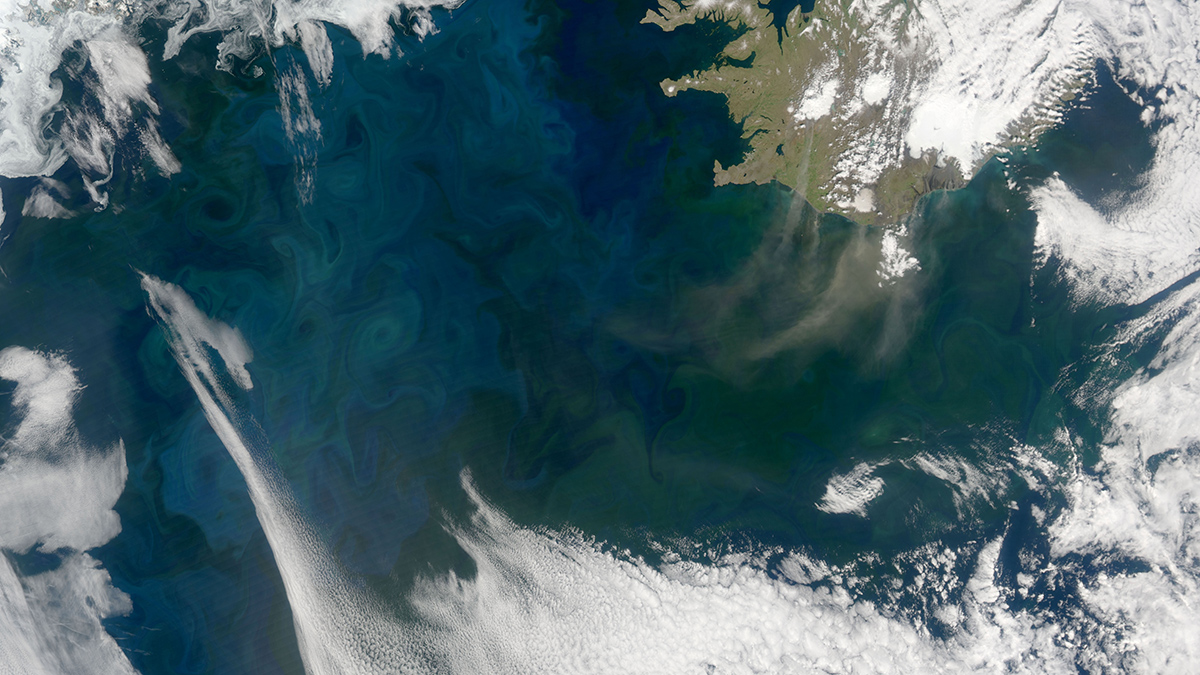
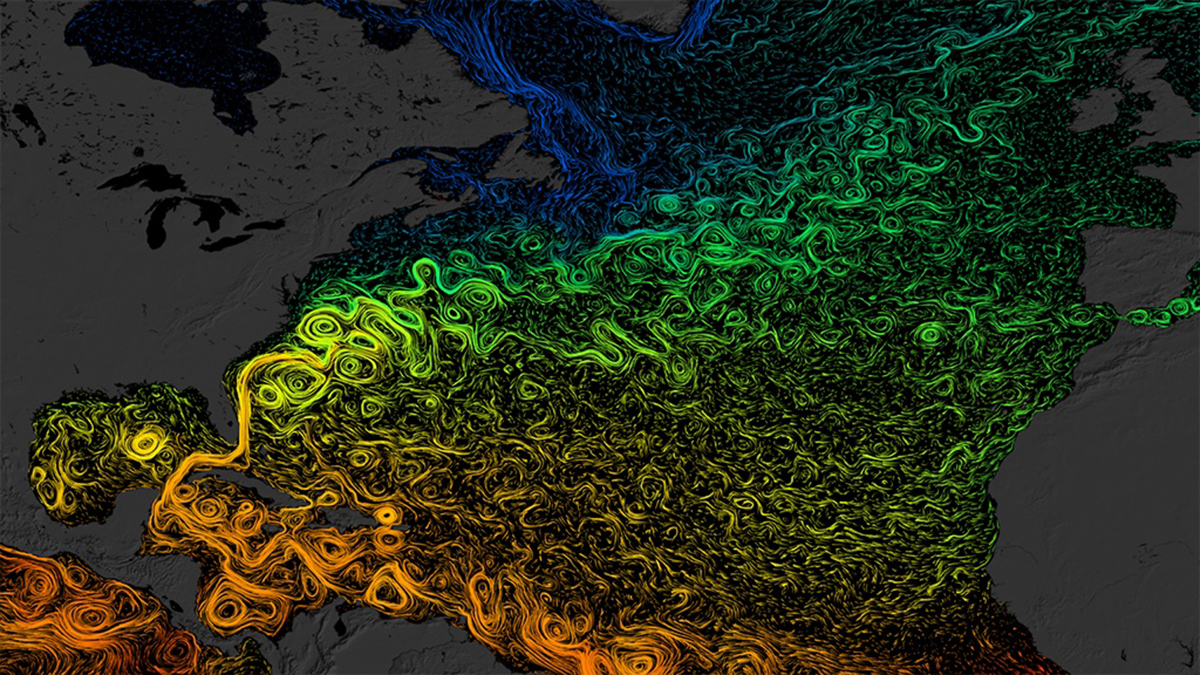
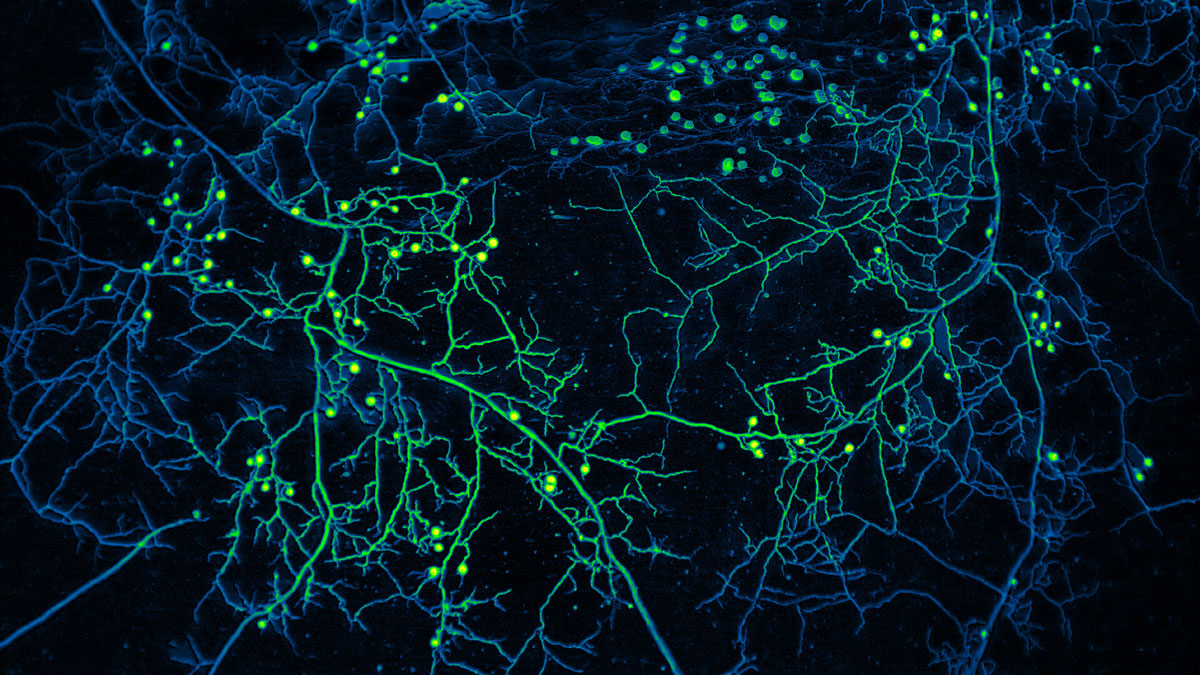
Dissolved organic carbon prevalence follows from how many bacteria are around to eat it, modeling suggests.
carbon
The Endangerment Finding Is Lost
Tomorrow, the EPA will revoke the 2009 Endangerment Finding, finalizing a July proposal to do so, Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt said in a 10 February announcement.
Marine Snow Grows Faster and Fluffier as It Sinks
New observations highlight how abiotic and biotic processes influence the tiny oceanic particles.
What Could Happen to the Ocean’s Carbon If AMOC Collapses
Mass glacier melting may have led this influential ocean current system to collapse at the end of the last ice age. A pair of modeling studies examines how such a collapse could affect dissolved inorganic carbon and carbon isotopes in Earth’s oceans.
How a Move to the Shallows 300,000 Years Ago Drove a Phytoplankton Bloom
And what that could mean for today’s ocean.
How Can We Tell If Climate-Smart Agriculture Stores Carbon?
Quantitative data at real-world scales are needed to assess the effects of cover cropping and other practices on soil carbon storage. Large-scale medical studies provide a proven methodology.
How Plant-Fungi Friendships Are Changing
A new framework shows how much carbon plants allocate to their endosymbionts and how that amount might change in the face of warming soil and rising carbon dioxide levels.
Free-Roaming Bison Graze Life into Grasslands
A new study suggests that Yellowstone’s herd of bison accelerates nutrient cycling, offering a glimpse into the North American plains of yesteryear.
Public Speaks Out Against EPA Plan to Rescind Endangerment Finding
Advocates, scientists, doctors, members of Congress, kids, parents, and other individuals spoke out in a series of hearings last week to let the Environmental Protection Agency know how they feel about a potential sea change in climate and environmental policy: the proposed repeal of the 2009 Endangerment Finding.
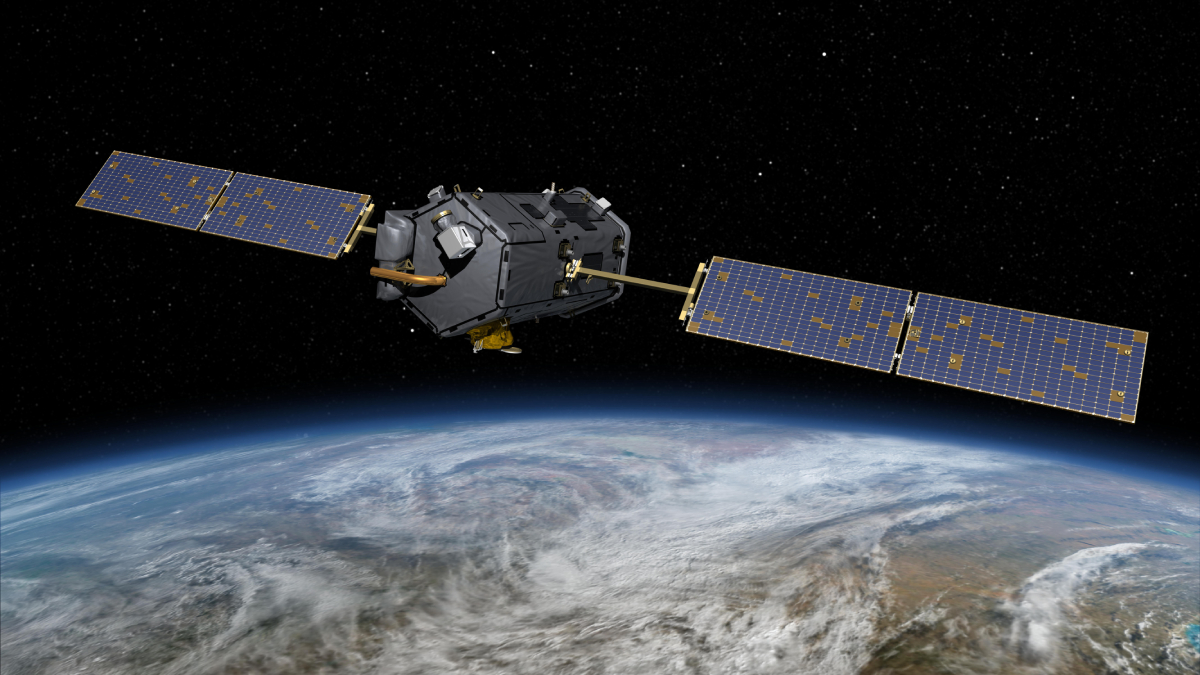
NASA Planning for Unauthorized Shutdown of Carbon Monitoring Satellites
Despite warnings that their actions are illegal, Duffy and other senior NASA officials have continued to secretly direct NASA employees to draw up plans to end at least two major satellites missions specifically designed to monitor global carbon dioxide.