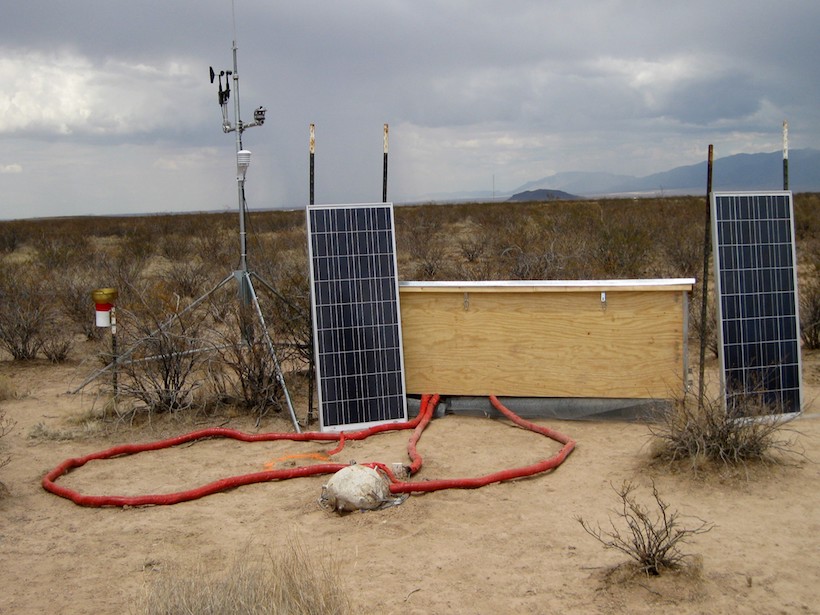
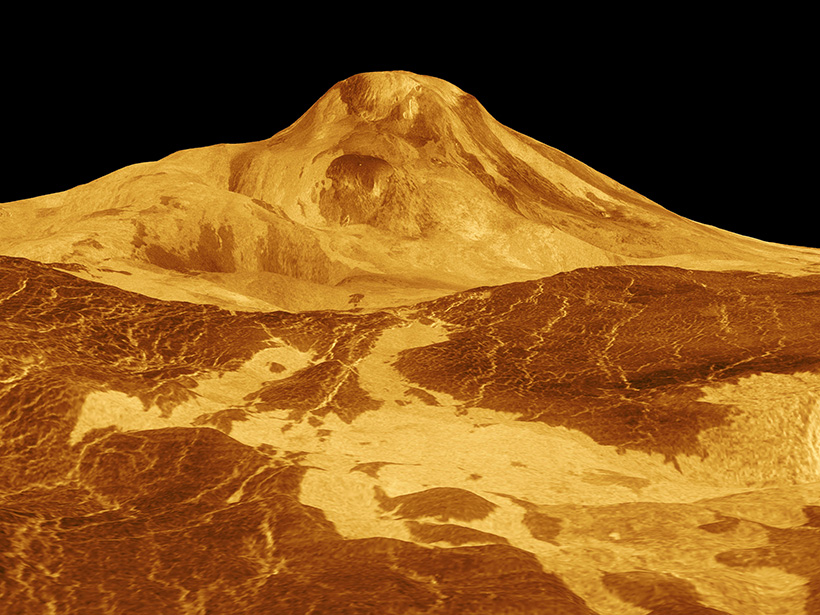
A strategy that combines geologic mapping with data on how the planet’s surface emits and absorbs microwave radiation could potentially identify recent lava flows.
erosion & weathering
Megaripples on Mars—How to Name Wind-Shaped Features on the Red Planet
New research suggests a more settled terminology for Martian aeolian landforms based on size and geomorphology.
La primera mirada de la meteorización a escala angstrom
Investigadores observan cómo el vapor de agua y el líquido alteran las rocas sedimentarias a través de procesos físicos y químicos.
After the Dust Cleared: New Clue on Mars’ Recurring Slope Lineae
An imaging campaign after the 2018 planet-encircling dust storm on Mars revealed a significant increase in detections of enigmatic recurring slope lineae and new insights into how they might form.
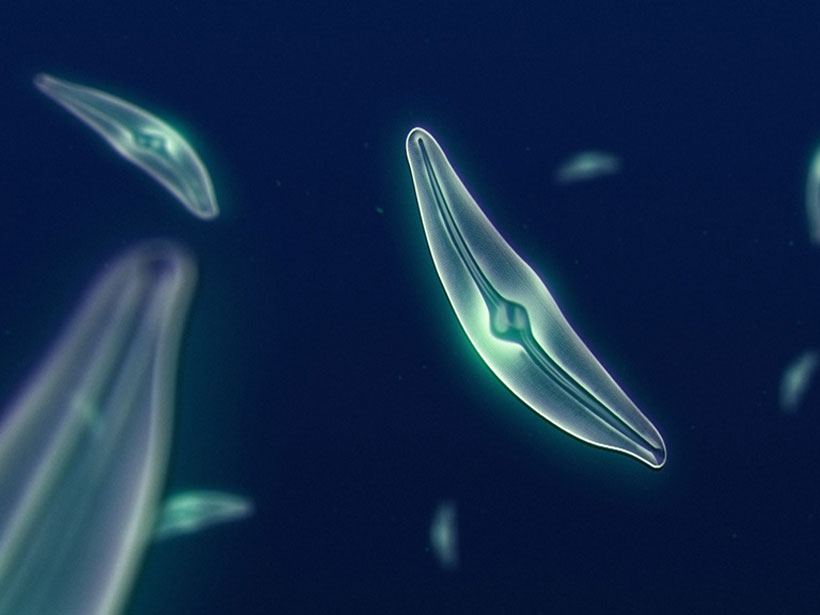
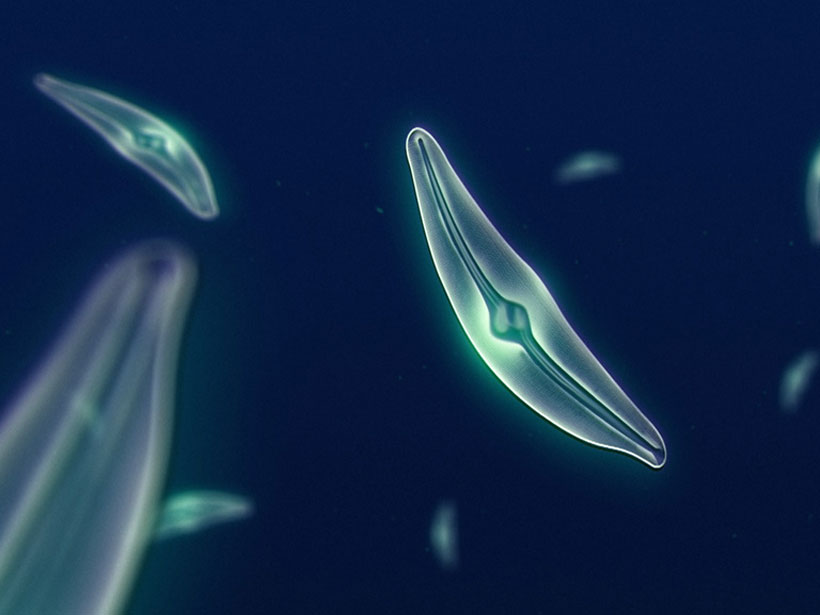
How Did Diatoms Evolve to Swap Zinc for the Toxic Metal Cadmium?
New network analysis suggests that zinc and cadmium sulfides weathered simultaneously in geological history, making cadmium a suitable substitute in photosynthetic pathways when zinc was scarce.
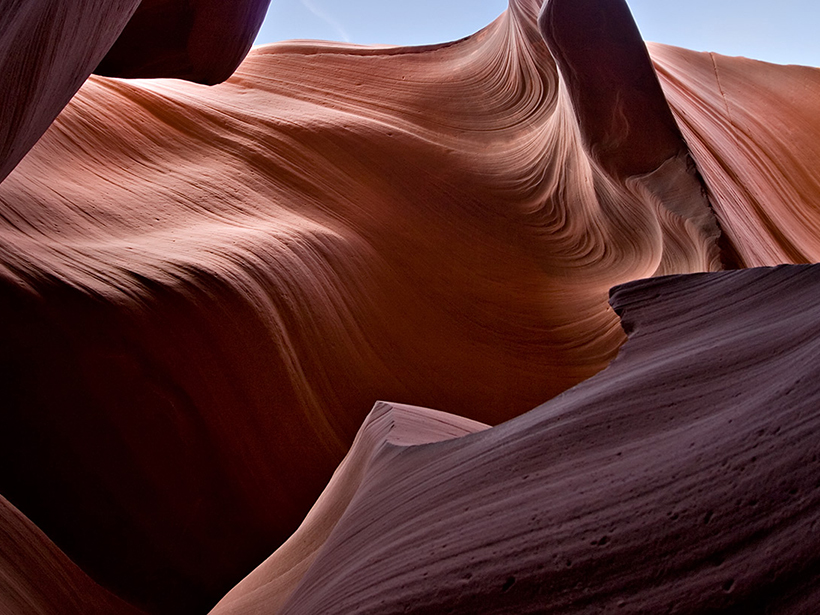
The First Angstrom-Scale View of Weathering
Researchers observe how water vapor and liquid alter sedimentary rocks through physical and chemical processes.
Weighing Inputs of Waves and Precipitation to Coastal Erosion
Conducting weekly lidar surveys of coastal cliffs for 3 years enabled a California team of coastal erosion researchers to quantify and separate marine effects from subaerial effects.
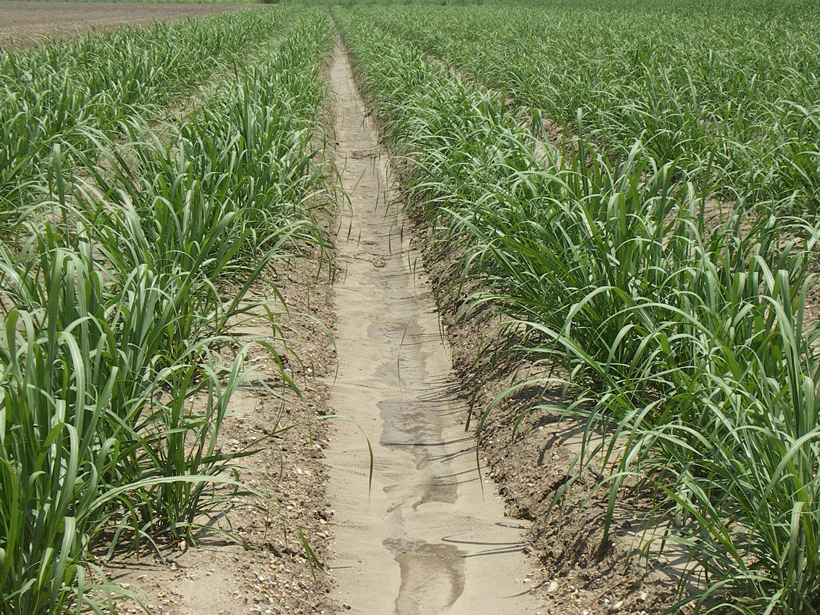
European Colonists Dramatically Increased North American Erosion Rates
Around 200 years ago, when conversion of land for agriculture became more widespread, the amount of sediment accumulating in riverbeds across the continent jumped tenfold.
Warmer Climates Speed Breakdown of Rocks
Researchers listened to boulders for thousands of hours to investigate how they weathered.