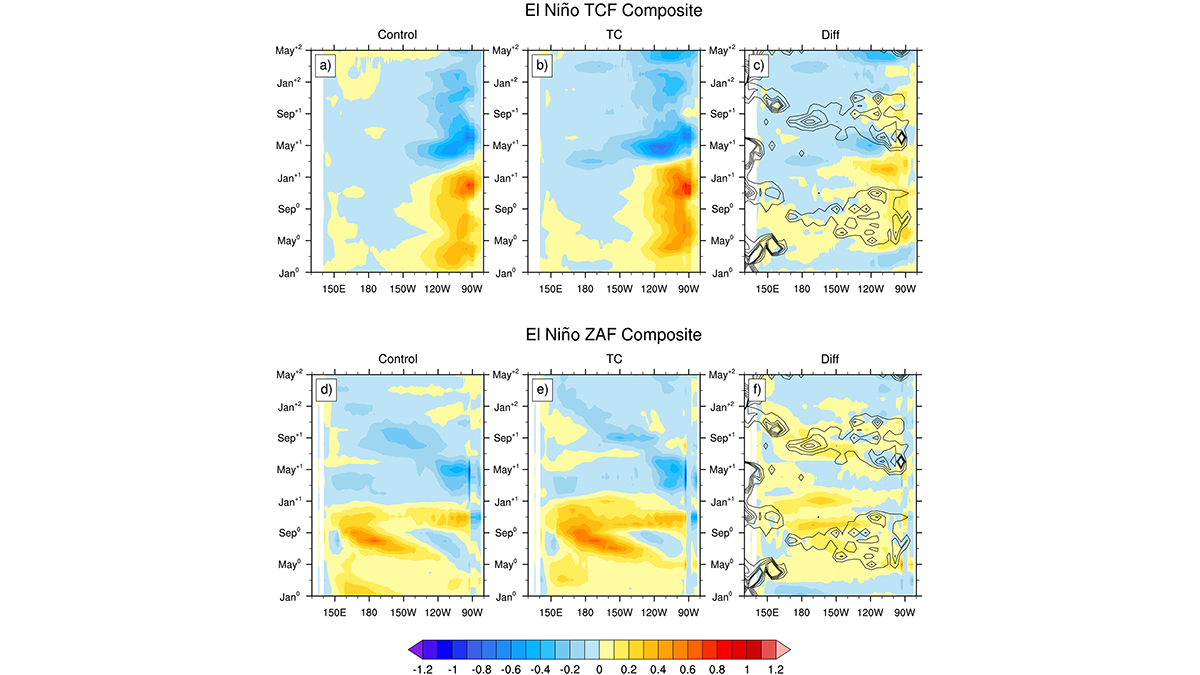
A suite of Earth Systems model experiments is used to explore how tropical cyclones influence the frequency, magnitude, and timing of El Niño-Southern Oscillation events.
hurricanes, typhoons, & cyclones
Back-to-Back Hurricanes Could Become Common by 2100
New research shows back-to-back hurricanes could strike the United States every few years by 2100.
How Kicked-Up Dust Forms Cirrus Clouds
Dust lifted into the air by cyclones provides anchor points for cloud-forming ice.
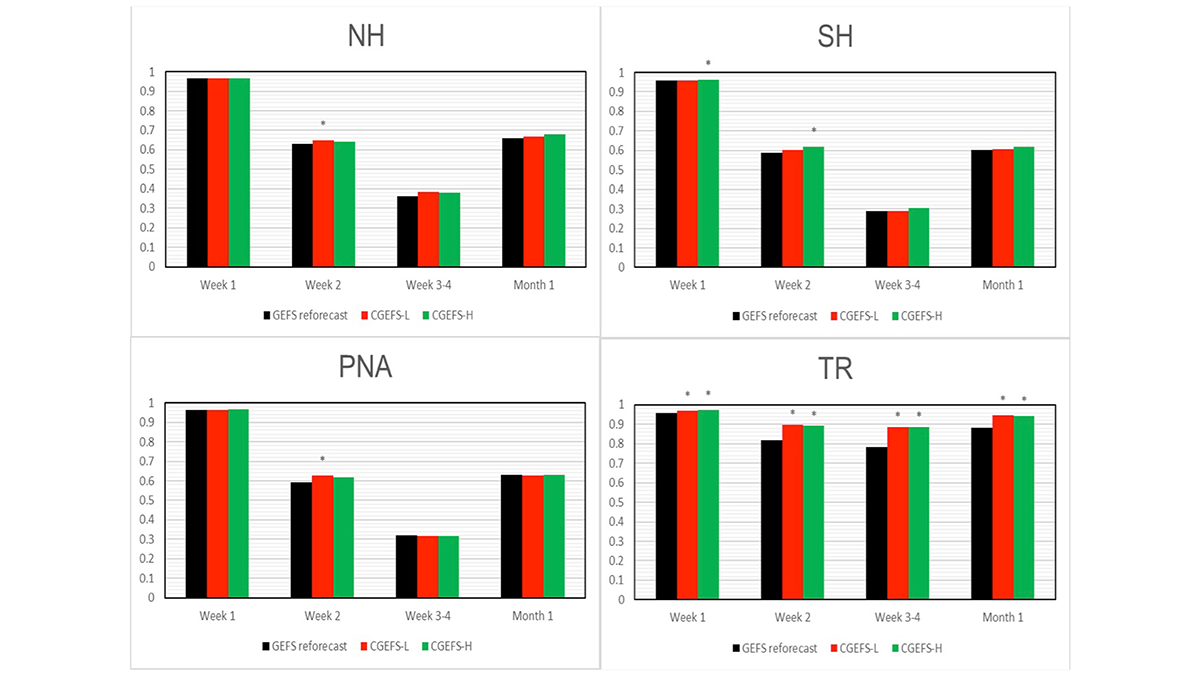
A New Coupled Modeling System Improves Forecast Skills
Building on older versions, the new Global Ensemble Forecast System with coupled atmosphere-land-ocean-ice-wave models has better forecasting skills of the atmosphere than the uncoupled system.
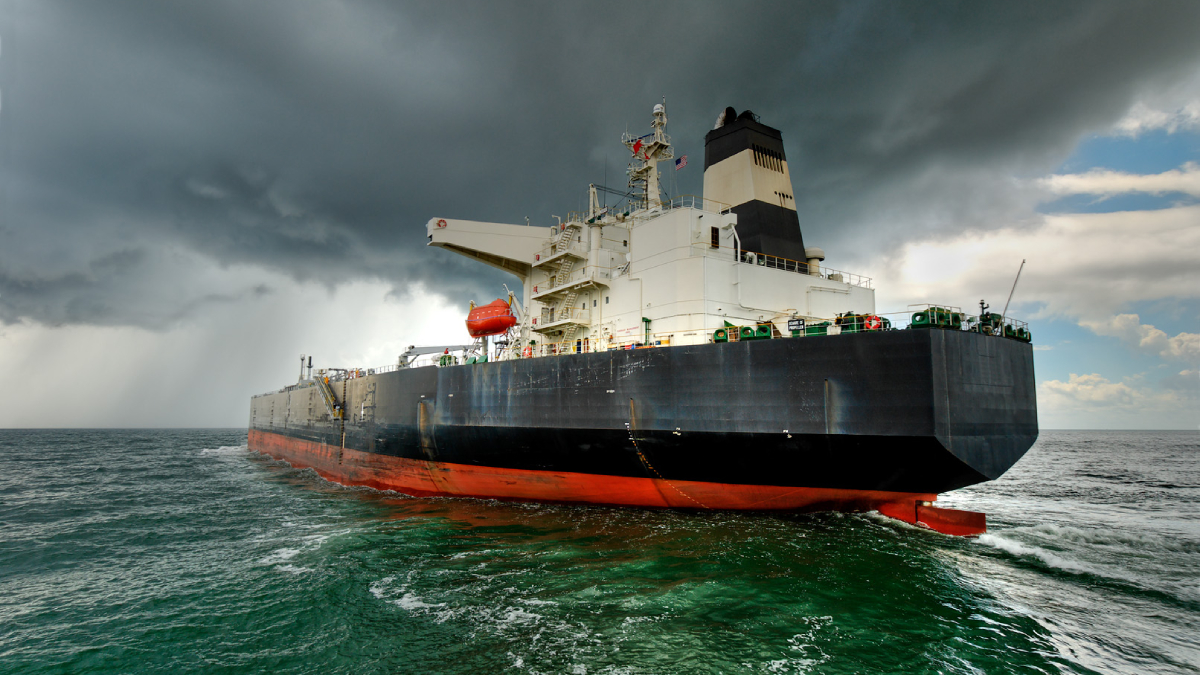
Seaports Could Lose $67 Billion Yearly from Natural Disasters
Small islands and low-income nations face the largest relative monetary losses to their ports and maritime trade.
The Role of Insurance in Climate Adaption
New research tests the promise of insurance to harden the U.S. economy to tropical storms.
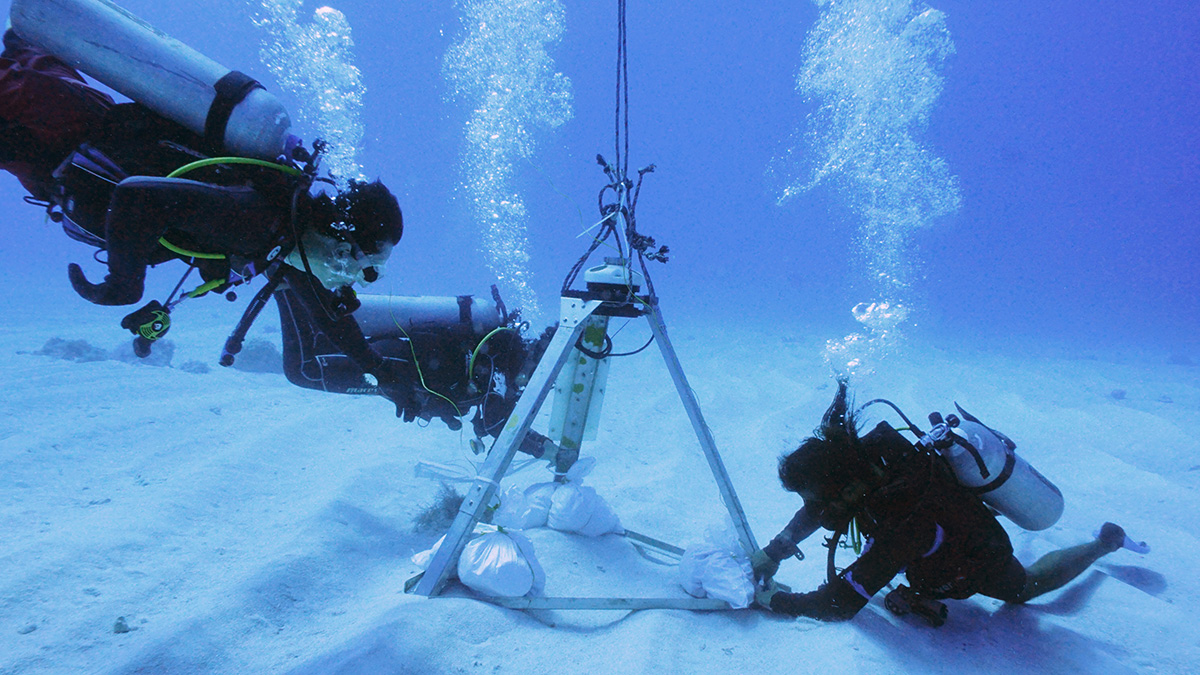
Scientists Improve Hurricane Resilience in the Colombian Caribbean
Scientists are using acoustic sensors to collect data and improve hurricane preparedness and coastal resilience in the archipelago of San Andrés.
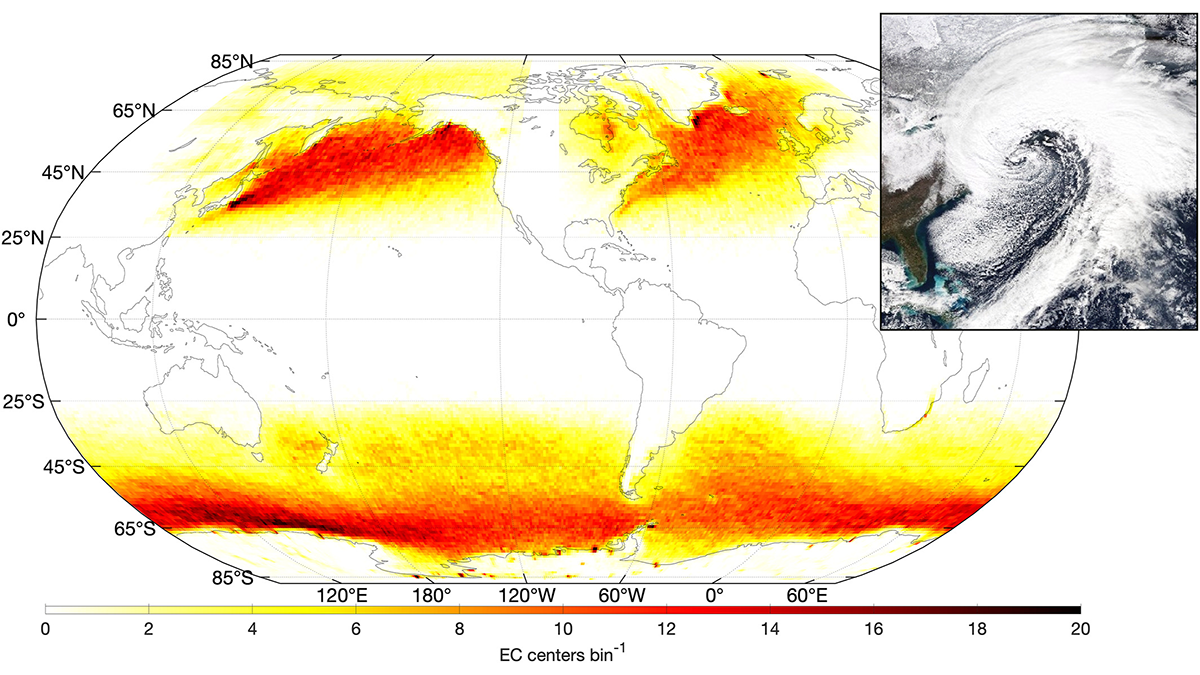
Tracking Ocean Waves from Extratropical Cyclones on Global Scale
A new way of tracking ocean waves with satellite measurements was developed and applied to extratropical cyclones, revealing the effects of storm characteristics on extreme sea states.
An Innovative Approach to Model Complex Hurricane Flood Hazards
A new study shows that it is possible to produce regional assessments of how hurricane flood hazards change due to both evolving storm tides and precipitation rates in a warming climate.