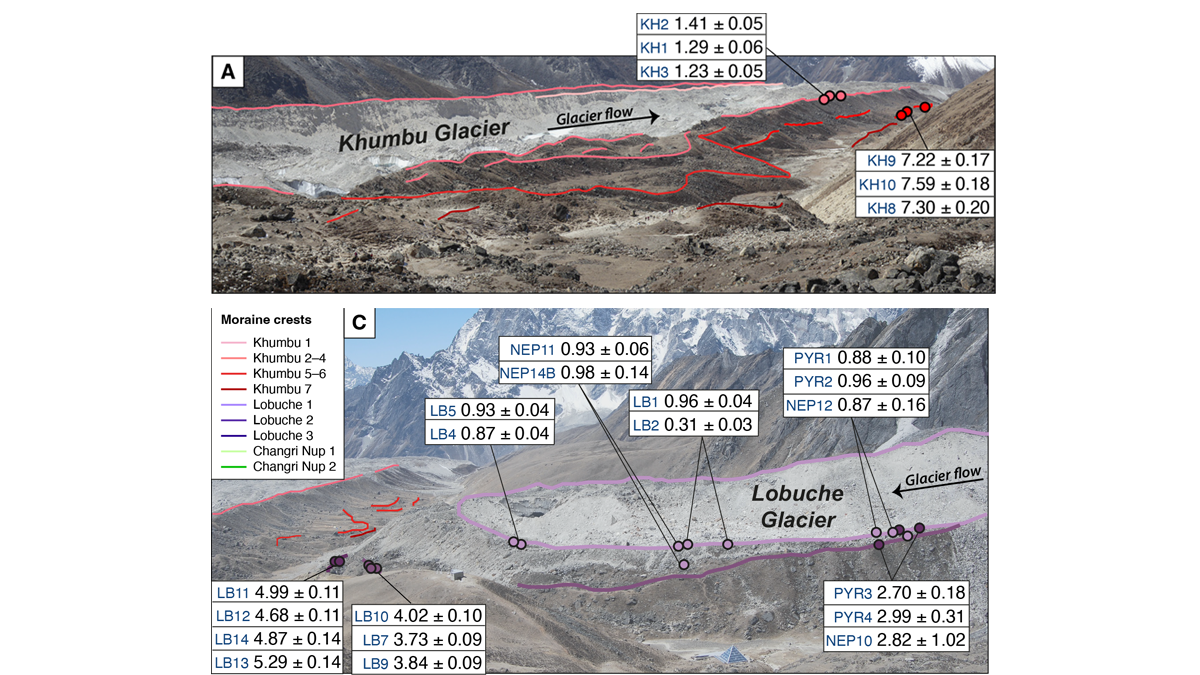
New dating of glacial features reveals predictable glacier behavior in response to climate warming and cooling in the Everest region in the past 8,000 years.
geochemistry
A Post-Impact Deep Freeze for Dinosaurs
New research supports the hypothesis that dinosaurs were done in by climate change after an asteroid impact kicked up a massive plume of sulfur gases that circled the globe for several decades.
Toxic “Forever Chemicals” Accumulate Above the Water Table
PFAS pose a public health risk, but there are major gaps in our knowledge of how these chemicals move through the ground.
A New Look at Preindustrial Carbon Release from the Deep Ocean
New research could help inform future studies of how the release of carbon dioxide from the Southern Ocean might affect global climate change.
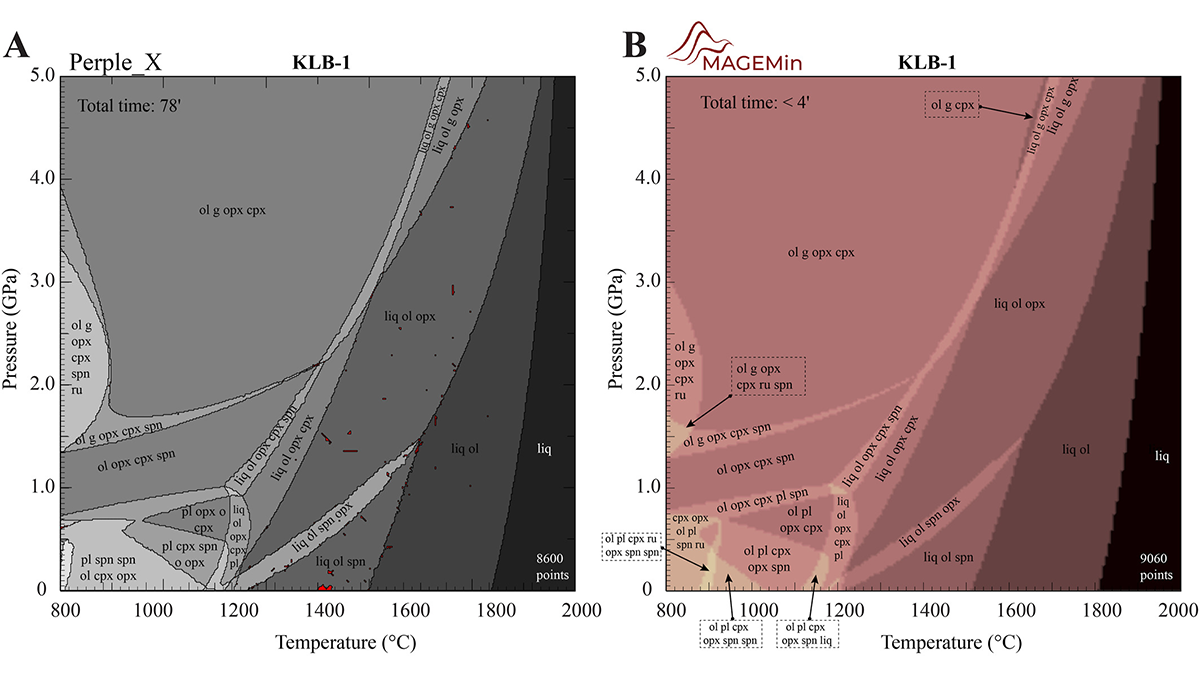
A New, Fast Computational Tool for Magmatic Phase Equilibria
Thermodynamic calculations in multiphase, multicomponent magmatic systems can be slow and buggy. A new parallel architecture solves the free energy minimization problem much faster than alternatives.
Earth’s Lower Mantle Is Drier Than Previously Thought
Scientists have long known that the two layers of Earth’s mantle have different chemical compositions. Now, modeling shows that different water concentrations may keep them from mixing.
Evidence of Drought Provides Clues to a Viking Mystery
A persistent drying trend, not plunging temperatures, may have played a role in the unexplained disappearance of Norse settlers from Greenland, according to researchers.
Impact of Climate on River Chemistry Across the United States
Findings of a new study have implications for water quality, aquatic ecosystem health, and water treatment and management as the world warms.
Fernando Temprano-Coleto: Going with the Flow
A career in fluid mechanics is both intellectually stimulating and well suited to solving environmental problems.
Lina C. Pérez-Ángel: Proud to Study Paleoclimate in Colombia
As a young Latina, Pérez-Ángel brings a fresh perspective to paleoclimatology.