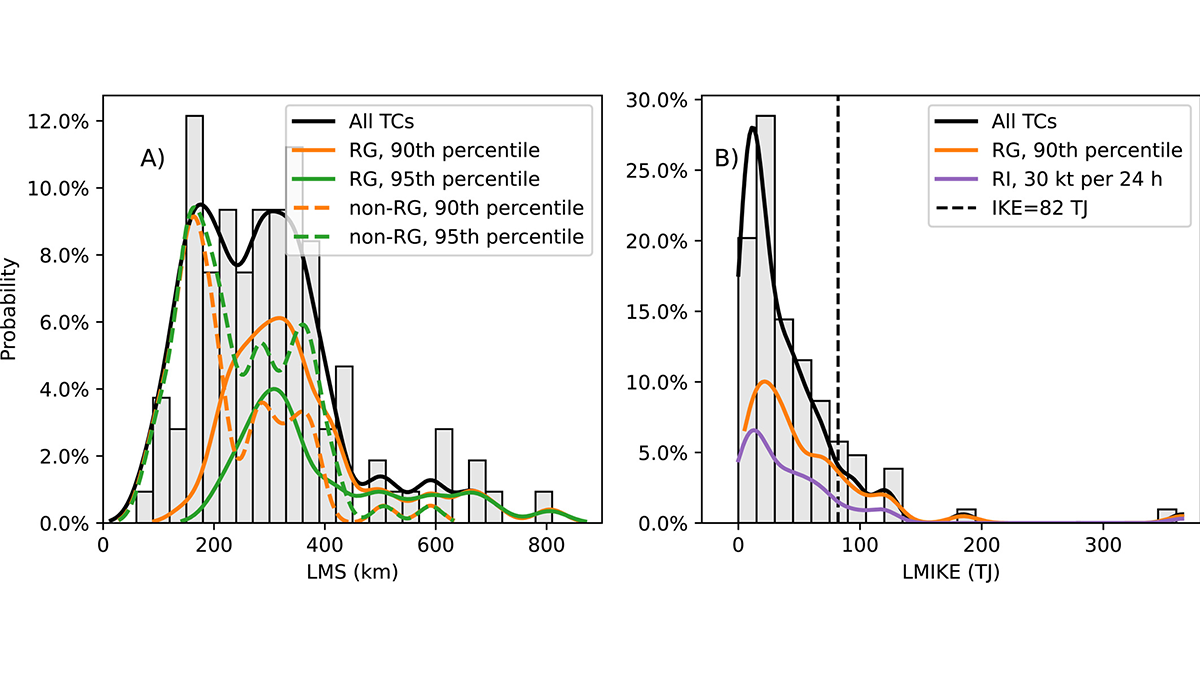
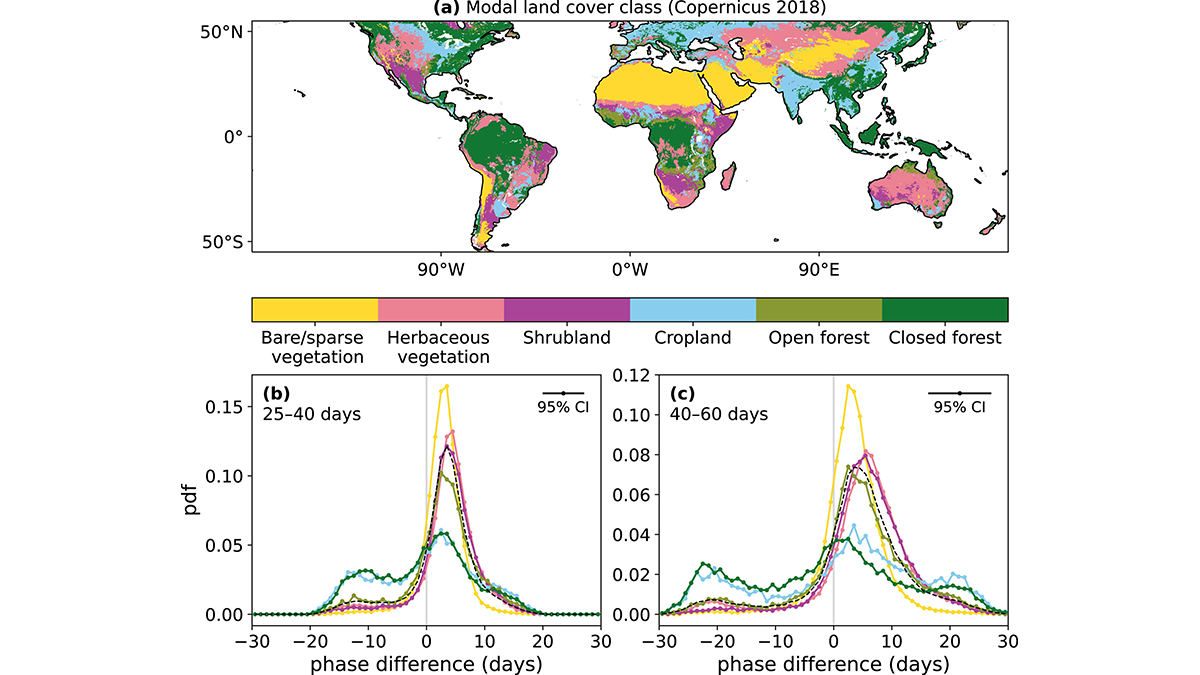
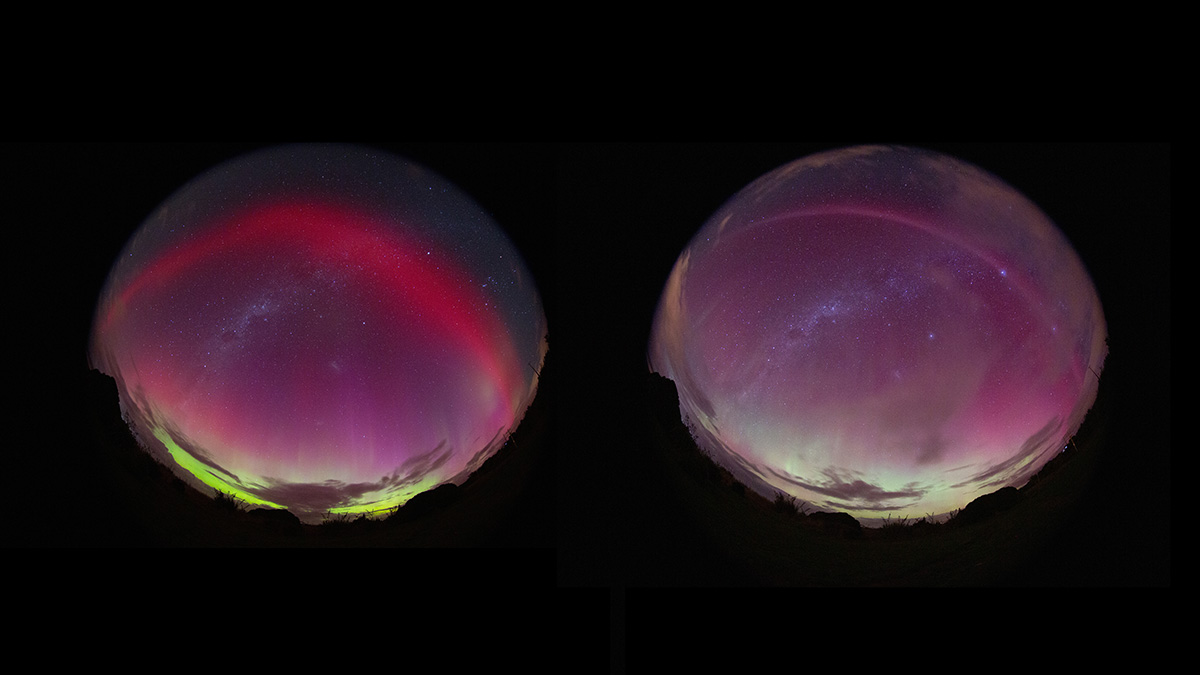
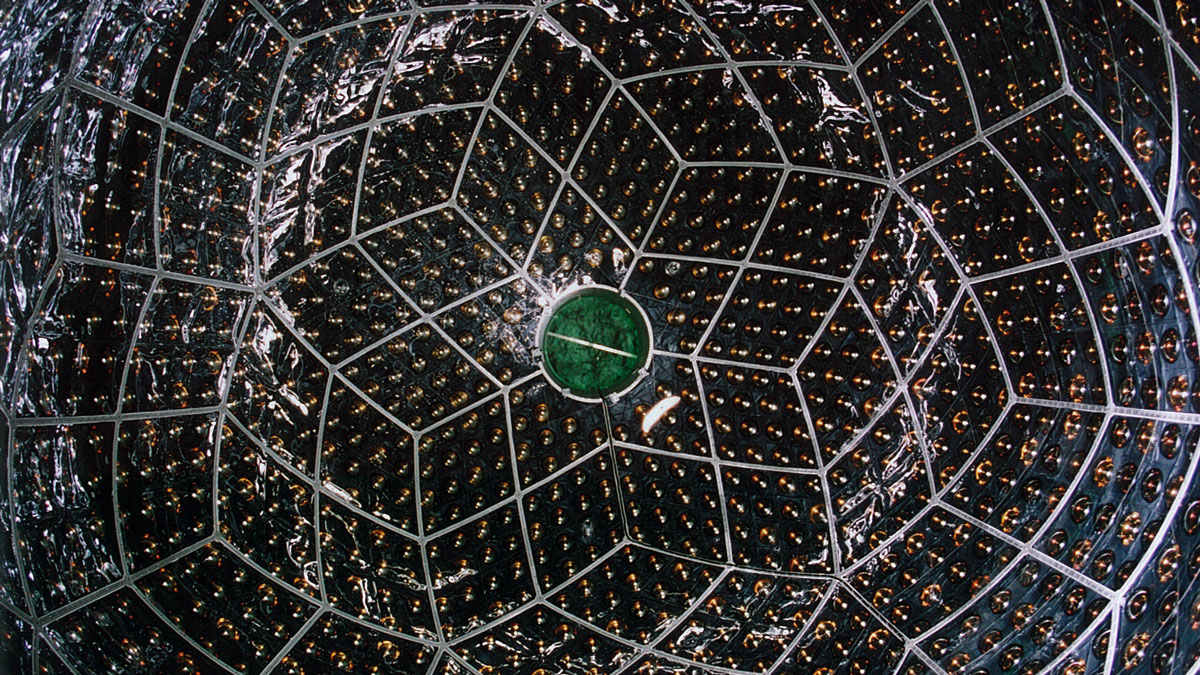
A new study focuses on the rapid growth of tropical cyclones and their destructive potential.
Geophysical Research Letters
Quantifying Changes in Midlatitude Subseasonal Prediction Skill
The differences between future and present subseasonal predictability in the Northern Hemisphere provided by the tropics are evaluated using neural networks.
From SAR Arc to STEVE: An Atmospheric Evolution
A new study reports the first observation of a stable auroral red arc evolving into a strong thermal emission velocity enhancement during a geomagnetic storm.
Estimating Uranium and Thorium Abundance with Geoneutrinos
Terrestrial electron antineutrino observations provide new constraints on the contributions of radiogenic heat in the mantle.
What Drives Hillslope Connectivity?
Hillslopes play a critical role in linking ecosystems. Understanding the forces that drive their connections can help us to better understand adaptation in the face of climate change.
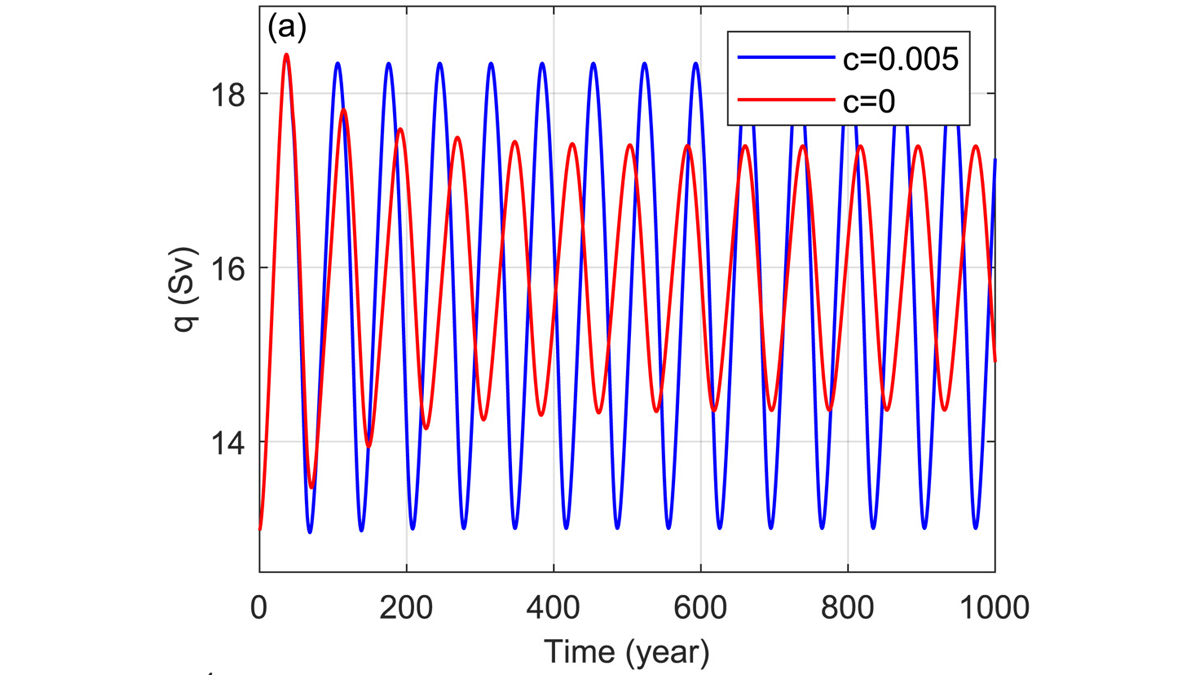
Arctic Salinity Pushes the AMOC Swing
A model of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), pioneered by Henry Stommel over 60 years ago, can exhibit realistic cyclic behavior if the role of Arctic salinity is included.
Landfalling Hurricanes Intensify Due to Coastal Downwelling
Hurricane winds can lead to coast downwelling, which brings warmer surface water near the coast and can contribute to the intensification of the landfalling hurricane.
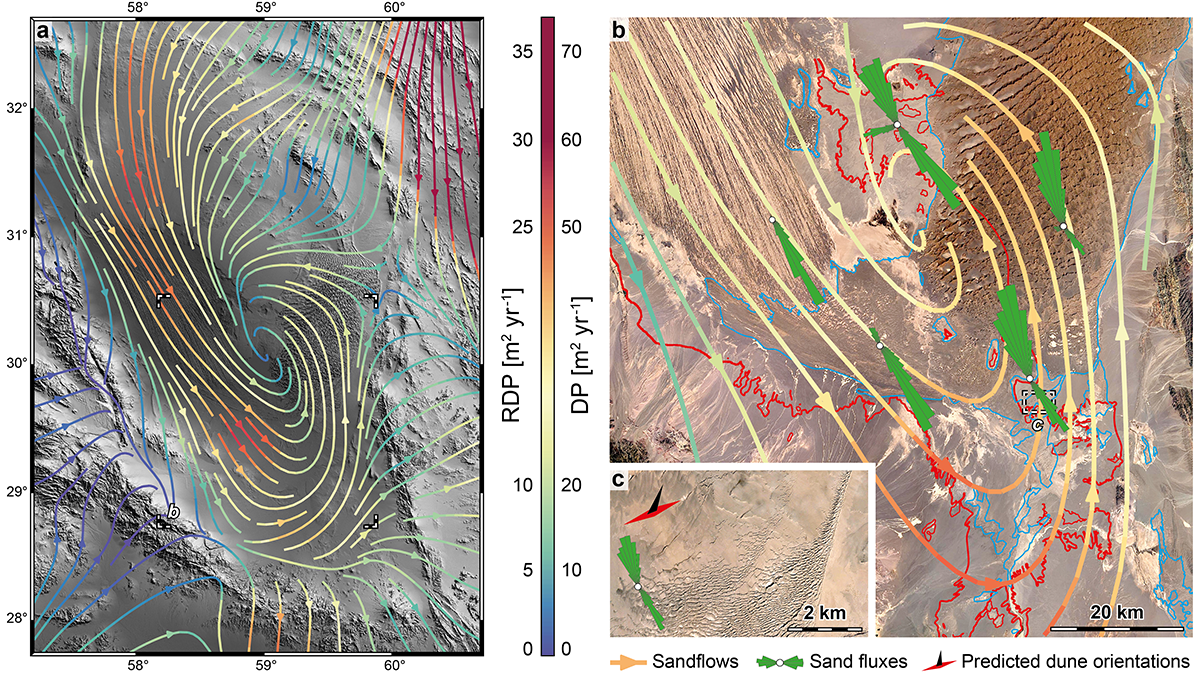
A Unique Glimpse at Sediment Erosion and Deposition by Wind
The Lut Desert in Iran is an exceptional natural laboratory to study how wind moves sediment across the landscape. A new study quantifies erosional and depositional sediment fluxes of the desert.
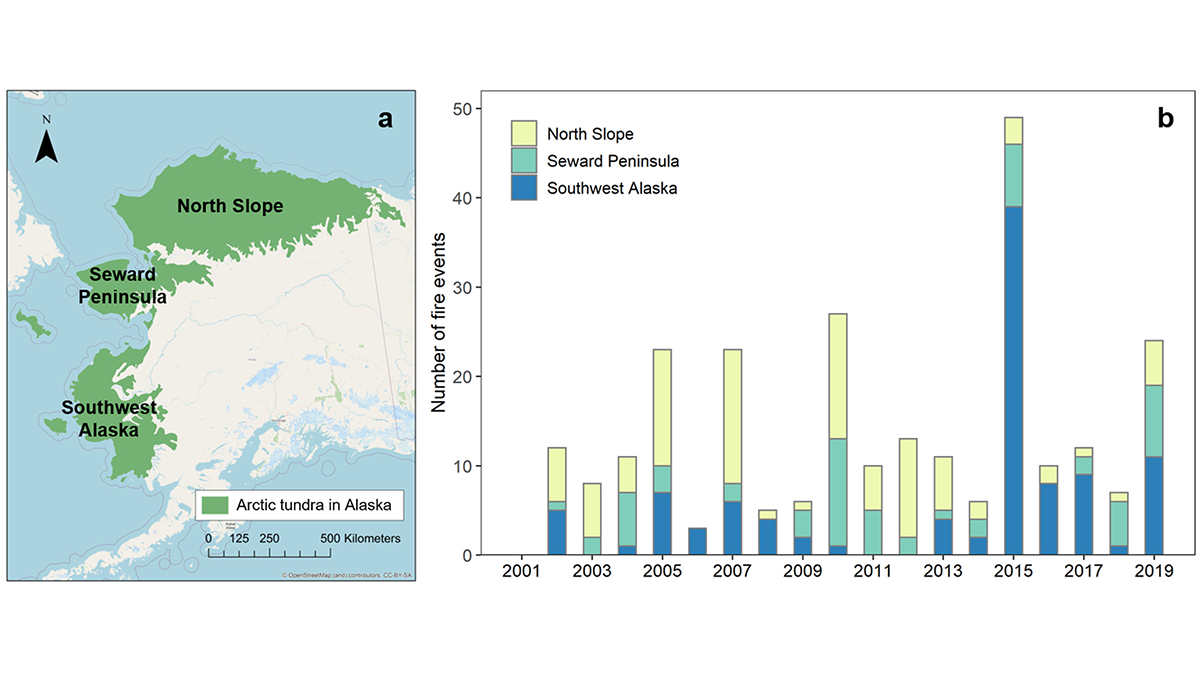
Lightning in Alaskan Tundra Ignites Most Fires
Cloud-to-ground lightning is found to be the most important controller of wildfire occurrence in the Artic tundra of Alaska from 2001 to 2019.
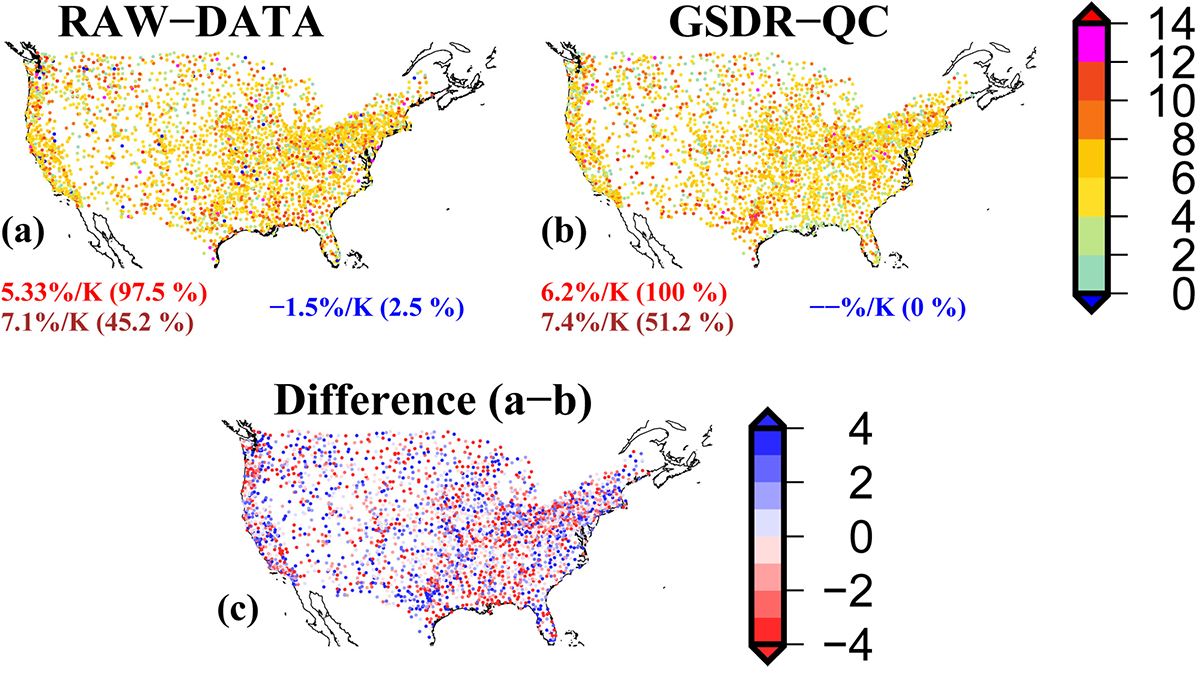
Explaining Uncertainty in Estimates of Rain Response to Warming
Humidity increases with warming. Theory and observations about how increased humidity translates into more extreme rainfall can be reconciled if attention is paid to data and methods.