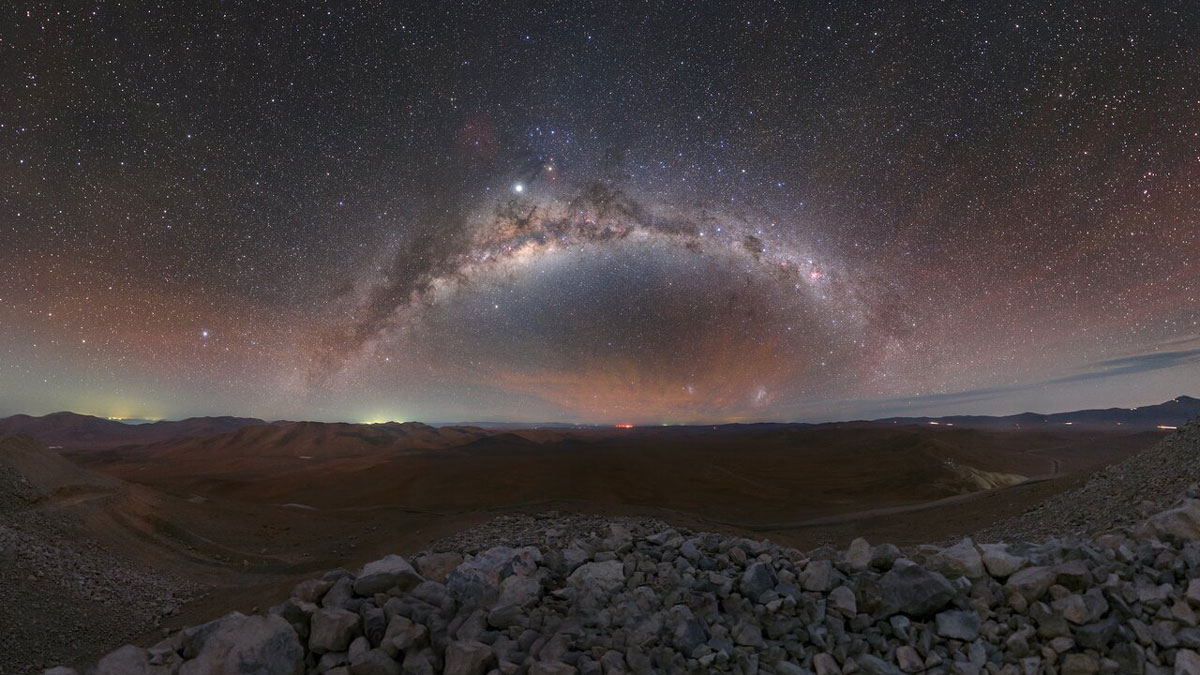
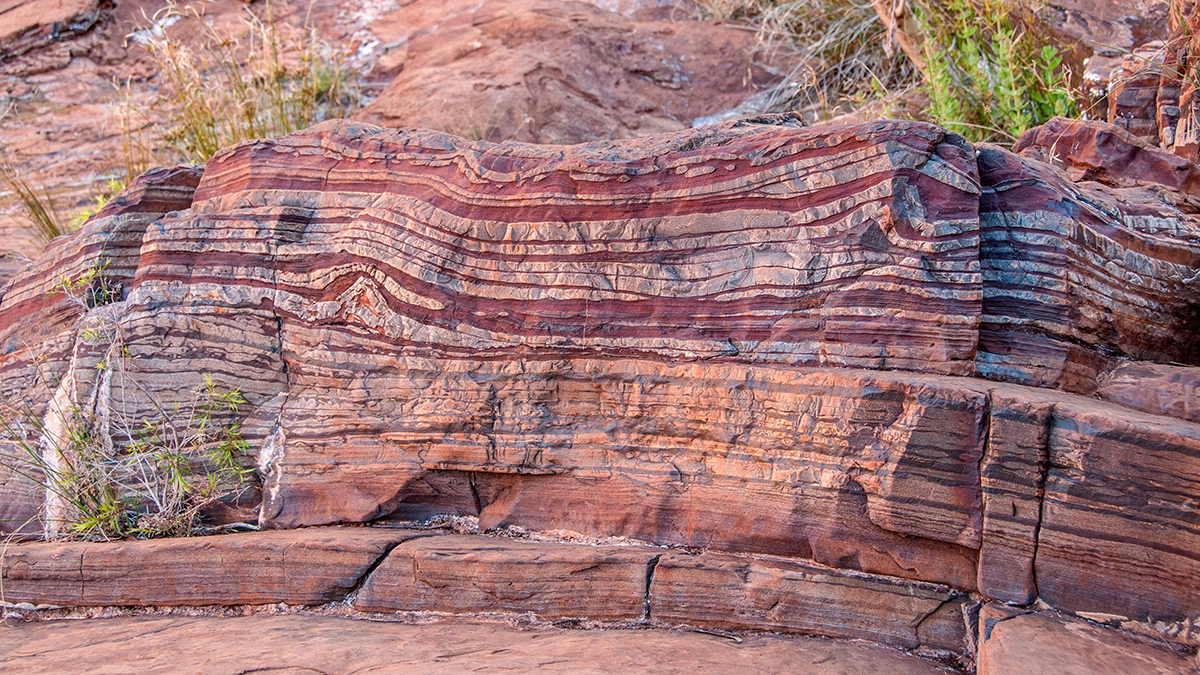
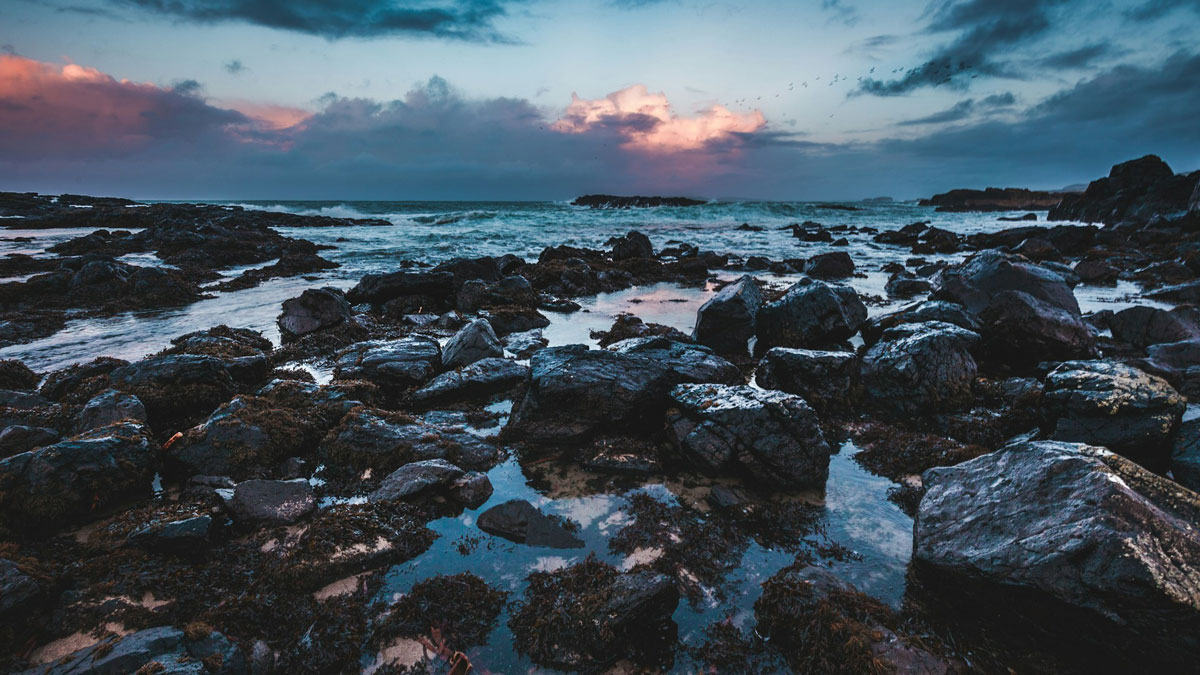
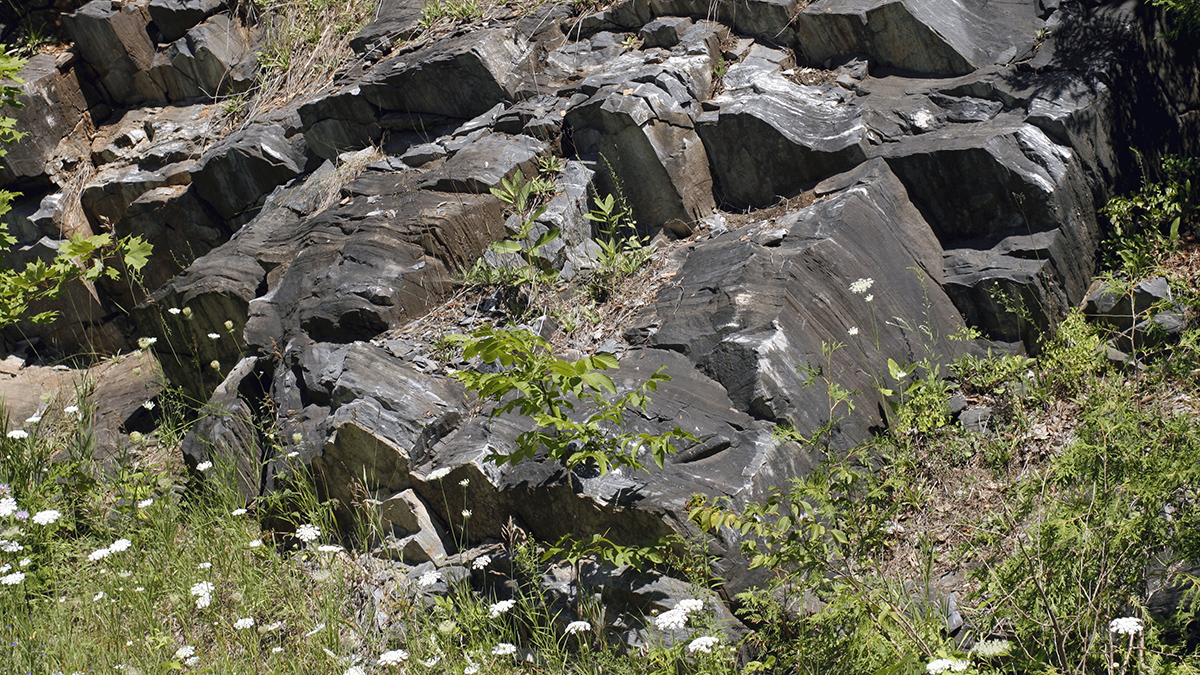
Researchers found signs of melting in zircon crystals in the crust that correspond to our planet’s journey through the galaxy’s spiral arms.
early Earth
Bacteria Battled for Iron in Earth’s Early Oceans
Billions of years ago, iron-oxidizing microbes may have competed for dissolved iron in the ocean, with some strains producing toxic gases that smothered their rivals.
How Did Magma Oceans Evolve on Early Earth and Mars?
New insights into the early timelines of rocky planets are emerging, thanks to clues from iron chemistry and primordial atmospheres.
Lost City’s Plumbing Exposed by the Longest Mantle Core Ever Drilled
The core, which is 71% complete, reveals millions of years of geologic history and the plumbing underlying hydrothermal vents.
Circones de 4,000 millones de años podrían contener nuestras evidencias más antiguas de la existencia de agua dulce
Cristales australianos apuntan a la existencia de agua dulce, así como de continentes que se elevaban sobre el océano Hadeano de la Tierra.
Sedimentos radiactivos podrían haber construido los cratones de la Tierra
La meteorización de los primeros continentes podría haber puesto en marcha la formación de cratones, las raíces inmutables de los continentes.
Four-Billion-Year-Old Zircons May Contain Our Earliest Evidence of Fresh Water
Australian crystals hint at fresh water, as well as land rising above Earth’s Hadean ocean.
Radioactive Sediments May Have Built Earth’s Cratons
Weathering of the earliest continents could have set in motion the formation of cratons, the immutable roots of continents.
A Magnetic Low May Have Paved the Way for Complex Life
Multicellular life blossomed when Earth’s magnetic field was at an all-time low.
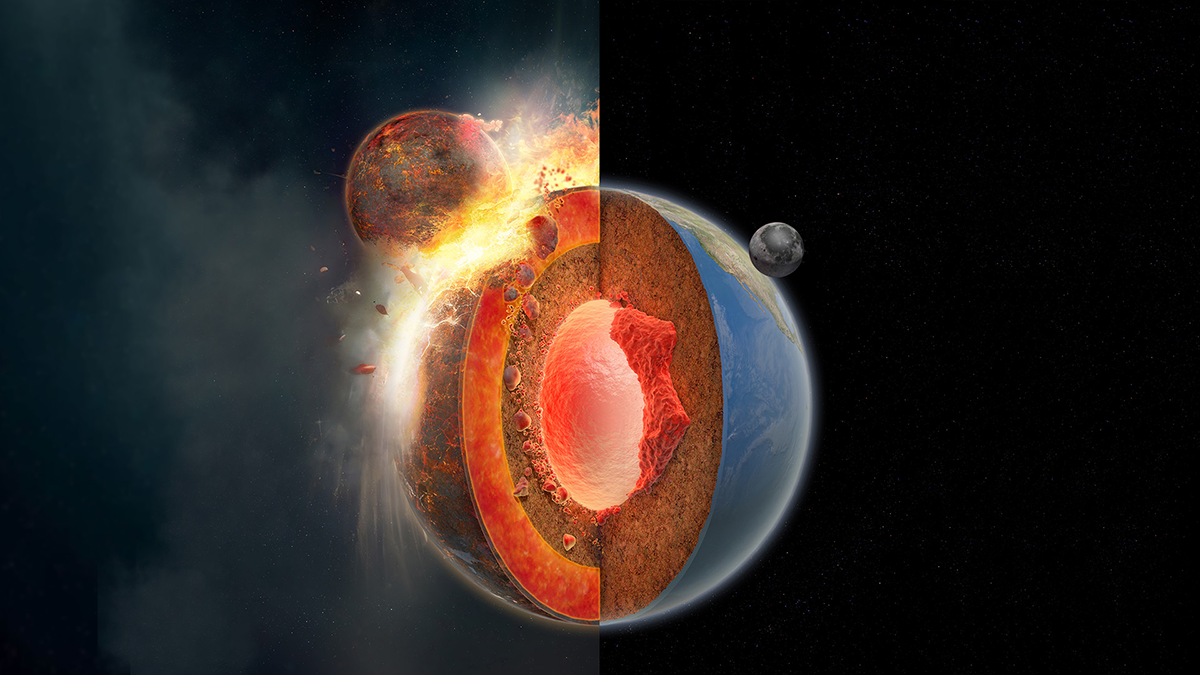
Earth’s Subduction May Have Been Triggered by the Same Event That Formed the Moon
The giant impact that formed the Moon may also have led to extrastrong mantle plumes that enabled the first subduction event, kick-starting Earth’s unique system of sliding plates.