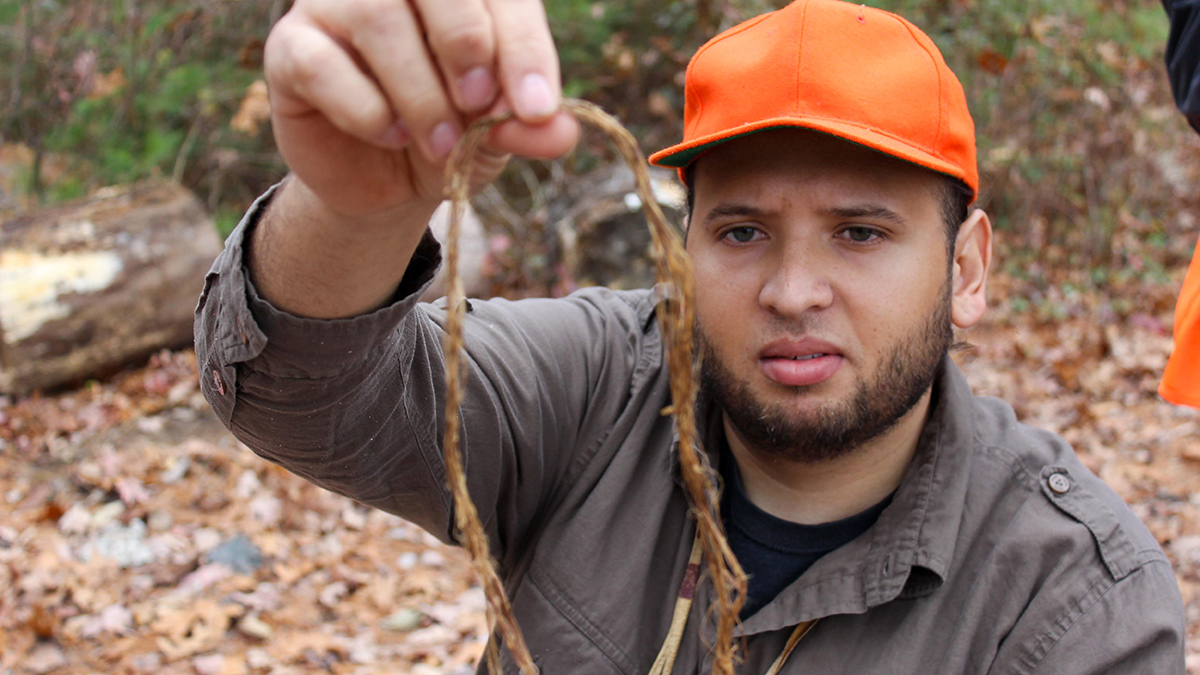
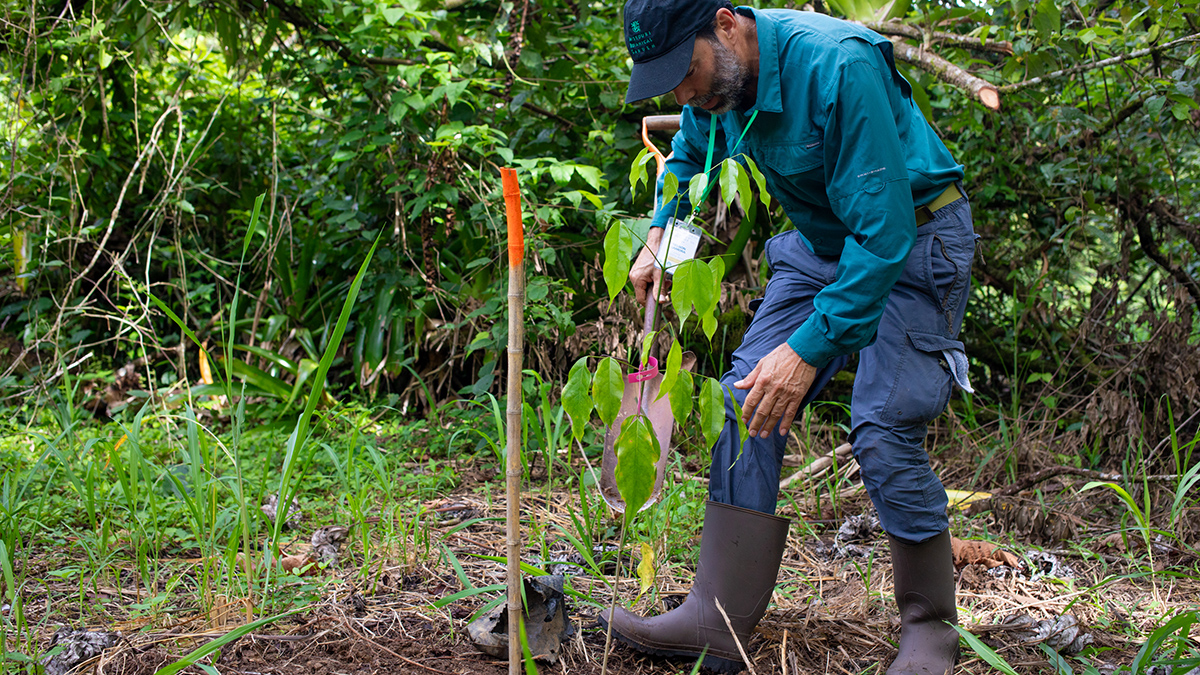
This soil scientist braids the Traditional Ecological Knowledge of his ancestors with modern soil conservation practices to help Rhode Island’s farmers and land stewards.
Earth science
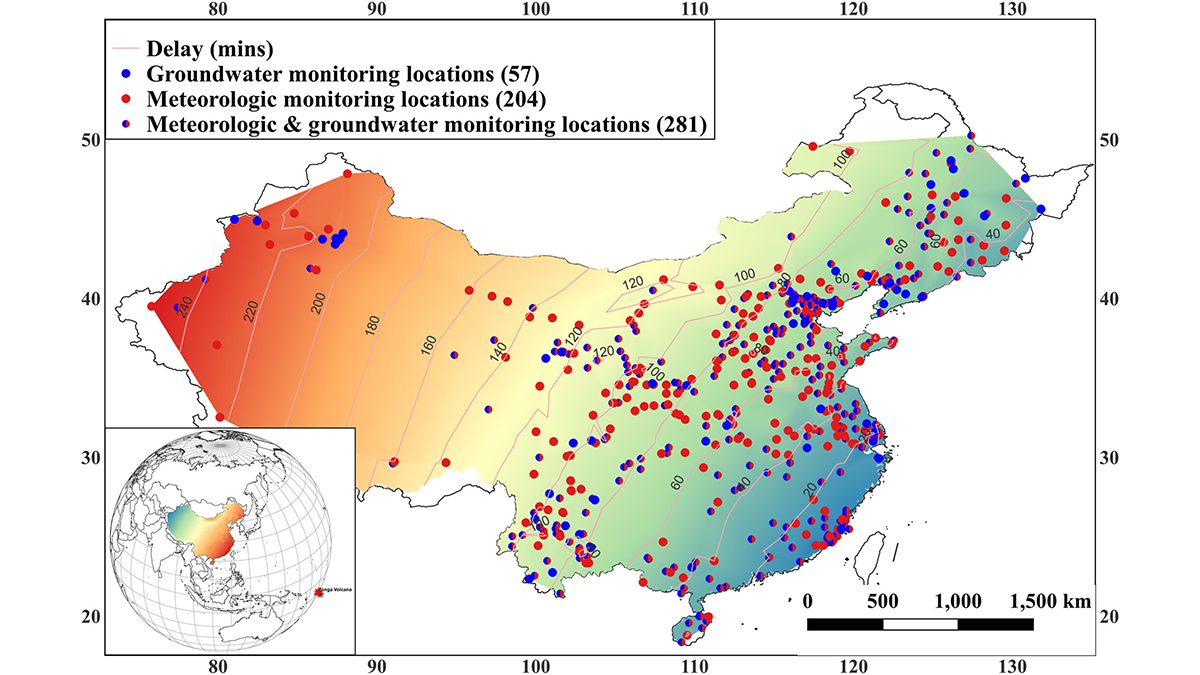
A Volcanic Boom Puts the Squeeze on Remote Confined Aquifers
A new study shows that ground water levels responded to forcing by barometric pressure pulses from the 2022 Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcanic Eruption.
Getting Schooled in Complex Earth System Modeling
Training schools focused on modeling solid Earth responses to ice mass changes offer lessons on how early-career scientists can build professional networks and learn skills to solve complex problems.
How Earthquakes Shake Up Microbial Lake Communities
After an earthquake, a lake’s geological, chemical, and biological components get reconfigured. A new study dives into the effects of seismic shifts on the Himalayas’ Lake Cuopu.
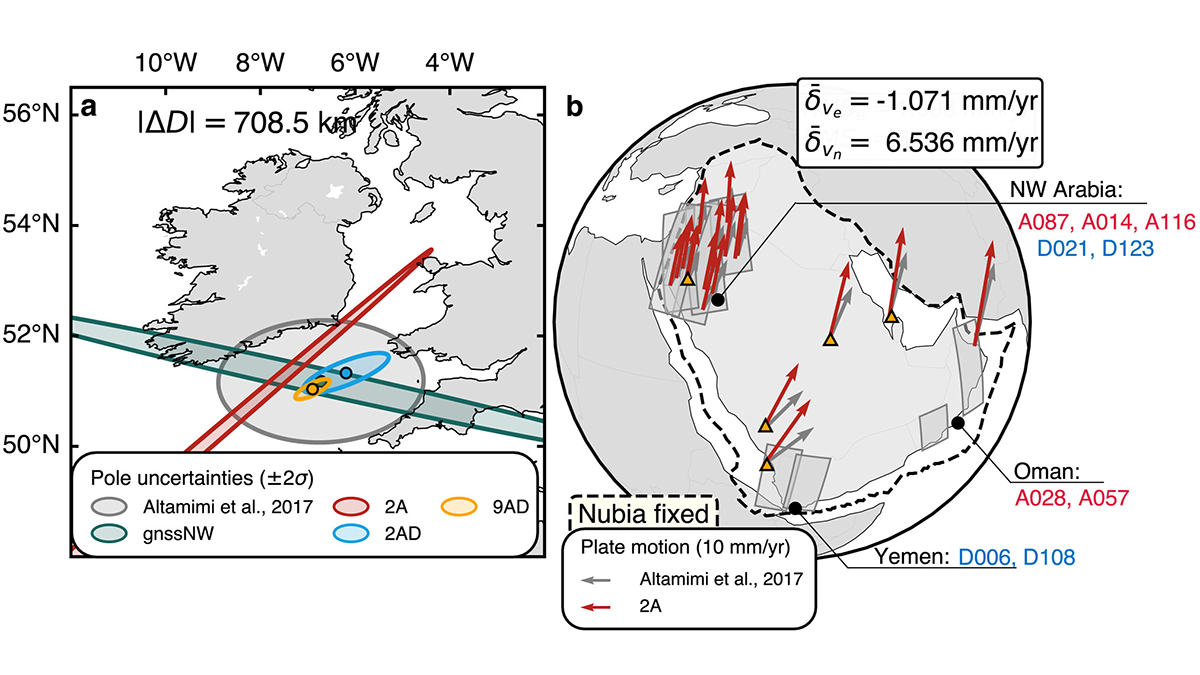
Mapping the Whereabouts of Continents
A new method integrates Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) with conventional ground geodetic networks, taking us closer to high-resolution mapping of plate motions.
First Species-Level Assessment Reveals Extinction Risk in Mesoamerica
Forty-six percent of tree species in Mesoamerica are threatened with extinction. Researchers hope a new regional study will inform targeted conservation strategies.
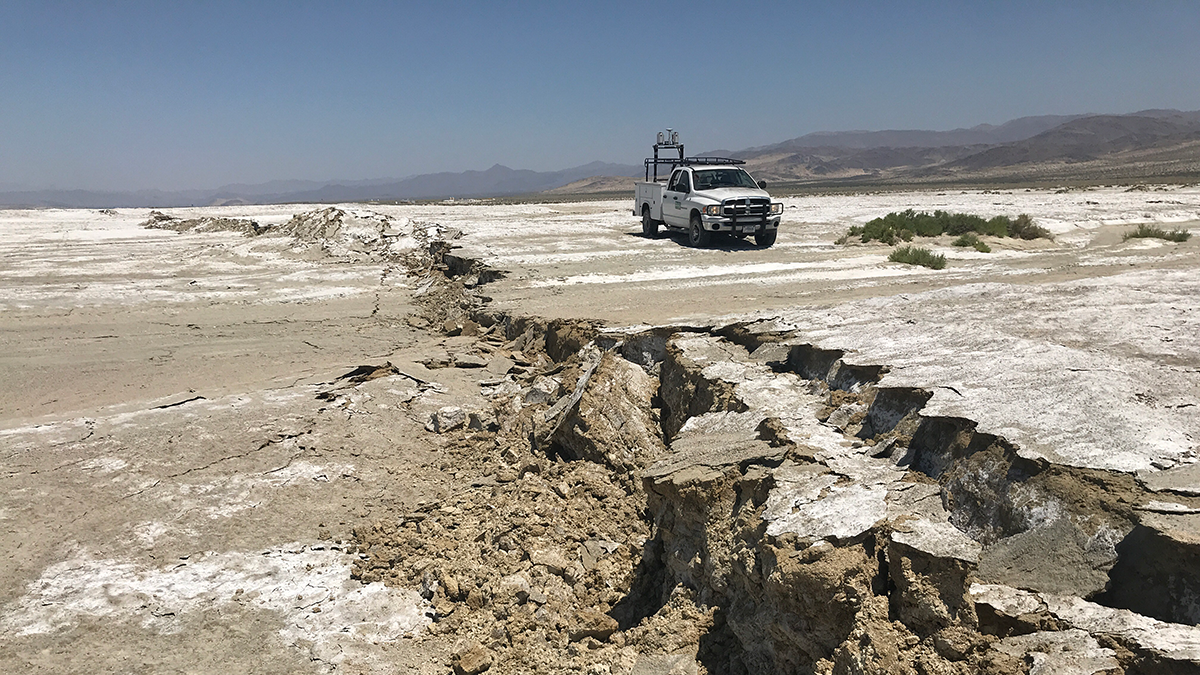
New Insights into How Rocks Behave Under Stress
New 3D imaging techniques show hidden patterns of stress that help explain how and why rocks break.
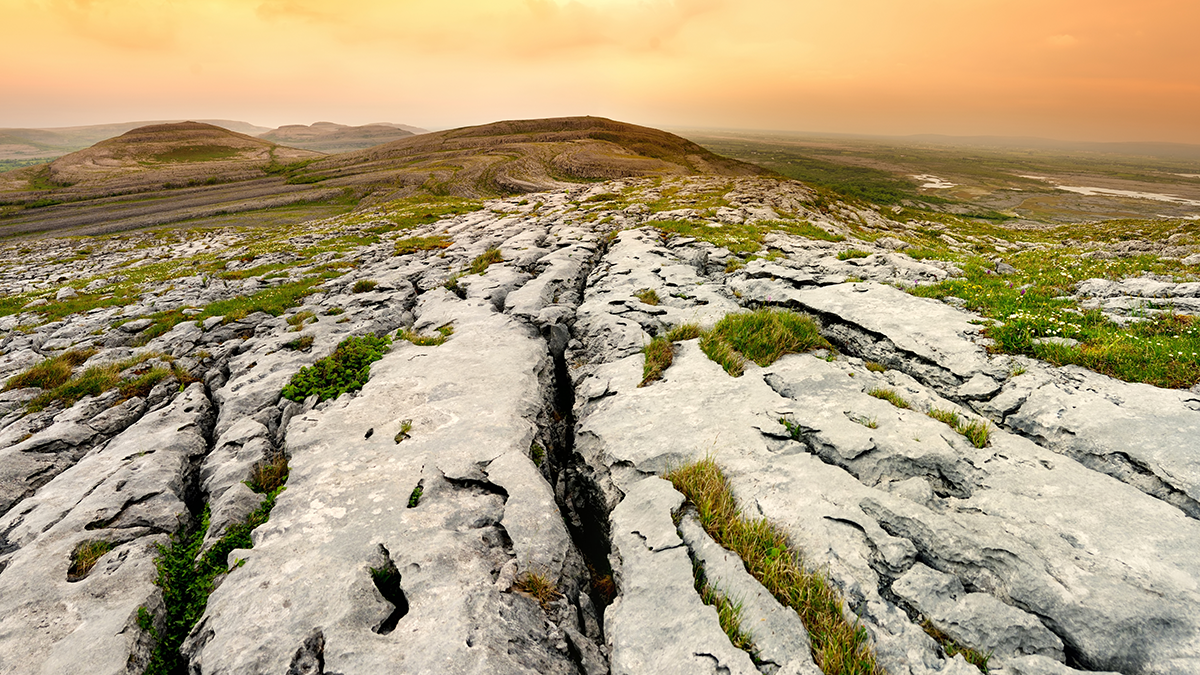
Groundwater Pollution in Karst Regions: Toward Better Models
New advances in modeling contaminant transport offer a clearer picture of how to protect karst aquifers.
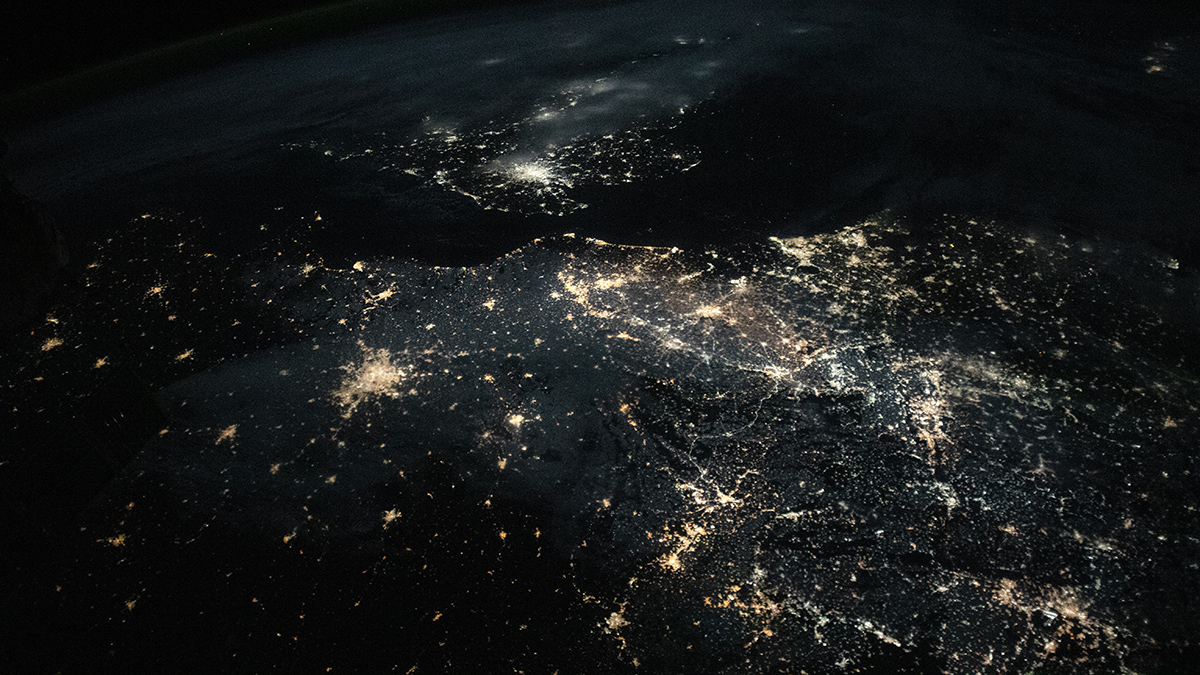
Artificial Light Lengthens the Urban Growing Season
New research shows that artificial light at night lengthens the plant growing season in cities, overshadowing the effect of high urban temperatures.