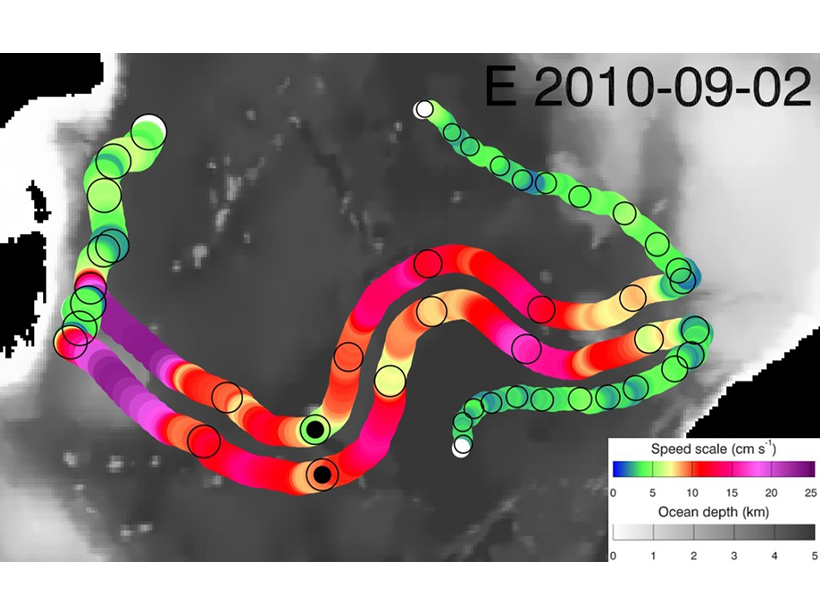
The first observational evidence of dipole eddy pairs (modons) in the southern midlatitude ocean reveals that they move faster, live longer, and travel greater distances compared to single eddies.
Geophysical Research Letters
First Near-Global Measurements of Isotopic Nitrous Oxide
By harnessing satellite data collected from low-Earth orbit, scientists can now track the distribution of atmospheric nitrous oxide and its isotopes.
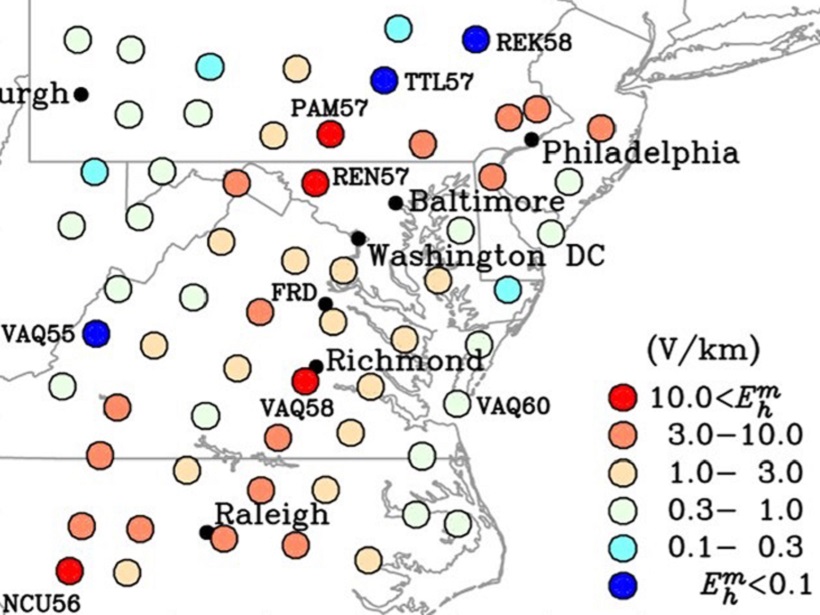
Mapping Extreme-Value Geoelectric Fields
To help mitigate magnetic storm interference on electric power grid operations, extreme-value geoelectric fields have been mapped across the mid-Atlantic United States.
Space Weathering Asymmetrically Alters Lunar Crater Walls
Directional differences in craters’ optical properties suggest that the solar wind, not tiny meteorites, is the main driver of space weathering on the Moon.
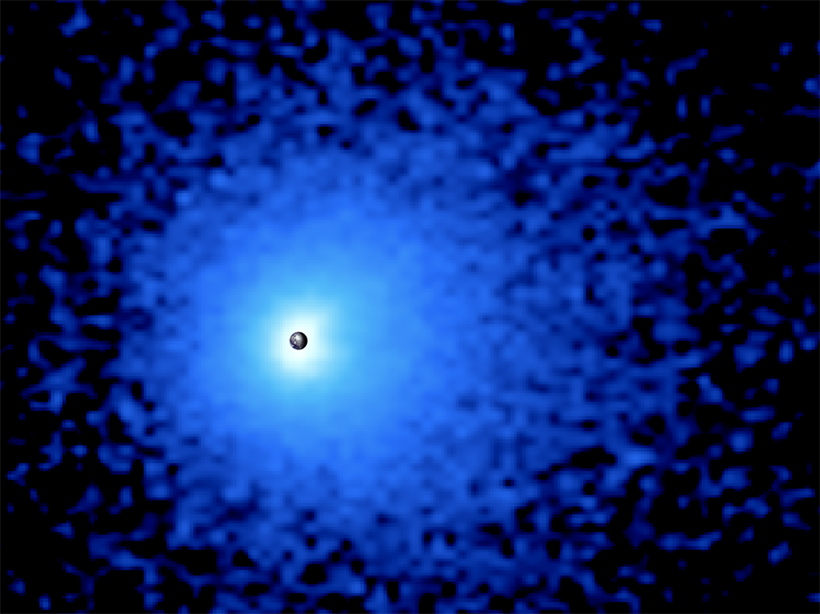
Tracing the Path of Gas Atoms from Earth to the Final Frontier
Scientists capture the first complete image of Earth’s luminous geocorona and prove its ecliptic north–south symmetry.
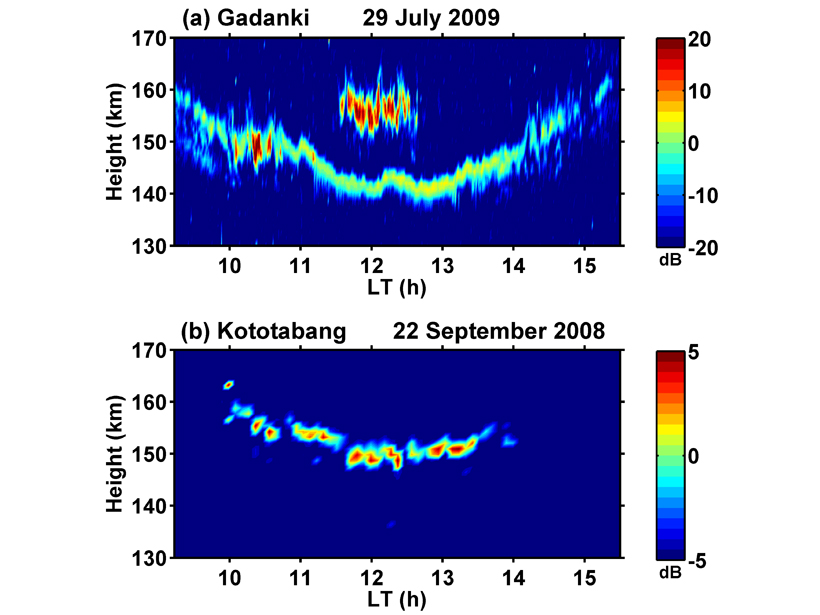
New Observations of Mysterious Radar Echoes
Exploring the relationship between solar extreme ultraviolet radiation flux and 150-km radar echoes.
Rethinking How Water Circulates Between the Oceans and Land
A reexamination of the global water cycle shows that tropical coastlines exert a profound influence on atmospheric water circulation by wringing water vapor from the atmosphere.
Humans to Blame for Higher Drought Risk in Some Regions
New observations and analysis dispel remaining doubts that anthropogenic climate change is expanding dry areas in northern midlatitudes.
Mapping a Valparaíso Earthquake from Foreshock to Aftershock
Using seismic data recorded along the Chilean coast, scientists retrace the development of a recent earthquake.
Reducing Errors in Satellite-Derived Arctic Sea Ice Thicknesses
Salty snow throws off satellite-based estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness by up to 25%. A new method seeks to fix that.