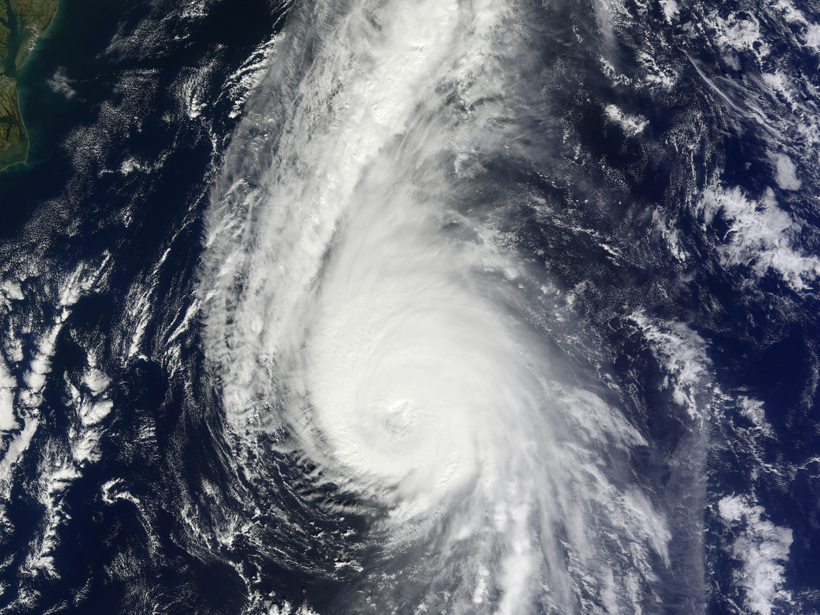
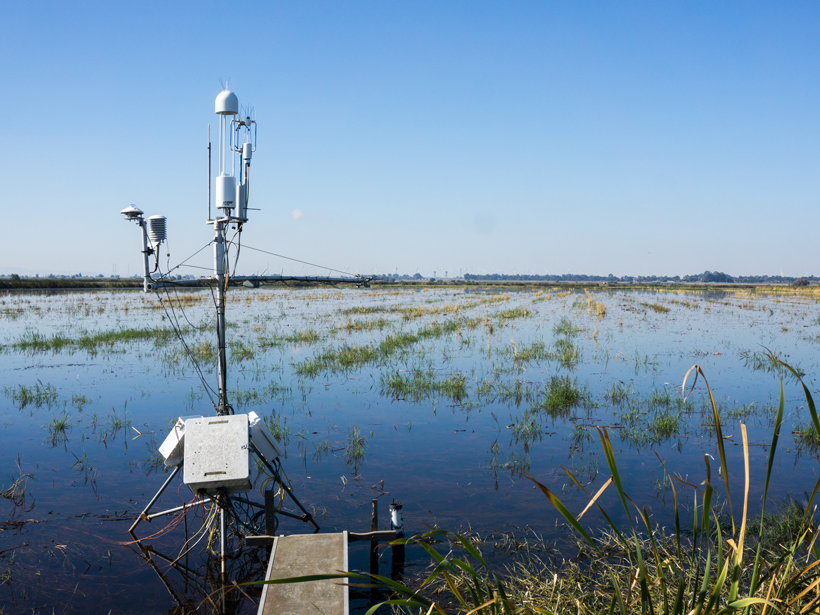
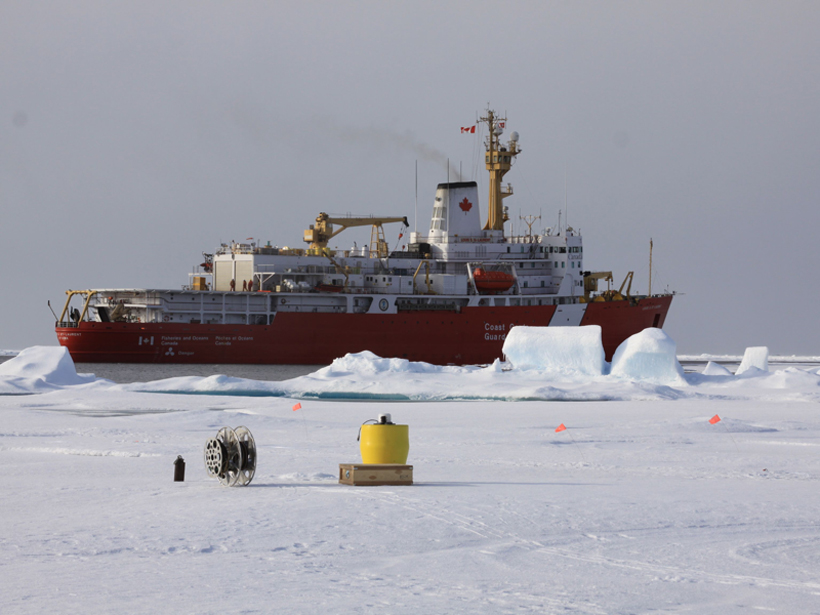
Every 25–30 years, the ocean and atmosphere conspire to produce an enhanced North Atlantic Oscillation
everything atmospheric
Geoacoustics Takes to the Sky
Airborne Geoacoustics Workshop; Albuquerque, New Mexico, 3 January 2017
Could Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Make Hadley Cells Expand?
Convection-driven Hadley cells are expanding poleward. Scientists now may have uncovered part of the reason why.
What to Expect from Cassini's Final Views of Titan
Cassini will fly close to Saturn's largest moon one last time. Here's a look back at what the spacecraft has revealed and ahead to scientists' final close glimpses of the moon.
A New Data Set to Keep a Sharper Eye on Land-Air Exchanges
FLUXNET2015, the latest update of the longest global record of ecosystem carbon, water, and energy fluxes, features improved data quality, new data products, and more open data sharing policies.
How Arctic Ice Affects Gas Exchange Between Air and Sea
Scientists begin to fill a major data gap by investigating carbon dioxide dynamics in a remote region of the Arctic Ocean.
Volcanic Ash Particles Hold Clues to Their History and Effects
Volcanic Ash as an Active Agent in the Earth System (VA3): Combining Models and Experiments; Hamburg, Germany, 12–13 September 2016
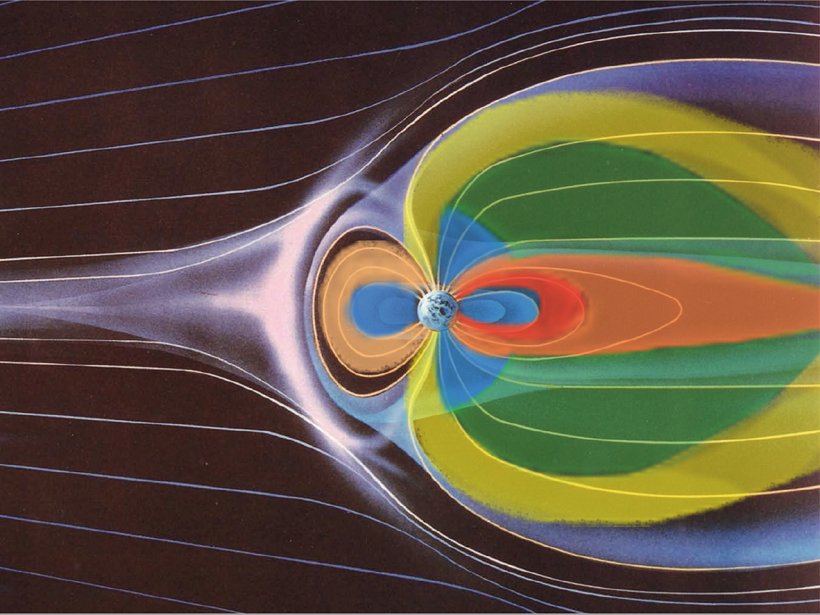
Filling Earth’s Space Environment from the Sun or the Earth?
The editor of a new book describes how a unique combination of the monograph and video show that a four-decade old paradigm in solar-terrestrial physics is changing.
Satellite Data Reveal Effects of Aerosols in Earth's Atmosphere
Combining data from multiple sources could aid in predicting the tiny atmospheric particles' effects on global warming.
Ralph Cicerone (1943–2016)
The former president of the National Academy of Sciences was an accomplished atmospheric scientist and a proponent of multidisciplinary collaboration, but most of all, he was a good friend.