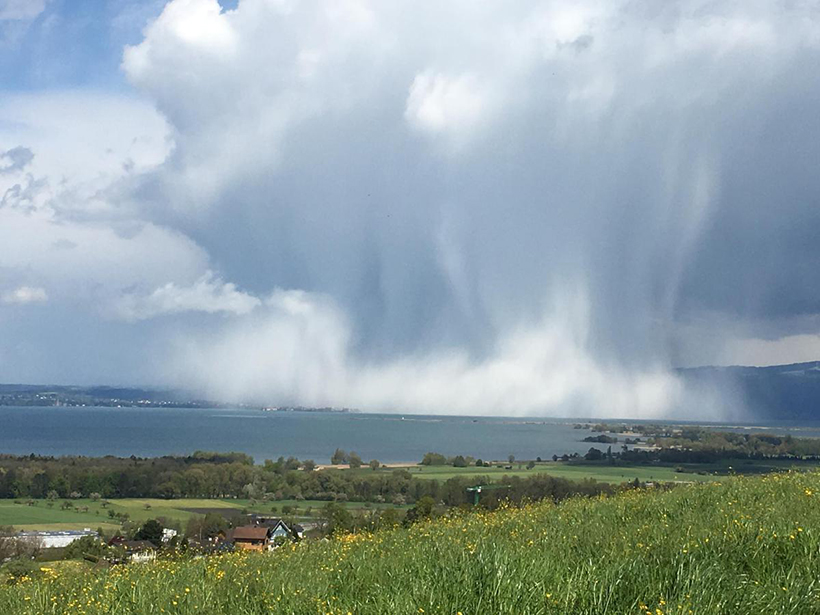
The Madden-Julian Oscillation drives storms across the Indian and Pacific oceans every 30 to 60 days. New research suggests that clouds absorbing and reemitting radiative energy play a key role.
everything atmospheric
Warm Waters in West Antarctica
A recent paper in Reviews of Geophysics describes the atmospheric and oceanic processes that are causing ice loss in the Antarctic.
Global Atmospheric Observations May Need Tweaking for Turbulence
A new study that overturns an 80-year-old assumption about atmospheric turbulence may finally resolve discrepancies in observations of atmospheric heat, water vapor, and carbon.
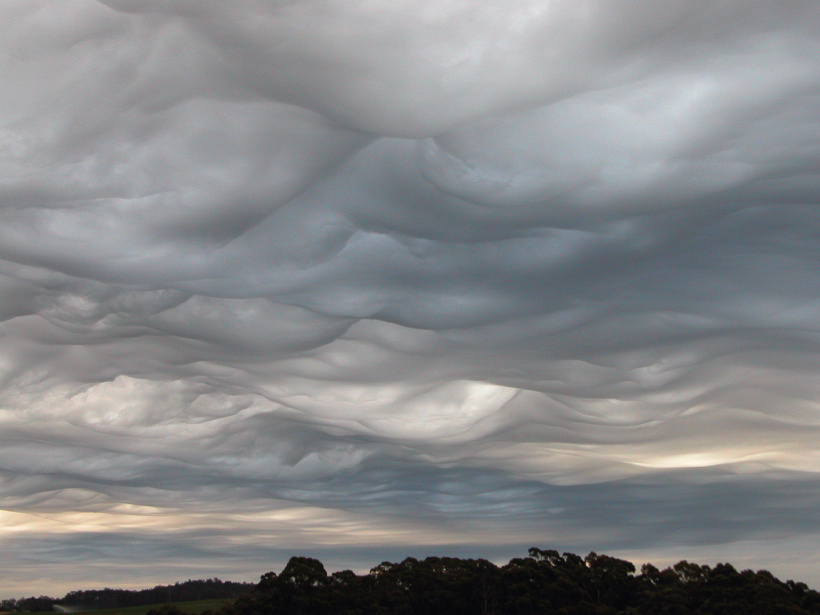
Science Explains “Rough and Chaotic” Cloud Feature
Research on the newest entry in the International Cloud Atlas produces insights into what these cloud features are made of and how they form.
The Asian Summer Monsoon Launches Pollutants Around the Globe
New research provides a comprehensive overview of the effect of the Asian summer monsoon (ASM) on atmospheric composition throughout the life cycle of the ASM anticyclone.
New Supercomputers Allow Climate Models to Capture Convection
Scientists evaluate the latest version of a fine-scale climate model by simulating a decade of precipitation patterns across Europe.
Seeing Soil Moisture from the Sky
A recent paper in Reviews of Geophysics describes techniques for improving the spatial resolution of satellite data on soil moisture.
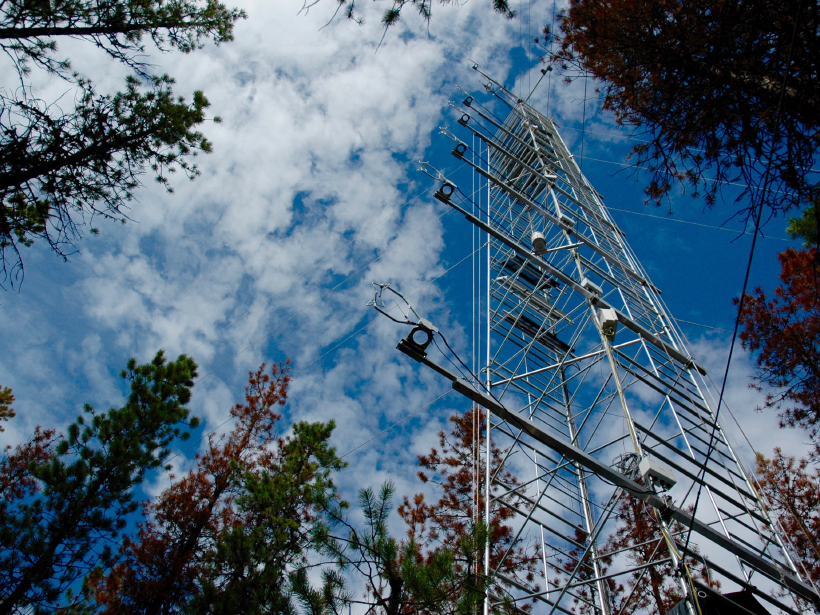
Antenna Towers Attract Additional Lightning Strikes
Atmospheric scientists evaluate the influence of human-made structures on lightning data.
Close Encounter with Jupiter
First results from the Juno mission shed new light on Jupiter’s atmosphere, gravity, magnetic field, aurora, history, and more.
Designing Mountaintop Cloud Experiments
Whiteface Mountain Cloud Chemistry Workshop; Wilmington, New York, 16–17 September 2016