Using electromagnetic waves originating in the ionosphere and magnetosphere, conductivity profiles reaching the deep upper mantle show surprising variability in water content.
Geophysical Research Letters
Bridging the Gap Between Weather and Climate Predictions
A special collection on subseasonal-to-seasonal prediction presents the latest progress in filling the gap between short-term weather prediction and longer-term climate prediction.
Extremely High Carbon Return in Certain Volcanic Arcs
By comparing measured volcanic output with subducted carbon fluxes from drill cores, the Lesser Antilles subduction zone shows nearly complete slab carbon release at sub-arc depths.
Improving Atmospheric Forecasts with Machine Learning
An efficient, low-resolution machine learning model can usefully predict the global atmospheric state as much as 3 days out.
Tracking Tropospheric Ozone Since 1979
Stratospheric ozone depletion between 1979 and 2010 resulted in a slight decrease of ozone in the troposphere during that period despite increased ozone production from anthropogenic emissions.
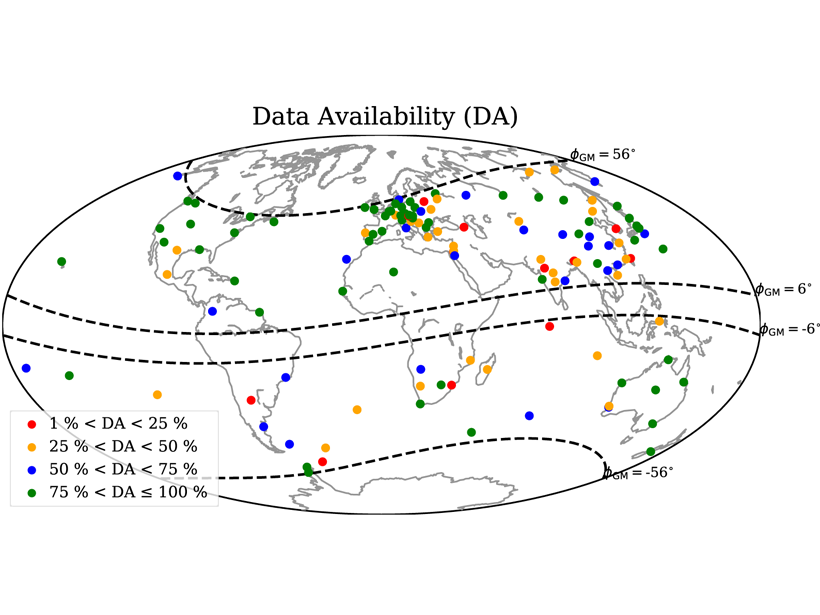
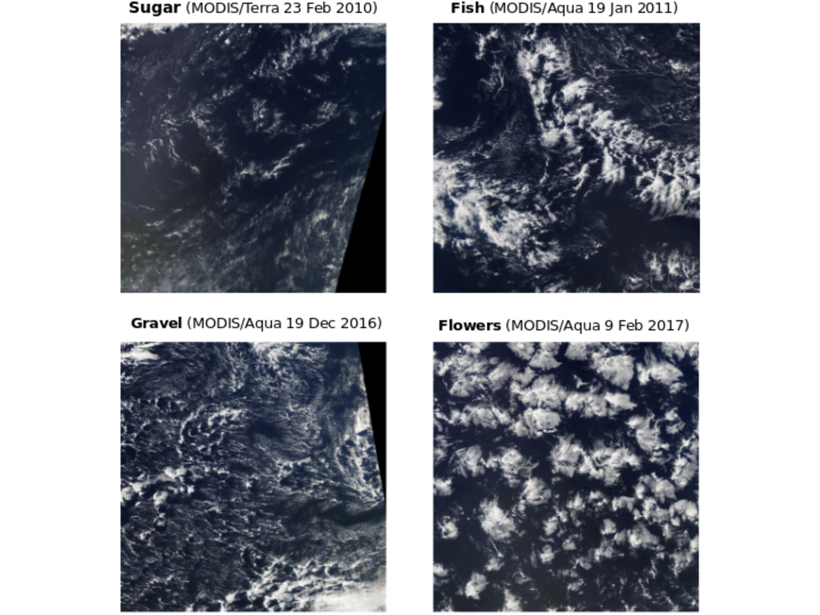
A New View of Old Clouds
Satellite images of marine shallow clouds are objectively classified into four distinct types, illuminating new ways to tackle a long-standing problem in climate predictions.
An Element of Randomness in Modeling Arctic Ice Cover
Incorporating random variation of temperature, humidity, and wind offers a computationally cheap alternative to improving resolution in an Earth system model when predicting when Arctic sea ice will disappear.
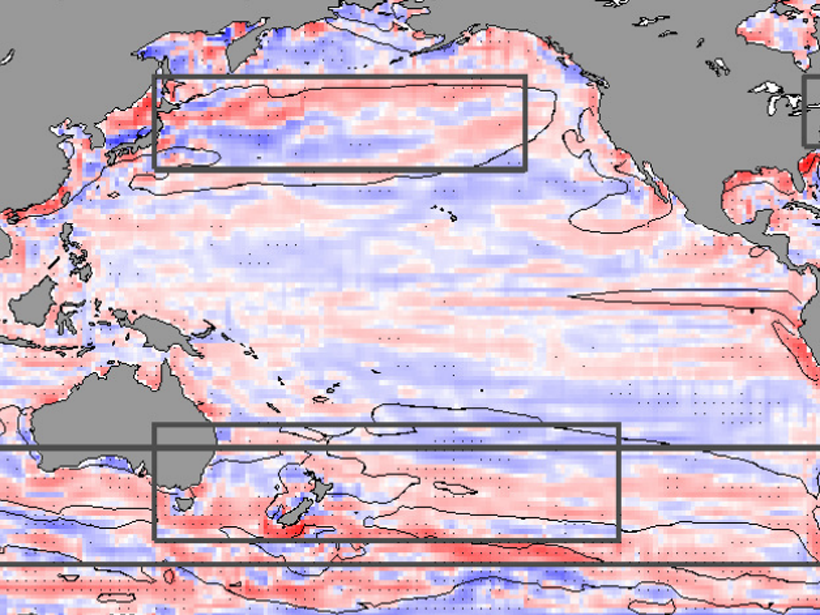
Ocean Gyres Observed to Move Poleward
Basin-wide ocean gyres have been observed to be slowly migrating toward the poles and, although natural variations contribute, climate simulations suggest the shift is in response to global warming.
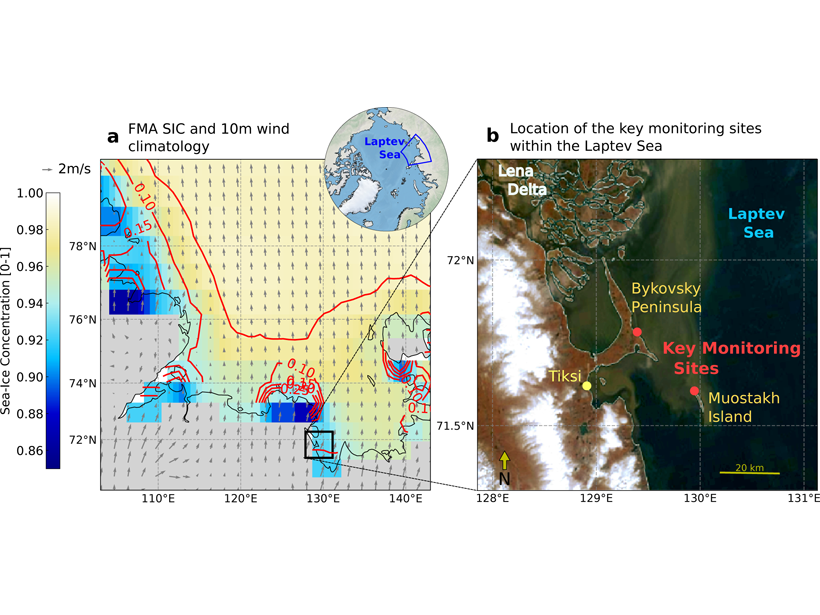
Arctic Coast Erosion Linked to Large-Scale Climate Variability
Changes in rates of Arctic coastal erosion detected from multi-decadal measurements are attributed to the shorter duration in the winter sea ice coverage and large-scale changes in the wind patterns.
Larger Role for Shallow Intermediate Waters in Ocean Circulation
Water masses formed off southeastern Greenland may contribute more than previously thought to the variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, which strongly influences global climate.