High-precision airborne measurements, in combination with atmospheric modeling, suggest that the Katla subglacial caldera may be one of the planet’s biggest sources of volcanic carbon dioxide.
Geophysical Research Letters
A More Detailed Look at Earth’s Most Poorly Understood Crust
The second-generation Antarctic Digital Magnetic Anomaly Project offers a powerful new tool for probing the structure and evolution of the southernmost continent’s lithosphere.
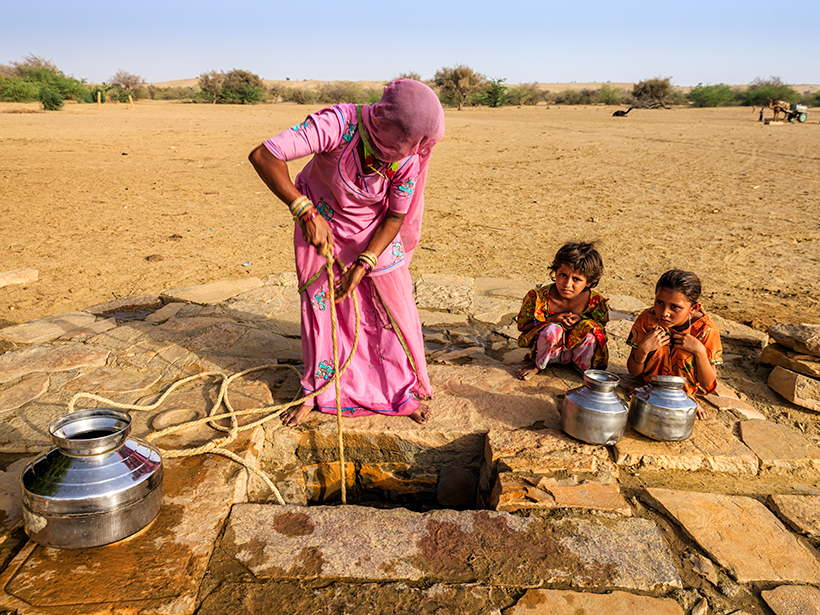
A Closer Look at the Sustainability of Our Groundwater Aquifers
Researchers use a new approach to assessing the world’s largest aquifers in hopes of improving groundwater management during drought periods.
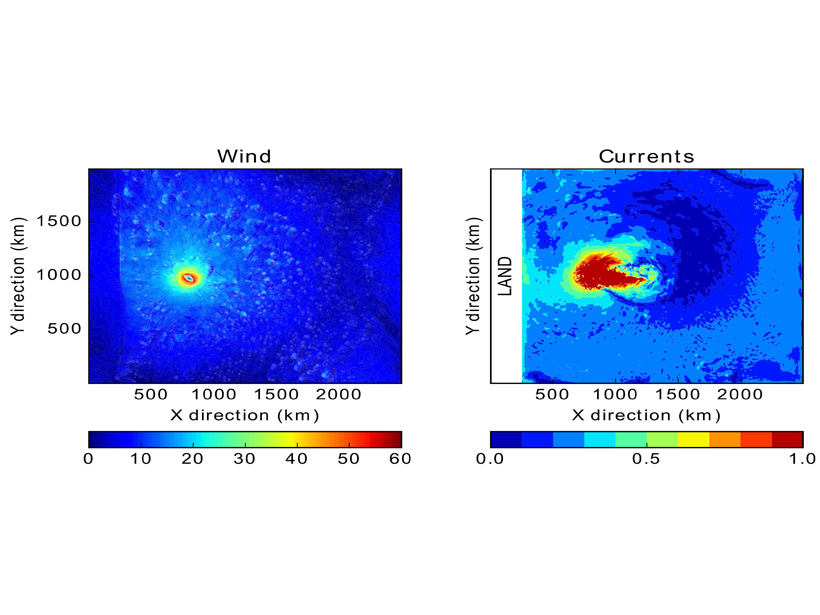
Can Coastal Surface Currents Improve Hurricane Forecasts?
An idealized model explores whether hurricane intensity forecasts could potentially be improved by incorporating coastal surface currents data.
Yellow Detritus in the Oceans May Help Reduce Warming
Dissolved organic matter in the oceans absorbs light near the water’s surface, leading to cooler waters that may help mitigate regional climate warming.
Autumn Warming No Longer Accelerating Carbon Loss in the North
An analysis of Point Barrow’s 40-year record points to the importance of calculating the carbon cycle’s response to temperature during the northern latitudes’ non-growing season.
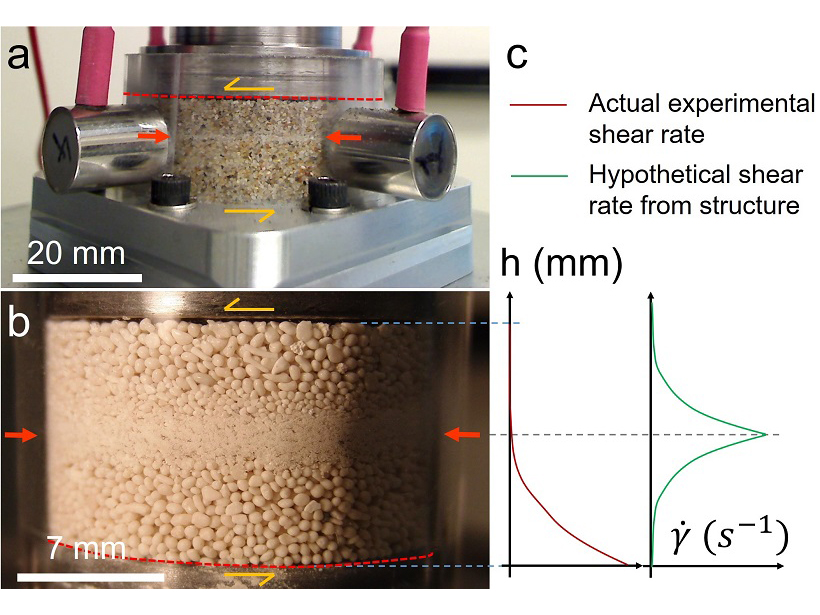
A New Spin on Grain Segregation in Fault Zones
Fine-grained layers in sheared fault gouge may be formed by shear-driven size-segregation in granular materials, rather than by shear localization.
Insensitivity of Total Sediment Flux to Hydraulic Details
The total sediment mass transported by flow under different sets of regimes is insensitive to the exact details of hydraulic forcing, but what matters is cumulative transport capacity.
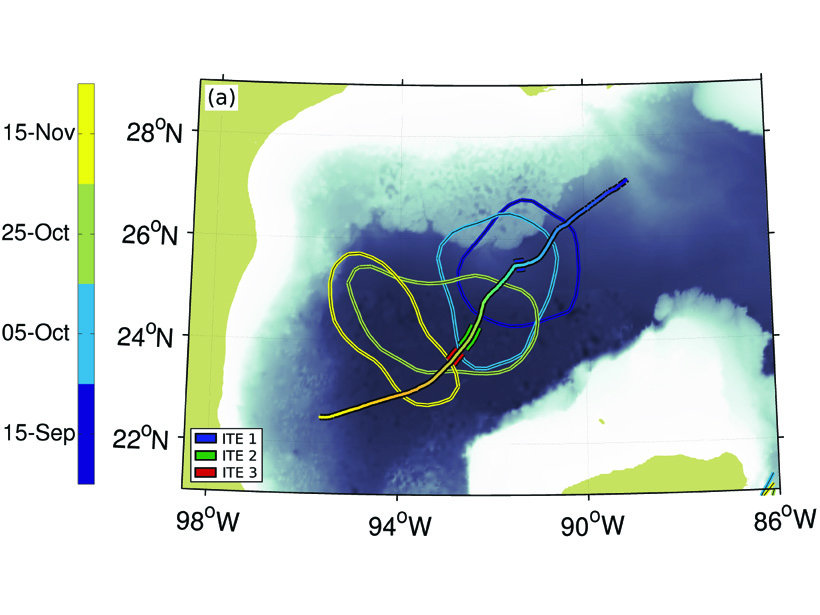
Smaller Eddies Found Within Eddies
A glider survey observed three small eddies embedded within a larger scale eddy associated with the Loop Current in the Gulf of Mexico.
New Modeling Framework Improves Radiative Feedback Estimates
A new approach offers insights into the relationship between surface temperature and top-of-atmosphere energy imbalances and improves the understanding of important climate feedbacks.