The amount of CO2 segregated from the mantle by carbonate melting beneath old oceanic crust may equal that emitted along the mid-ocean ridge system, thereby contributing to the global carbon cycle.
Geophysical Research Letters
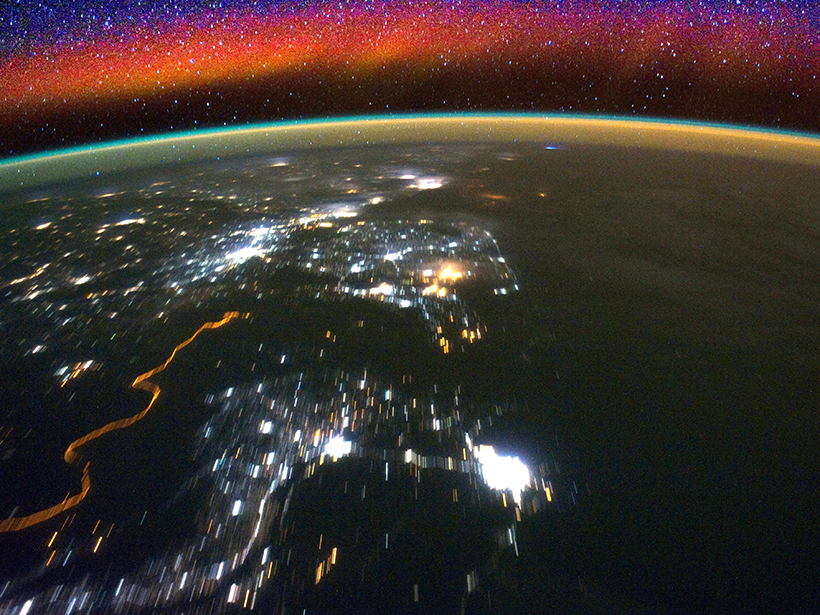
High-Altitude “Wind Walls” Discovered near Magnetic Poles
Satellite imaging reveals two narrow channels of extreme winds surrounded by gentle opposing flow 140–250 kilometers above sea level.
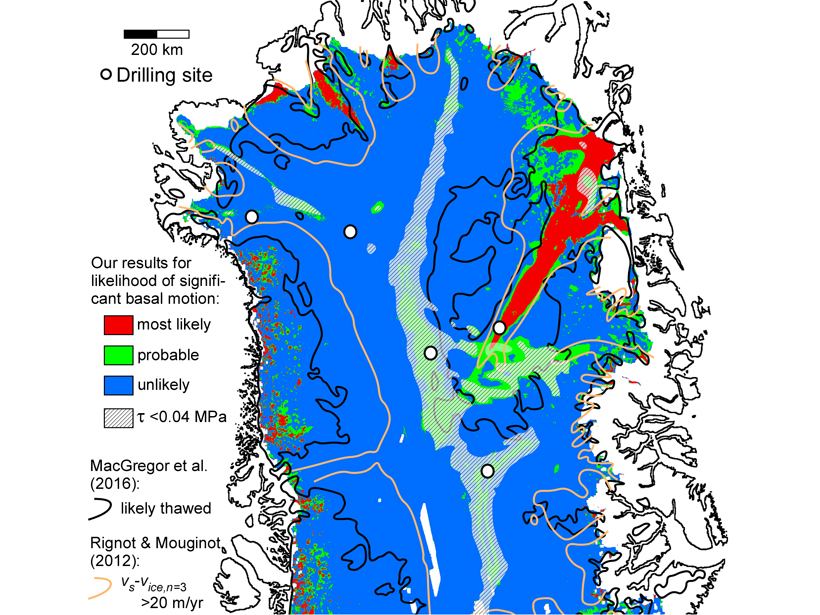
Greenland Basal Melting May Be Considerably Less Than We Think
New observations of surface ice velocity over northern Greenland challenge current assumptions used in ice sheet models to model the deformation mechanisms that govern ice flow.
Scraping Bottom: Iceberg Scours Reveal North Atlantic Currents
A 3-D seismic analysis of Pleistocene iceberg gouges indicates that surface currents in the Norwegian Sea flowed northward and remained consistent during numerous glacial cycles.
How Jupiter’s Icy Moons Got Their Bands and Grooves
Europa’s churning ice crust could reveal signs of ocean life, new study suggests.
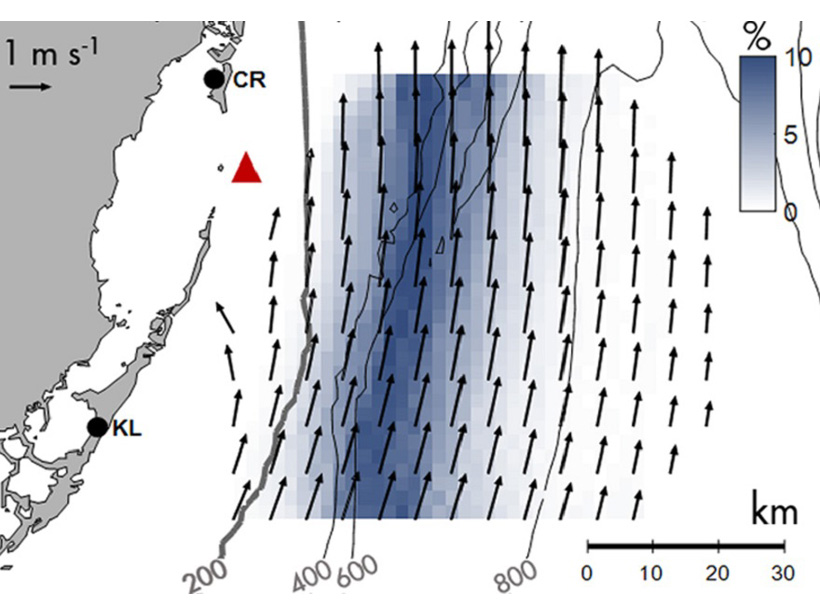
Energetics of Western Boundary Current Surface Flows Are Similar
Despite different wind forcing and air-sea heating conditions, the surface layer energetics of two Western Boundary Current systems in different ocean basins are surprisingly similar.
How Are Sediment Pulses Generated?
A new long-term flume experiment shows that bed load gravel travels downstream in recurring, 10-hour pulses even when water flow and sediment supply are constant.
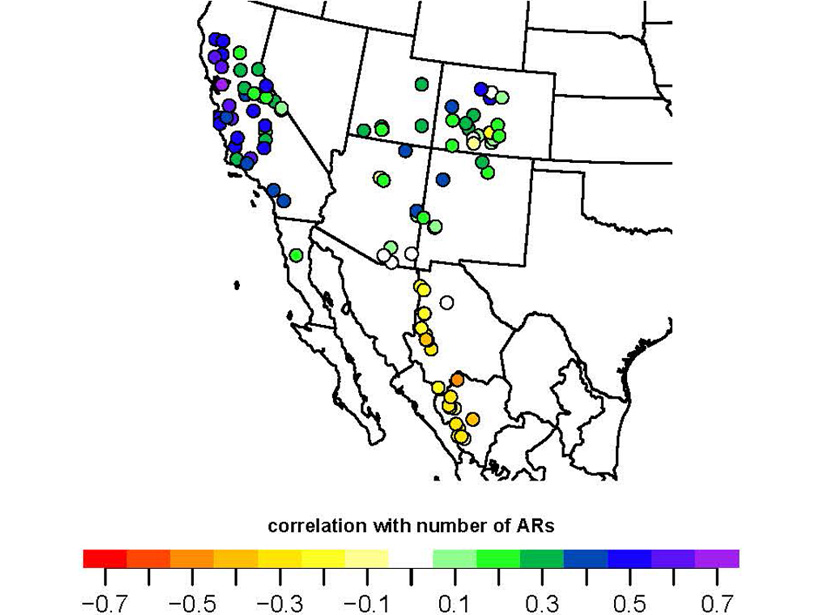
500 Years of Atmospheric River Landfalls in Southwestern USA
A network of tree-ring chronologies has been used to develop the first reconstruction of atmospheric river landfalls on the US Pacific Coast over the last 500 years.
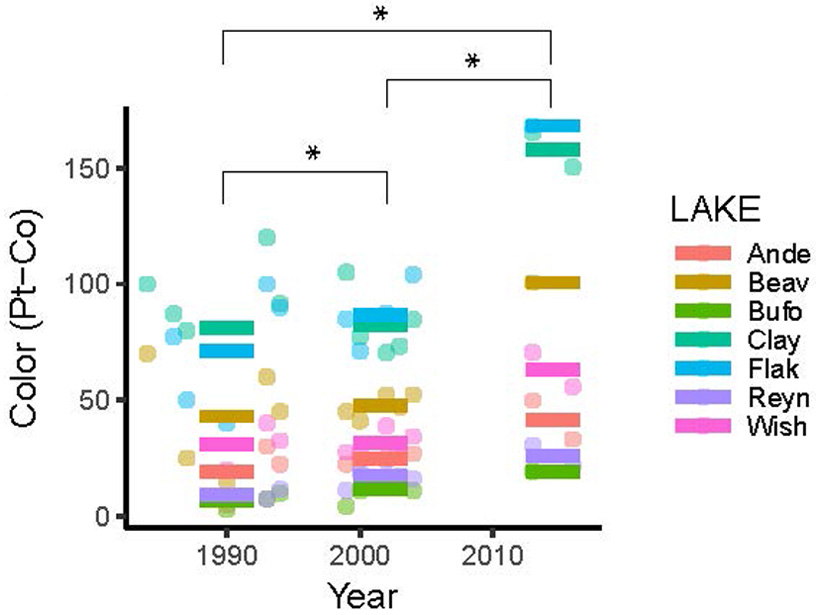
Nutrients May Change Flavor of “Meadow Tea” in Lakes
Lakes in the US and Europe have been getting more tea-colored over the past 30 years, and this “browning” trend may increase nutrient levels and affect lake water quality.
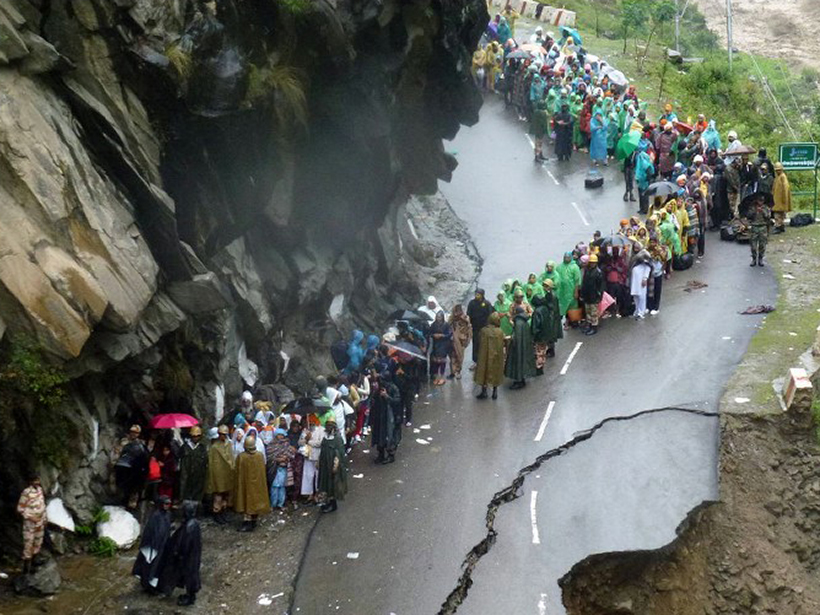
A Better Way to Predict the Indian Monsoon
A new study finds that including Himalayan topography and land-atmosphere interactions improves climate models.