Using seismic data recorded along the Chilean coast, scientists retrace the development of a recent earthquake.
Geophysical Research Letters
Reducing Errors in Satellite-Derived Arctic Sea Ice Thicknesses
Salty snow throws off satellite-based estimates of Arctic sea ice thickness by up to 25%. A new method seeks to fix that.
Where Did the Water Go on Mars?
Primordial solar storm conditions are believed to have significantly enhanced the loss of water and other atmospheric volatiles in Mars’ history.
How Earth’s Orbit Affected Ice Sheets Millions of Years Ago
A new study of the late Pliocene era could help scientists predict future sea level rise.
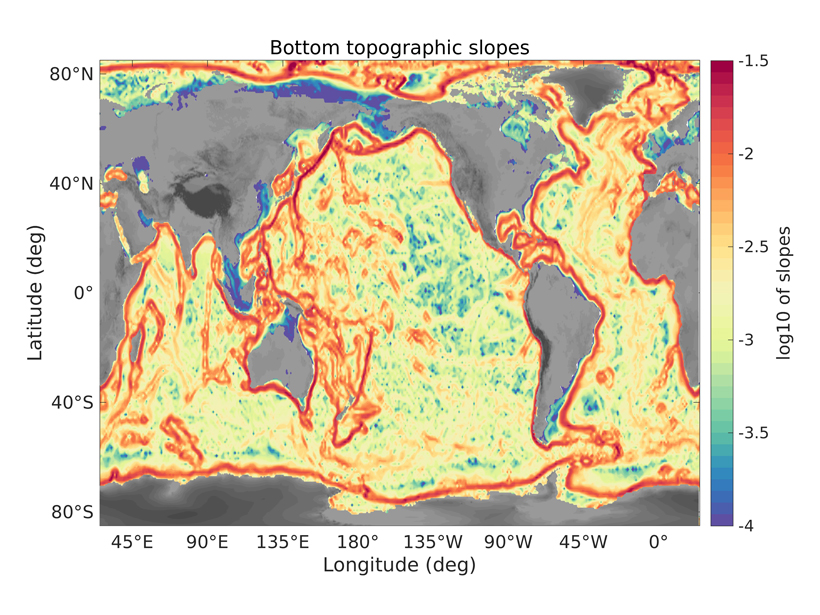
Sloping Topography and Oceanic Surface Modes
An accurate understanding of the influence of ocean bottom topography helps to diagnose the velocities of subsurface currents.
Comparing Craters
An analysis suggests that craters degrade faster on Mercury than the Moon, raising questions about landscape evolution on different planetary bodies.
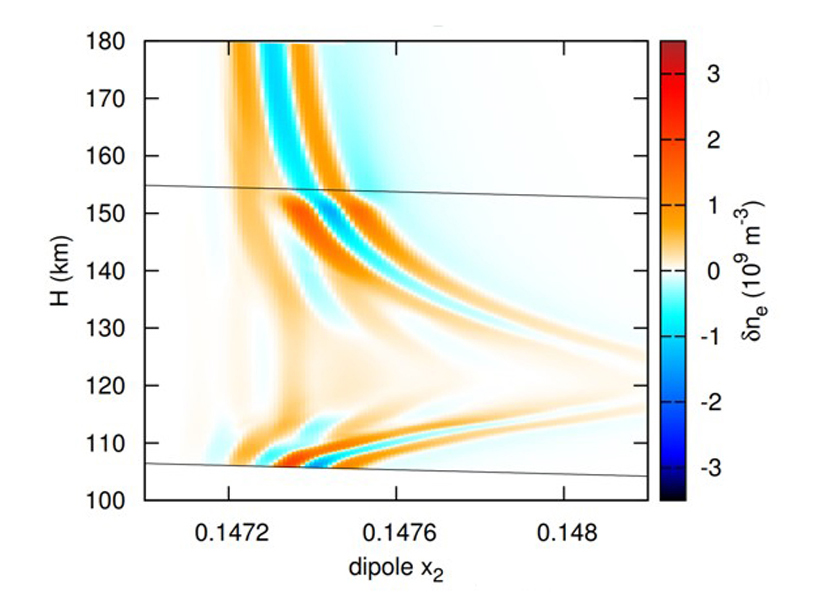
New Insight into Ionospheric Feedback Instability
A new modeling effort could change our understanding of auroral arc formation.
What Precursors Foretold Greenland’s Recent 100-Meter Tsunami?
Slippage began hours before a landslide-driven tsunami destroyed a village in northwestern Greenland.
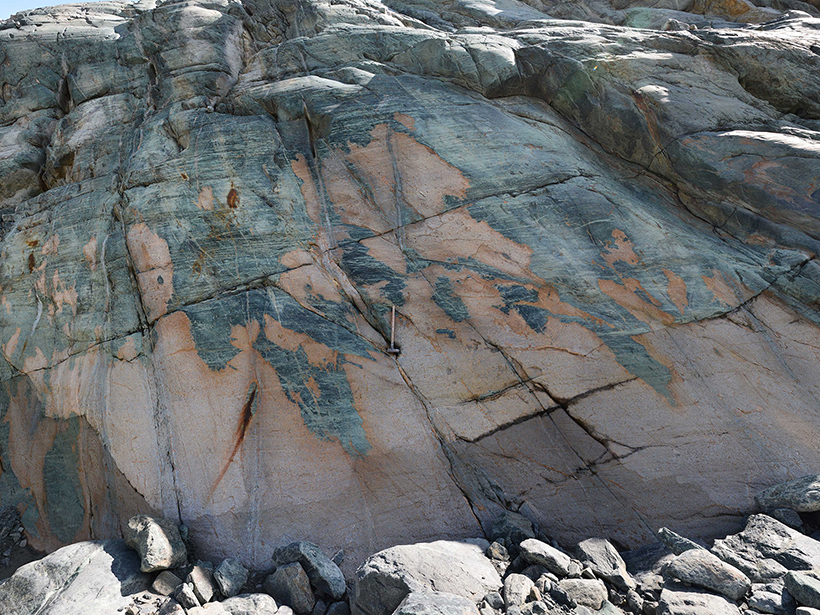
Scientists Simulate New Mechanism of Fluid Flow in Earth’s Crust
Three-dimensional high-performance computer modeling reveals the behavior of fluid transport waves generated by chemical reactions that take place during metamorphism.
Modeling Beijing’s Water Crisis
Beijing’s growing population is rapidly draining its water supplies. A new study examines how land use change affects groundwater storage beneath the megacity.