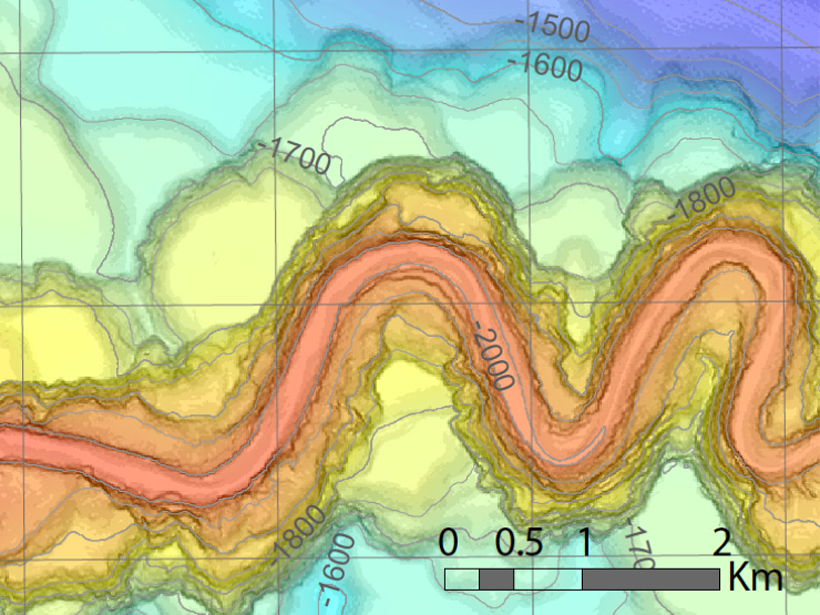
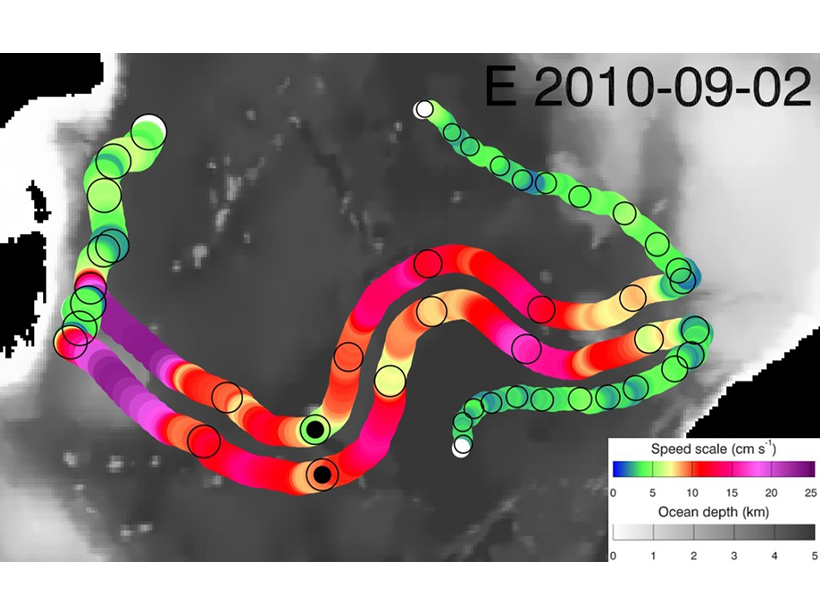
The first field measurements of turbidity currents flowing around submarine channel bends indicate spiral flow plays a key role in keeping sediment suspended for hundreds of kilometers.
Geophysical Research Letters
Measuring Hurricane Wind Speed from Space
A new technique based on GPS signals could provide better wind speed measurements during hurricanes and cyclones.
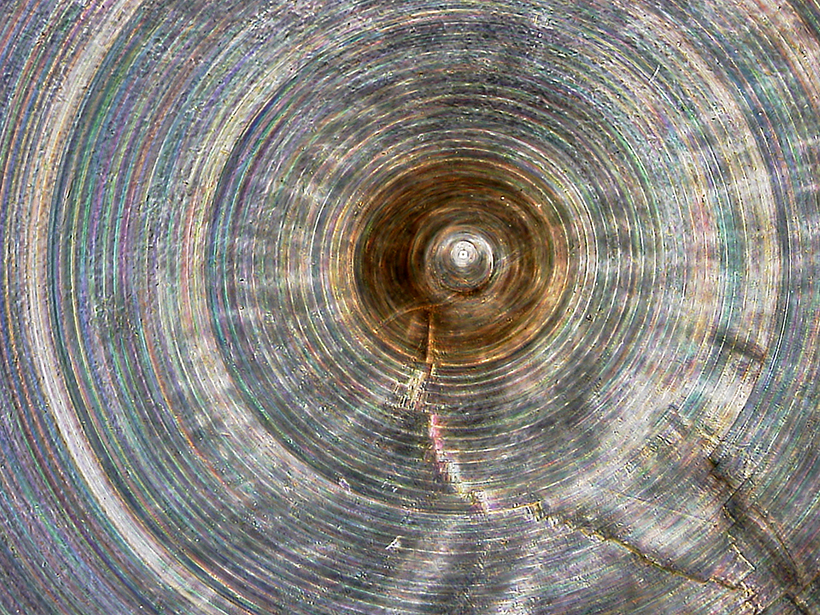
One of World’s Oldest Animals Records Ocean Climate Change
Researchers probe millennia-old deep-ocean sponges for links between ocean nutrients and climate.
Fiber-Optic Networks Can Be Used as Seismic Arrays
A new study repurposes telecommunications cables to harness sound from light. The method can accurately measure ground motion from distant earthquakes.
Shedding Light on the Southern Ocean Carbon Sink
One of the world’s largest carbon sinks is still poorly understood.
Pinpointing Effects of Hadley Cell Expansion
As a major atmospheric circulation system spreads farther poleward, some regions are drying out. But as time passes, will this drying be symmetrical across the globe?
Two Paired Eddies Travel Faster and Further Than One
The first observational evidence of dipole eddy pairs (modons) in the southern midlatitude ocean reveals that they move faster, live longer, and travel greater distances compared to single eddies.
First Near-Global Measurements of Isotopic Nitrous Oxide
By harnessing satellite data collected from low-Earth orbit, scientists can now track the distribution of atmospheric nitrous oxide and its isotopes.
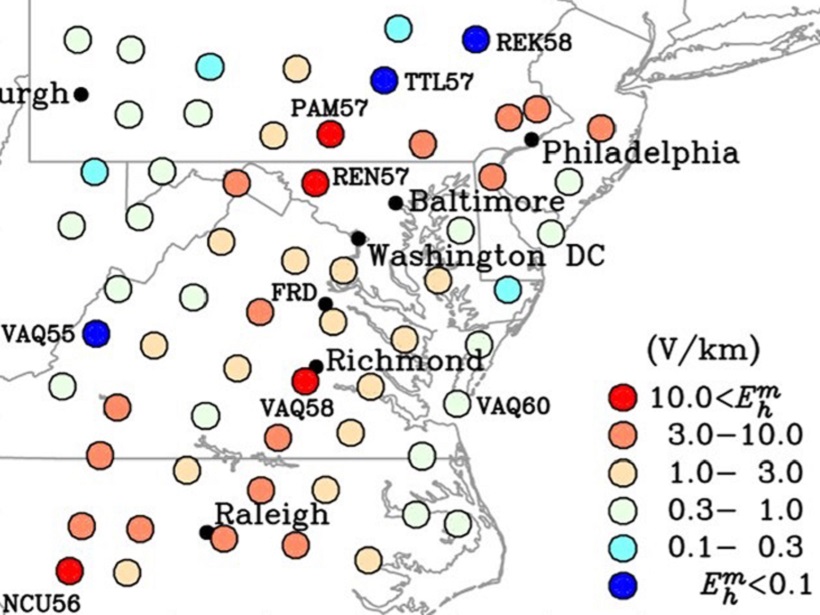
Mapping Extreme-Value Geoelectric Fields
To help mitigate magnetic storm interference on electric power grid operations, extreme-value geoelectric fields have been mapped across the mid-Atlantic United States.
Space Weathering Asymmetrically Alters Lunar Crater Walls
Directional differences in craters’ optical properties suggest that the solar wind, not tiny meteorites, is the main driver of space weathering on the Moon.