Late Cretaceous dinosaurs may have cut back vegetation, creating large floodplains. When the asteroid hit, those floodplains became forests, a new study argues.
Cretaceous
The Not-So-Quiet Cretaceous Quiet Zone
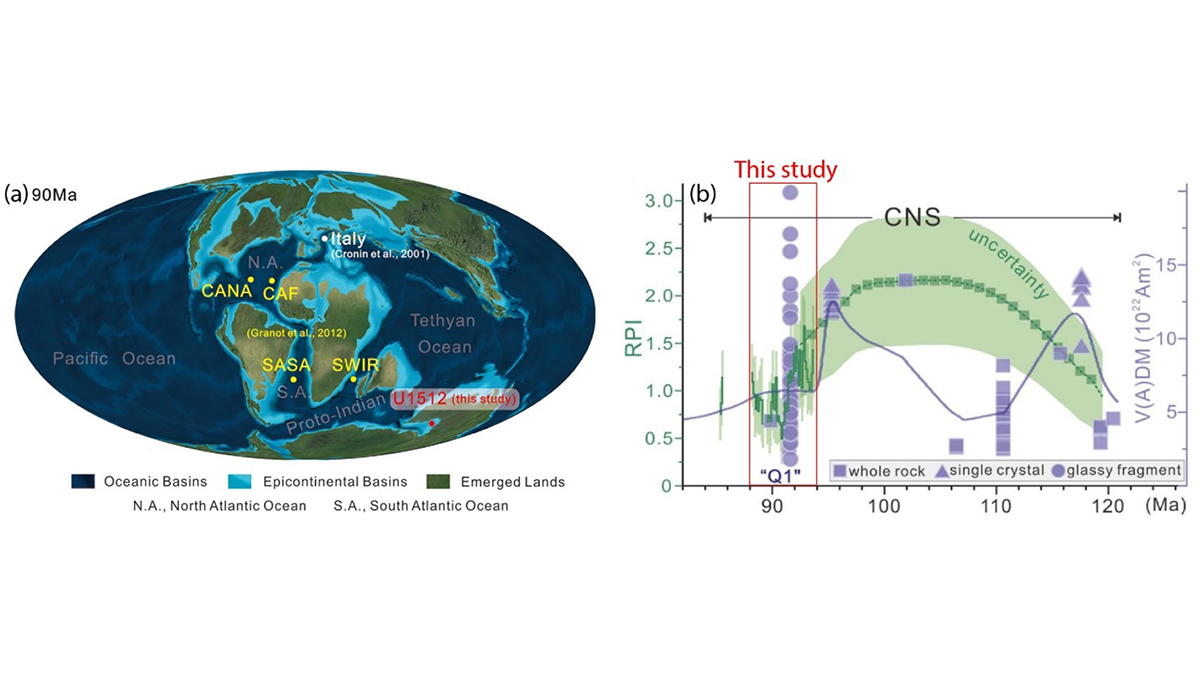
A new study finds that Earth’s magnetic field intensity varied significantly during the Cretaceous Normal Superchron, providing insights into the operation of the geodynamo during superchrons.
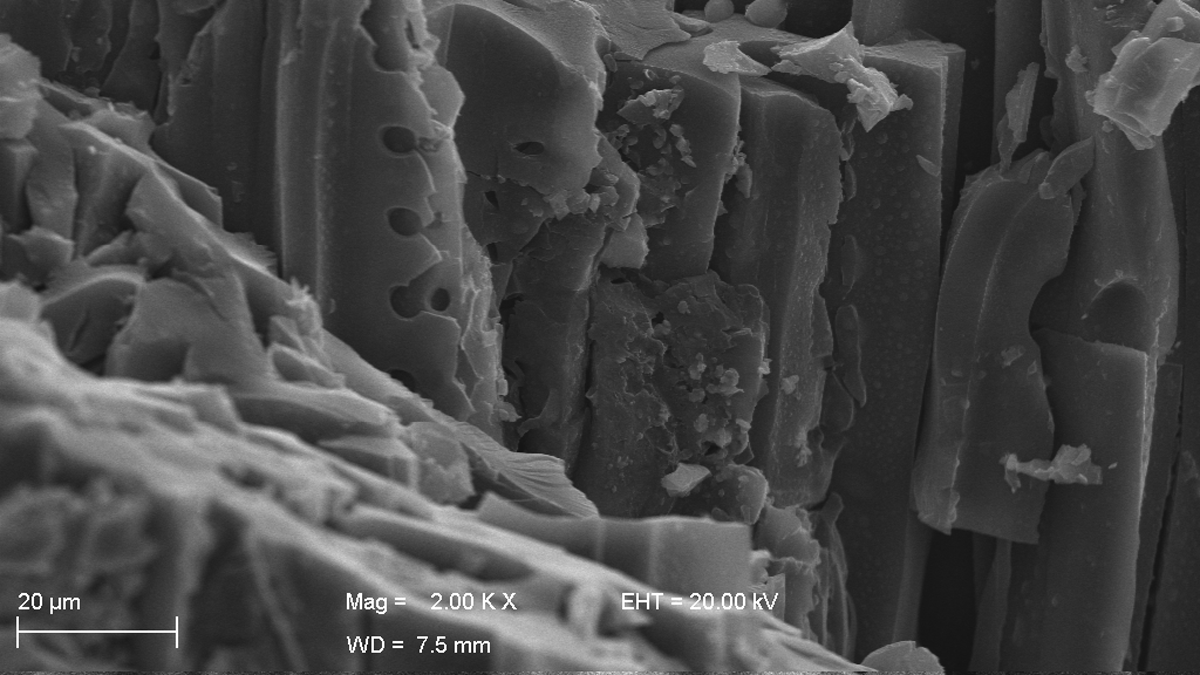
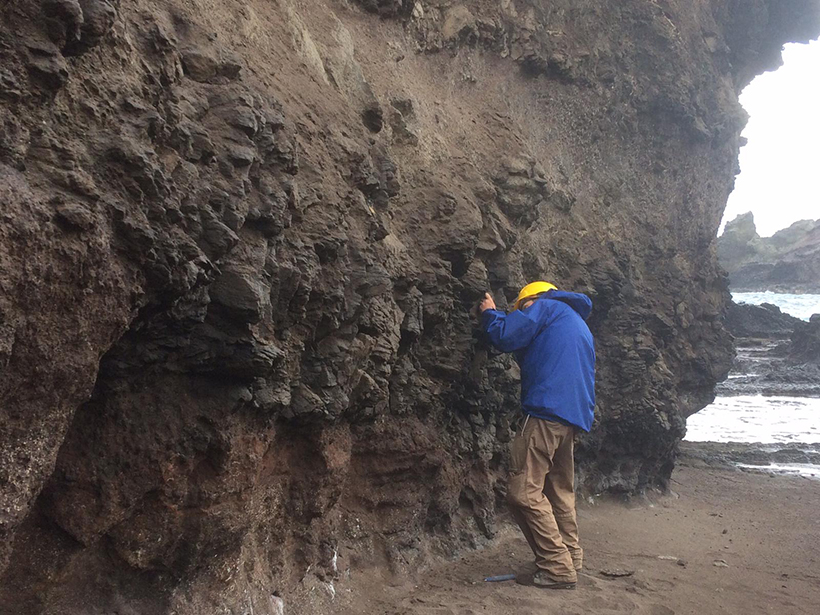
Cretaceous Charcoal Gives a Glimpse of Plant Evolution
New data from vegetal charcoal in northwest India supports the theory of paleowildfires as a global phenomenon and an evolutionary force for biodiversity.
A Robust Proxy for Geomagnetic Reversal Rates in Deep Time
The strength of Earth’s magnetic field in the distant past can tell scientists whether the planet’s magnetic poles were steady or prone to frequent reversals.
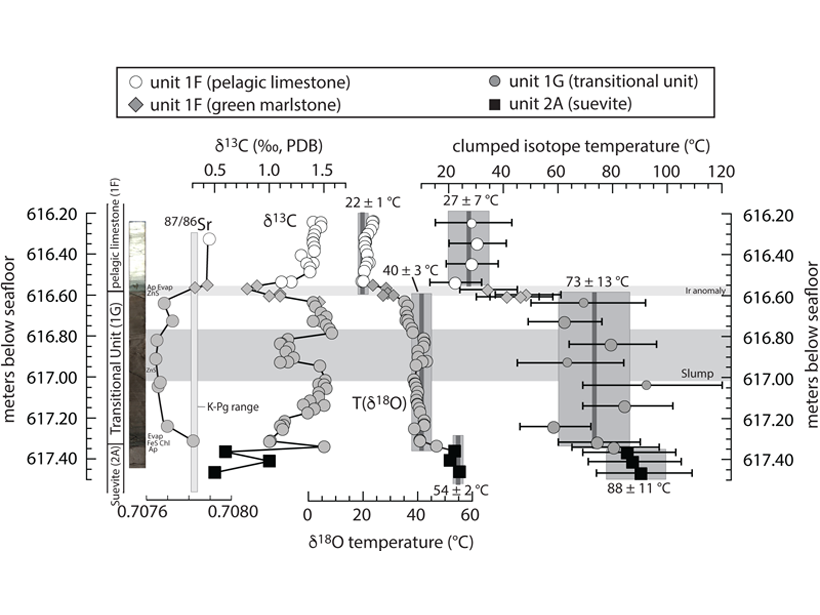
Life in the Chicxulub Crater Years After It Was Formed
While the seas were still churning from the impact and the seawater temperatures were high due to the hydrothermal activity, life was reestablishing itself inside the crater.
Past Climate Sensitivity Not Always Key to the Future
New research suggests that changes in continental configuration, solar brightness, and background atmospheric carbon dioxide levels all conspire to drive Earth’s climate sensitivity over geologic time.
Climate and Ocean Dynamics During the Cretaceous
Exploring the Cretaceous World with Data and Numerical Models; Capo Granitola, 2–4 October 2014