Use of deicing agents may sometimes raise sodium levels in drinking water beyond healthy limits for people on salt-restricted diets.
cities
Pollution Is Disrupting Rain Cycles in the Amazon
A team of researchers in Brazil and the United States uncovered the importance of the mechanism of oxidation—a process with the potential to affect climate and precipitation across the tropics.
Forest Edges Are More, Not Less, Productive Than Interior Forest
The boundaries of northeastern U.S. forests suck in more carbon dioxide than previously thought.
Weighing the Benefits of Urban Greening
City communities may need to consider whether water absorption or cooling benefits are more important when designing urban greening.
Urbanization and Surface Water Loss Go Together
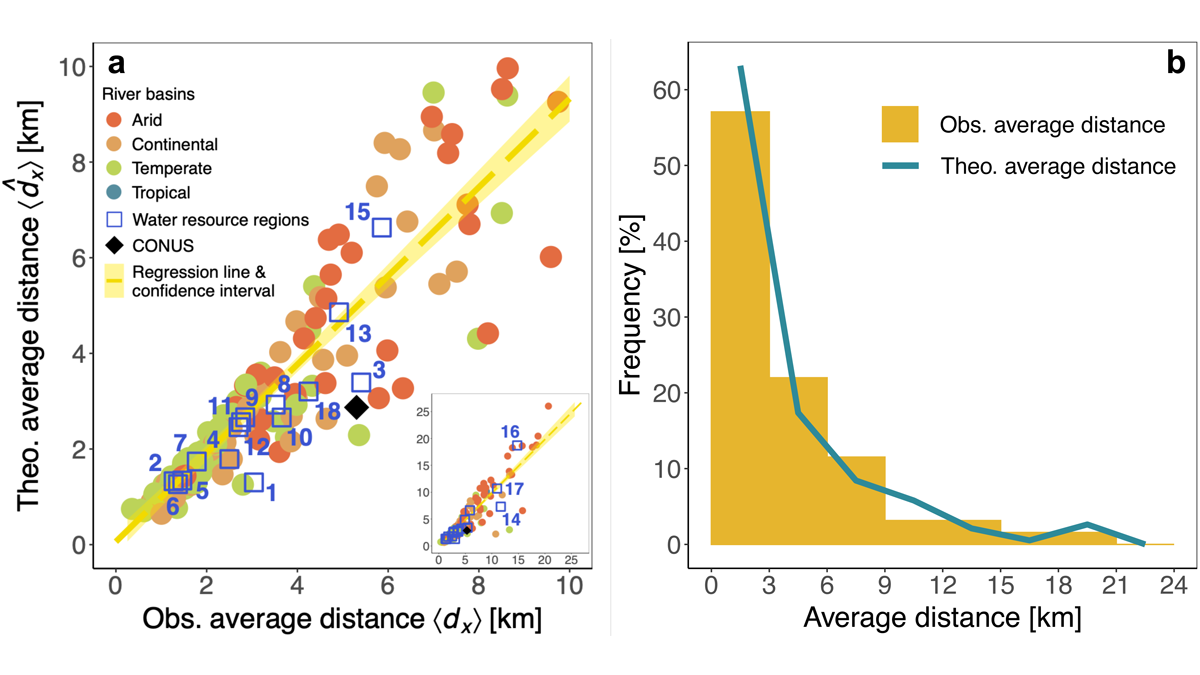
Mapping surface water loss from satellite data confirms decreases away from urban areas. A simple exponential distance-decay model approximates the impact of urbanization.
Continuity is the Father of Success
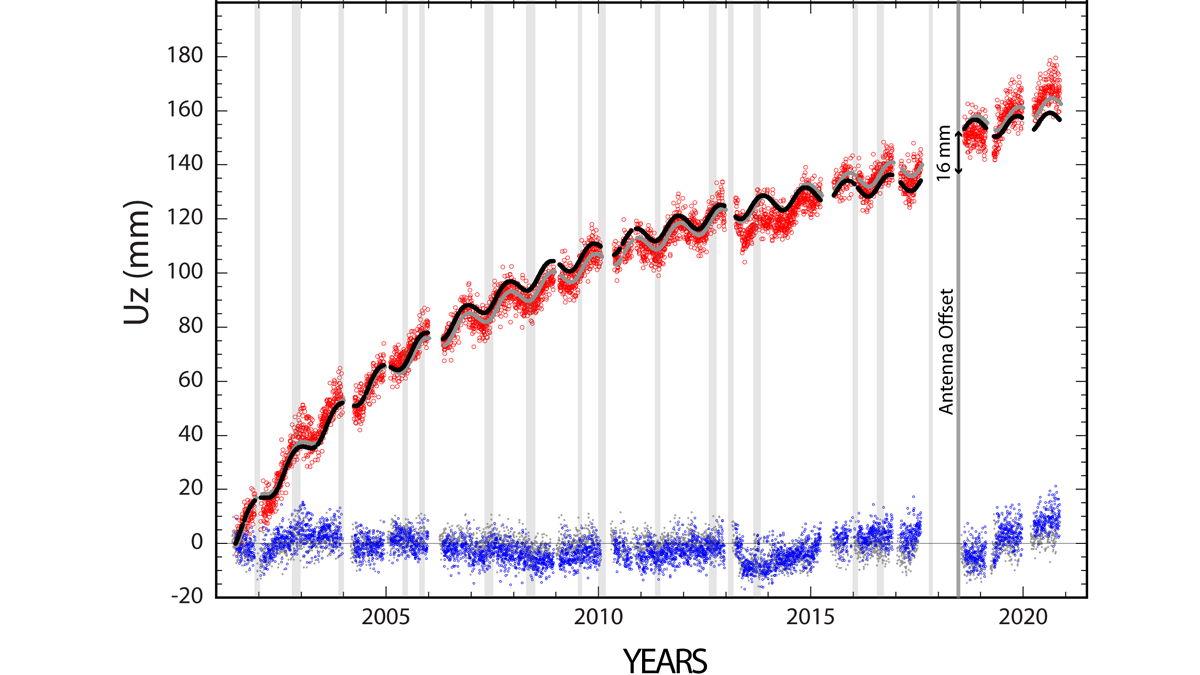
Geodetic measurements indicate that Three Sisters Volcano uplifted by almost 300 millimeters in the past 25 years without significant anomalies at the surface.
Fiber-Optic Cables Can Produce High-Resolution Underground Maps
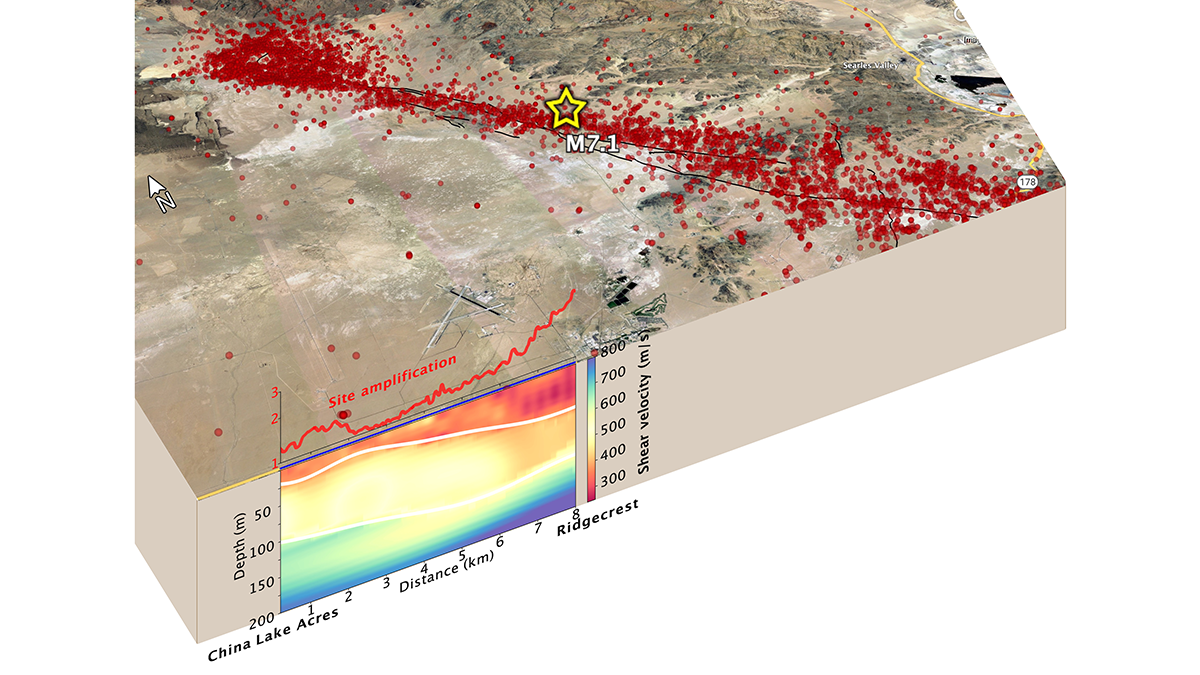
Telecom fiber repurposed as distributed acoustic sensing arrays can image near-surface structure and potentially improve seismic hazard mapping in urban areas.
Mapping Teotihuacan’s Past, Present, and Future
A new lidar project reveals how mining and urban expansion have put one of Mexico’s most iconic cultural heritage sites at risk.
Native Super Trees Could Provide Climate Solutions to Houston
A Houston nonprofit identified 14 native “super tree” species that are particularly promising for mitigating climate change and public health concerns.
Crowdsourced Science Helps Map Vancouver’s “Smellscape”
Exposure to stinky odors can affect human health, but quantifying smells can be difficult.