The West Pacific pattern correlates with high pressure, increased temperature, decreased precipitation, and higher burned area during autumn in the western United States.
everything atmospheric
Steering Geophysical Research Letters Forward: A Focus on Excellence and Global Inclusivity
Meet the new Editor-in-Chief of Geophysical Research Letters and discover his plans to shape the journal’s role in advancing the Earth and space sciences.
CT Scans Show How Giant Hailstones Grow
Dental office technology is giving scientists a peek inside giant hailstones.
Bringing Climate Change’s Effects on Atmospheric Circulation to Light
A lengthening observational record is being used to test predictions and improve understanding of the mechanisms behind changing circulation.
Human Activities Might Create Temporary Atmospheres on the Moon
Outgassing could pose problems for long-term habitation of the Moon, including health hazards for astronauts, hindrances for electronics, and hampered scientific study.
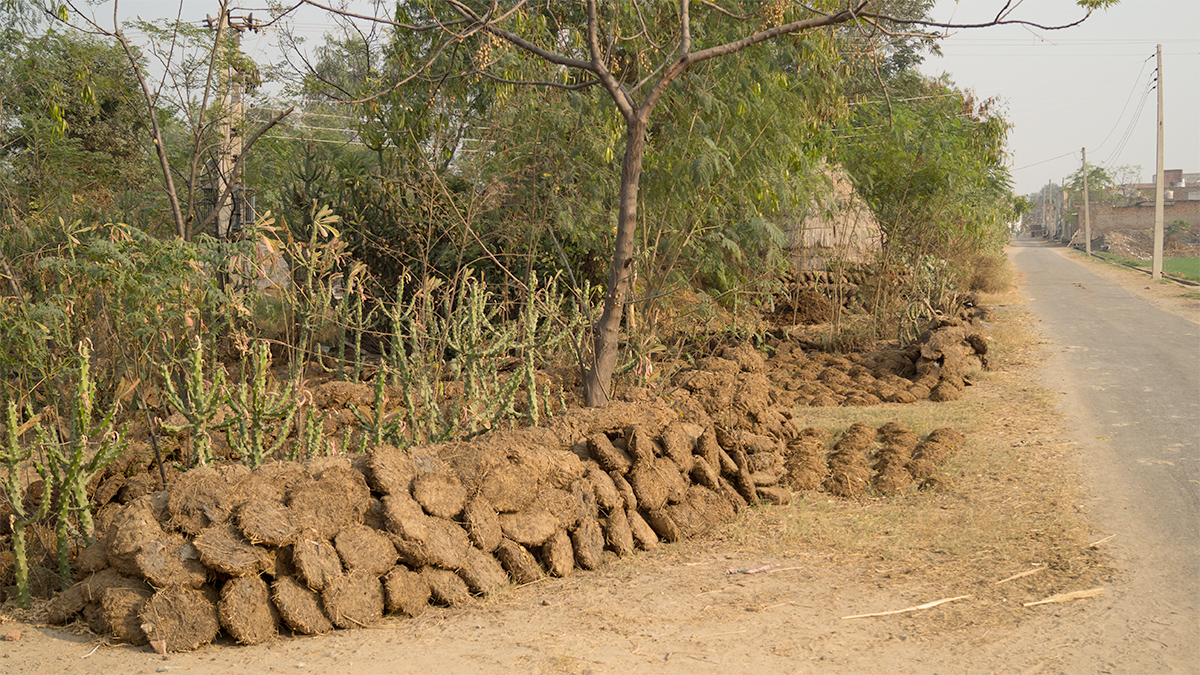
Burning Cow Dung Emits an Inordinate Amount of Air Pollution in India
Dried cow dung, a main source of household cooking fuel for many in rural India, releases more particulate matter across the country than wood and other biofuels.
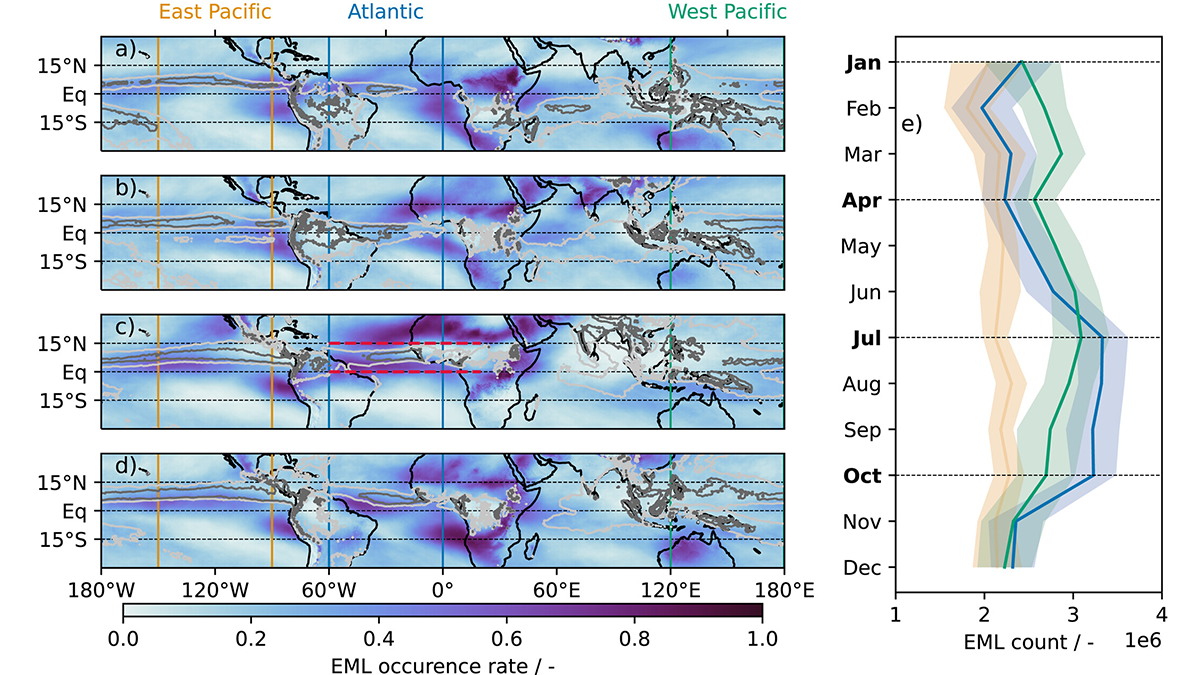
Characteristics of Moist Layers over the Tropical Atlantic
In a new study, characteristics of elevated moist layers, their seasonality, spatial distribution, structure, and the coupling of mid-tropospheric circulation and convection are examined over the tropical Atlantic.
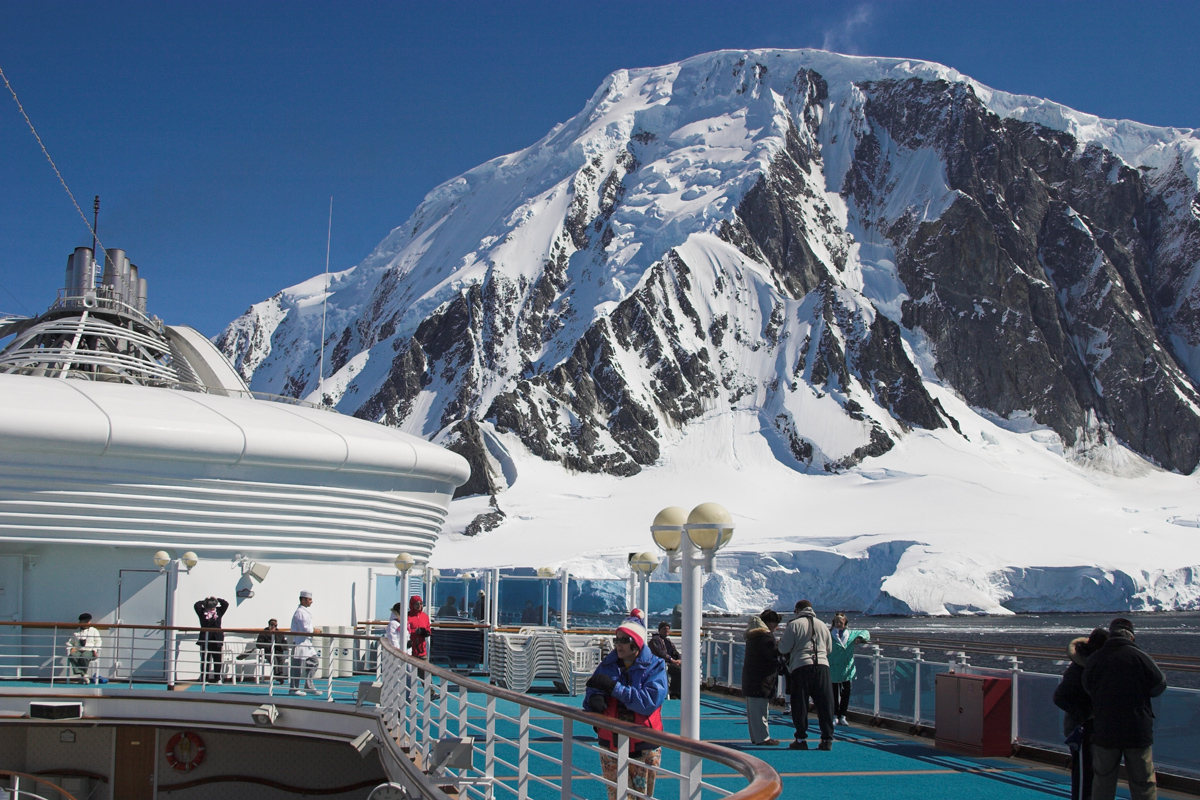
Tourism and Distant Fires Affect Antarctica’s Black Carbon Levels
Tourism and biomass burning in the Southern Hemisphere are boosting black carbon levels and accelerating ice melt in Antarctica.
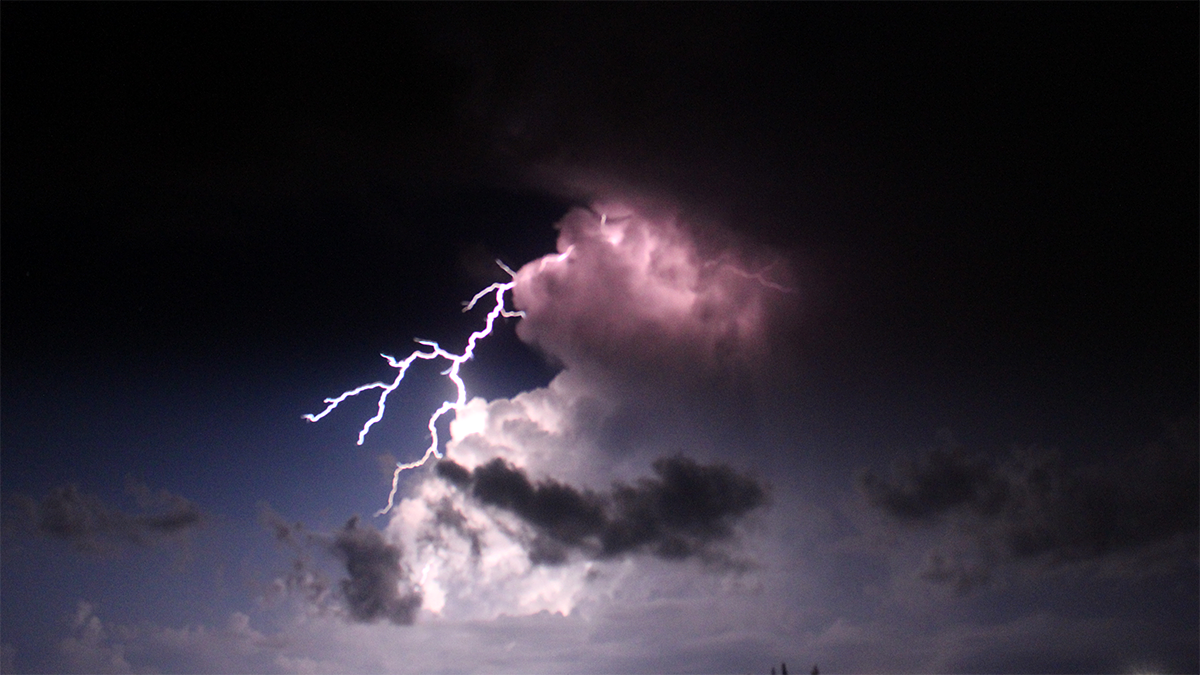
Lightning Initiating at High Altitudes May Develop Continuously
Recent radio observations reveal a new mode of initial lightning development in the form of continuous initial breakdown burst of several kilometers in length at high altitudes within thunderstorms.
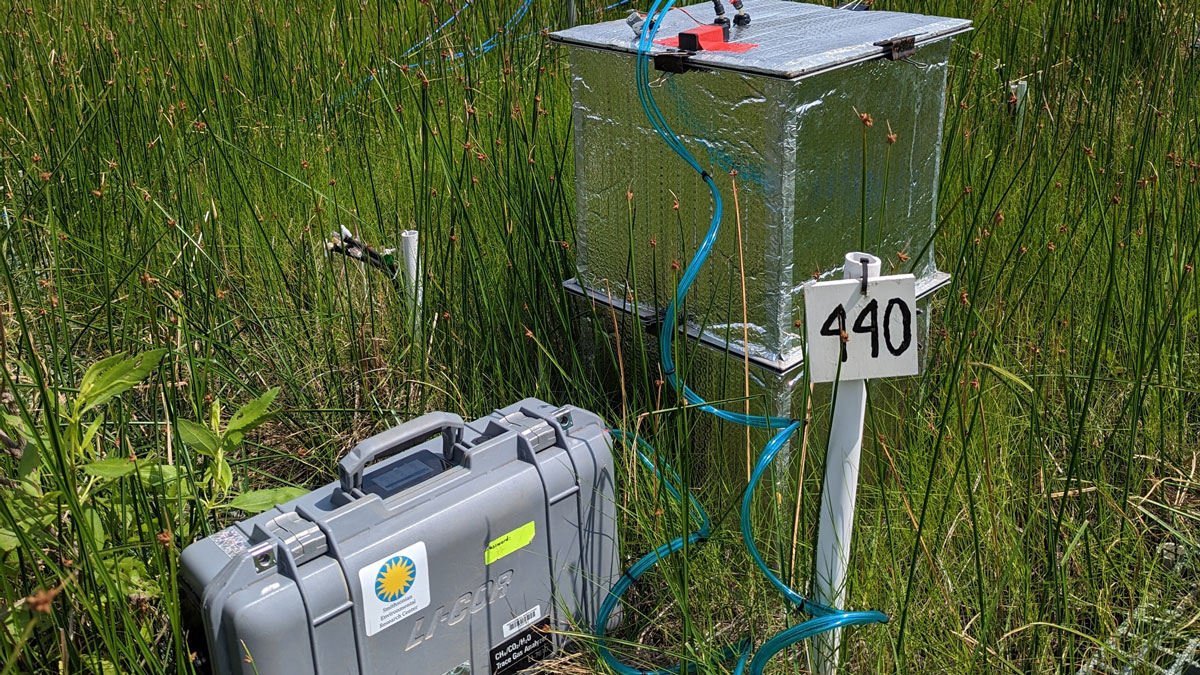
New Software Package Helps Scientists Find Flux
An easy-to-use R package offers a more efficient way to sort through and analyze data about greenhouse gas levels collected in static chamber experiments.