Tom Beer received the 2016 International Award at the American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting Honors Ceremony, held on 14 December 2016 in San Francisco, Calif. The award honors "an individual scientist, group, or a small team for making an outstanding contribution to furthering the Earth and space sciences and using science for the benefit of society in developing nations."
Climate Change
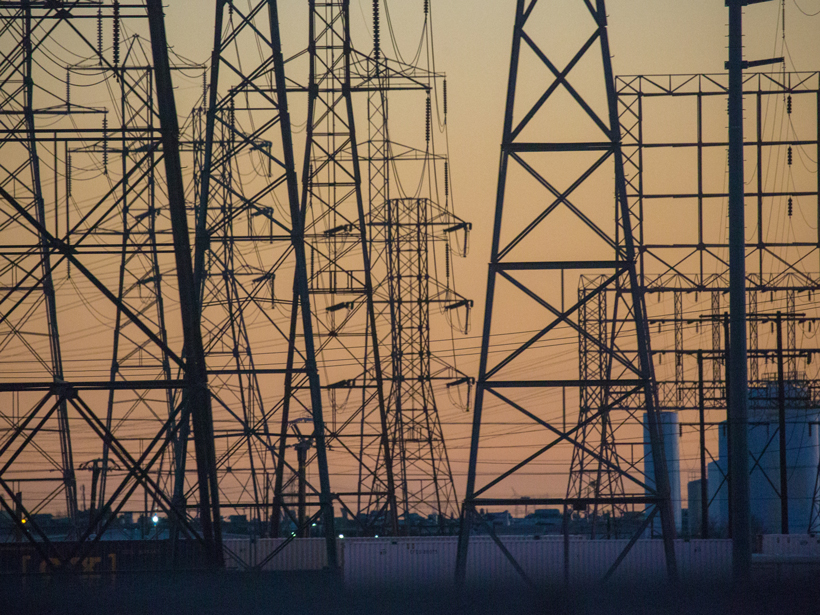
Achieving a Near-Zero Carbon Emissions Energy System
Getting Near Zero: Decarbonizing the Last 20%; Aspen, Colorado, 31 July to 5 August 2016
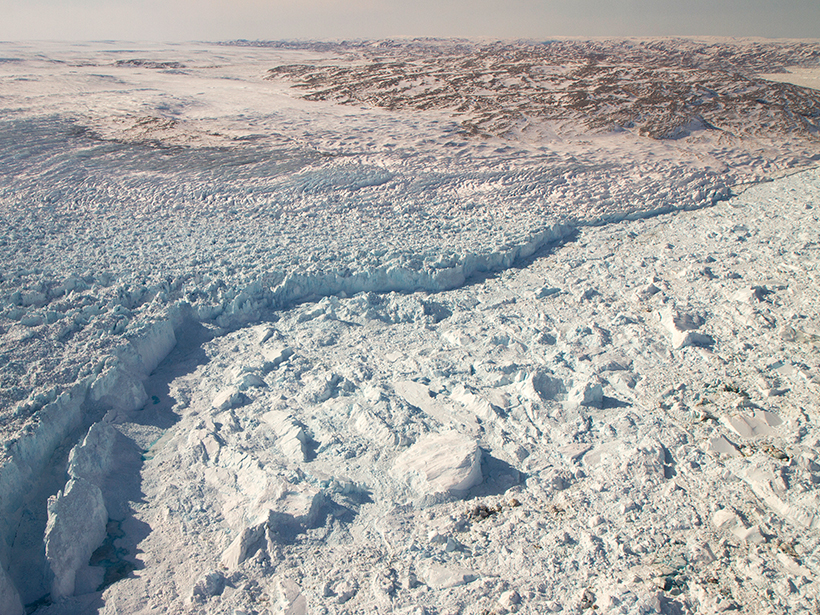
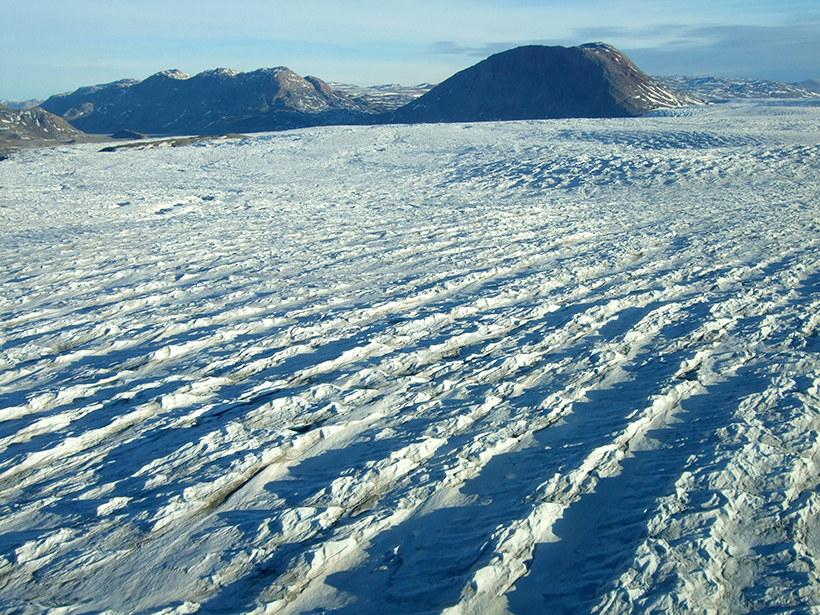
More Frequent Glacial Quakes on Greenland Signal Ice Retreat
Between 1993 and 2011, the annual number of earthquakes caused by gigantic blocks of ice breaking away from Greenland's glaciers has increased, further evidence of accelerating ice loss.
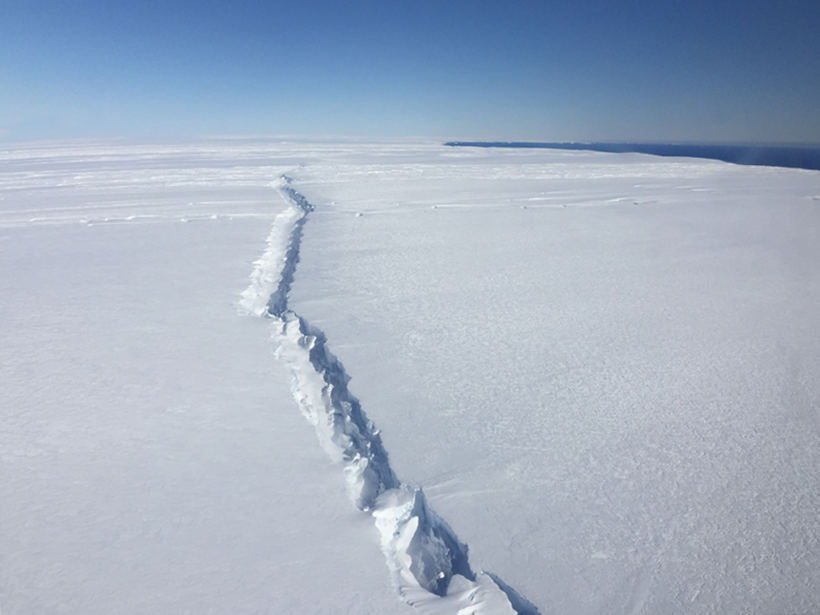
West Antarctic Ice Shelf Breaking Up from the Inside Out
Researchers trace the origin of a 2015 iceberg to a crack that formed deep beneath the ice.
Why We Must Tie Satellite Positioning to Tide Gauge Data
Accurate measurements of changes in sea and land levels with location and time require making precise, repeated geodetic ties between tide gauges and satellite positioning system equipment.
The Pace of Change on Tropical Landscapes
Emerging Issues in Tropical Ecohydrology; Cuenca, Ecuador, 5–9 June 2016
Using Landsat to Take the Long View on Greenland's Glaciers
A new web-based data portal gives scientists access to more than 40 years of satellite imagery, providing seasonal to long-term insights into outflows from Greenland's ice sheet.
How Global Warming's Effect on Clouds May Make It Rain Harder
More clustering of clouds due to higher temperatures increases the likelihood of heavy downpours.
Bringing Earth's Microwave Maps into Sharper Focus
New processing capabilities improve the spatial resolution of satellite microwave data, enabling scientists to analyze trends in coastal regions and marginal ice zones.
Major Ocean Circulation Pattern at Risk from Greenland Ice Melt
The current warming trend could mean the collapse of ocean's global conveyor belt, which would have far-reaching effects on climate around the world. But this collapse could still be avoided.