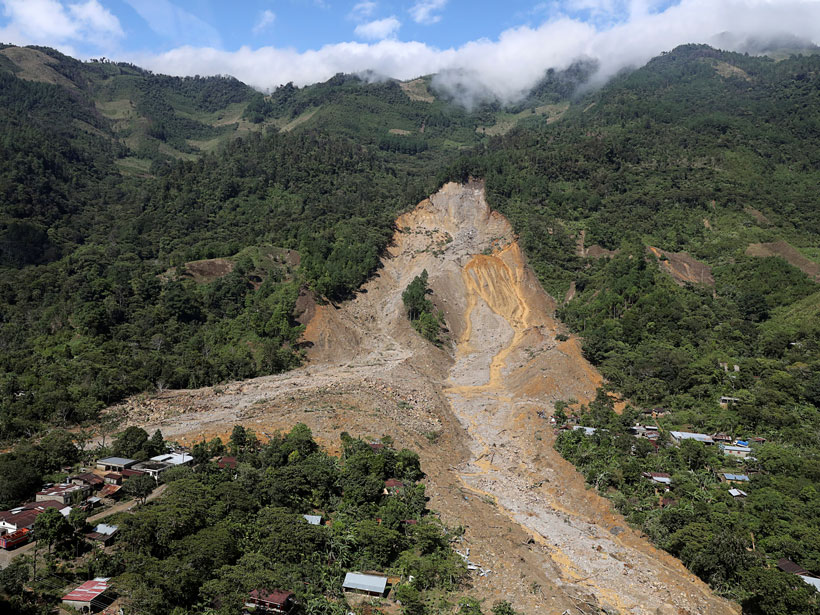
Satellites Support Disaster Response to Storm-Driven Landslides
Extreme precipitation can trigger deadly landslides. Satellite-based tools provide regional perspectives on landslide hazards, help assess risks in near-real time, and guide emergency responses.
A New Practical Guide to Using Python for Earth Observation
A new book presents an example-driven collection of basic methods, applications, and visualizations to process satellite data sets for Earth science research.
Una mirada global al carbono orgánico superficial del suelo
El carbono orgánico del suelo es un elemento importante para la salud de los ecosistemas y del clima. En la actualidad la teledetección permite a los científicos observar globalmente esta importante pieza del rompecabezas del carbono.
Realizing Machine Learning’s Promise in Geoscience Remote Sensing
Machine learning and signal processing methods offer significant benefits to the geosciences, but realizing this potential will require closer engagement among different research communities.
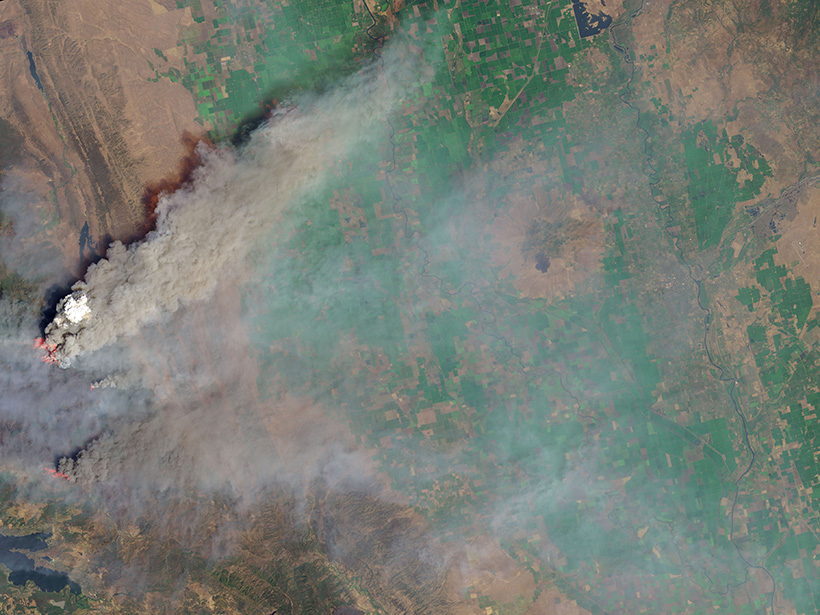
Improved Algorithms Help Scientists Monitor Wildfires from Space
Wildfires release pollutants that harm human health. Quality satellite monitoring can help track these pollutants and predict where they may become health hazards.
Observations from Space and Ground Reveal Clues About Lightning
In a coordinated monitoring effort, scientists have uncovered the timing and triggering of high-energy lightning events in the sky.
The Earth in Living Color: Monitoring Our Planet from Above
A new special collection invites papers on a new era of remote sensing missions and instruments that will provide insights into human and climate driven changes on planet Earth.
Chasing Cyclones from Space
The pioneering use of satellite-based synthetic aperture radar to characterize tropical cyclones in near-real time has provided a crucial new tool with which to forecast powerful storms.
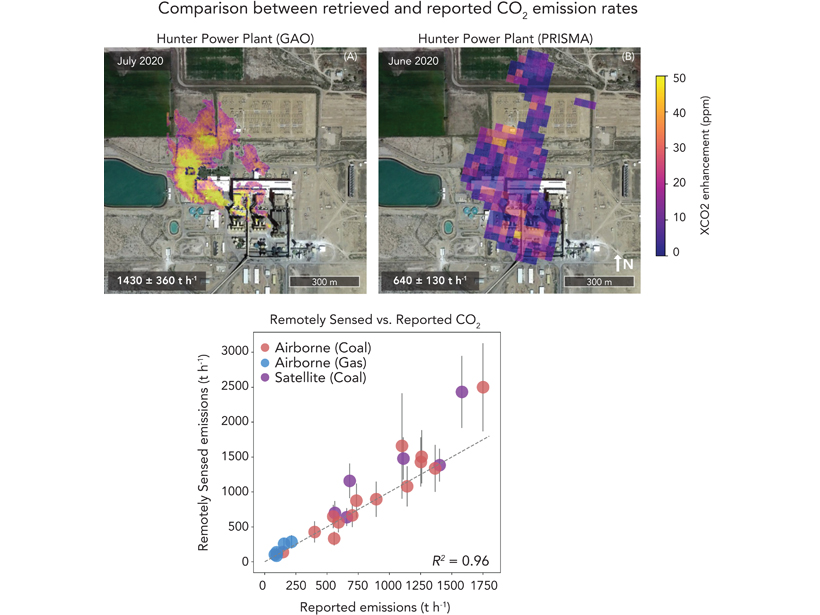
Constraining Global Power Plant Emissions of Carbon Dioxide
Airborne and satellite imaging spectrometers provide accurate quantifying of CO2 emissions at the facility scale, which is important to emission budgets and policy constraints.