The chief scientist at Esri wound her path into and out of academia.
GPS & GIS
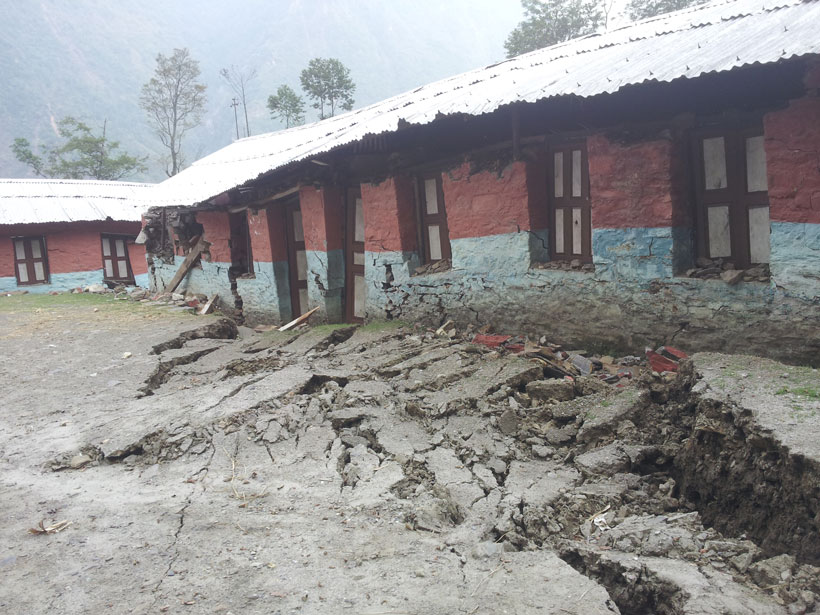
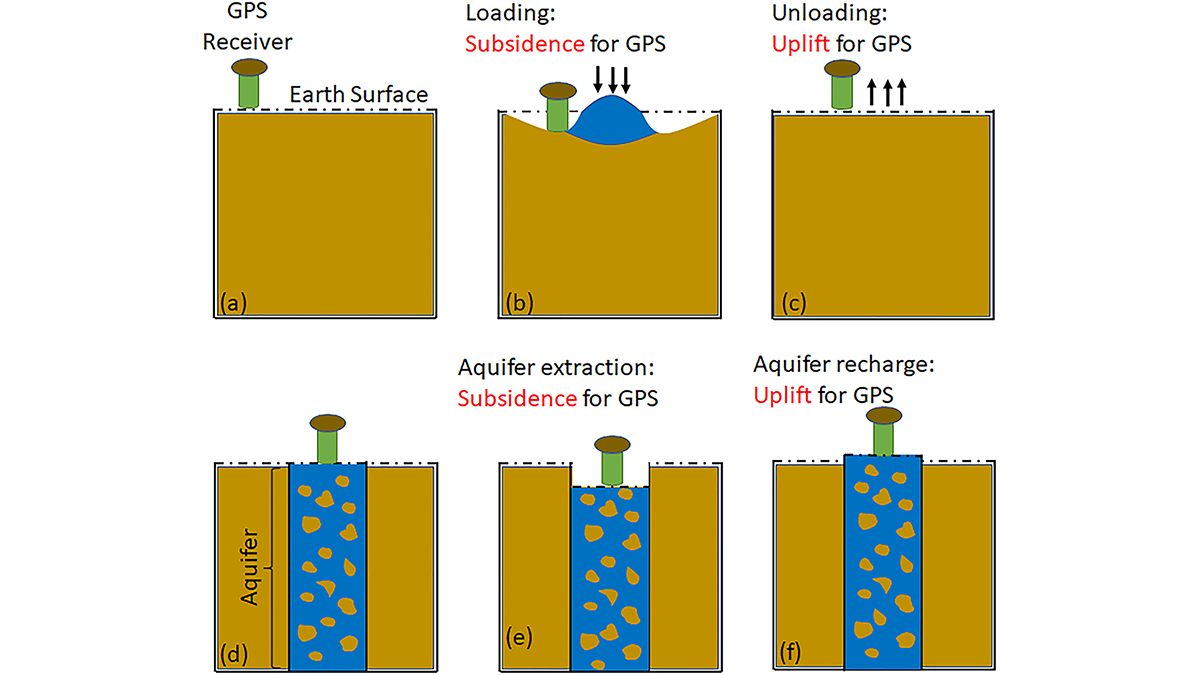
GPS Observations Sense Groundwater Change in Australia
By exploiting the fact that changes in groundwater cause deformations of the Earth’s surface, GPS receivers are used to detect groundwater changes related to extreme events and to seasonal oscillations.
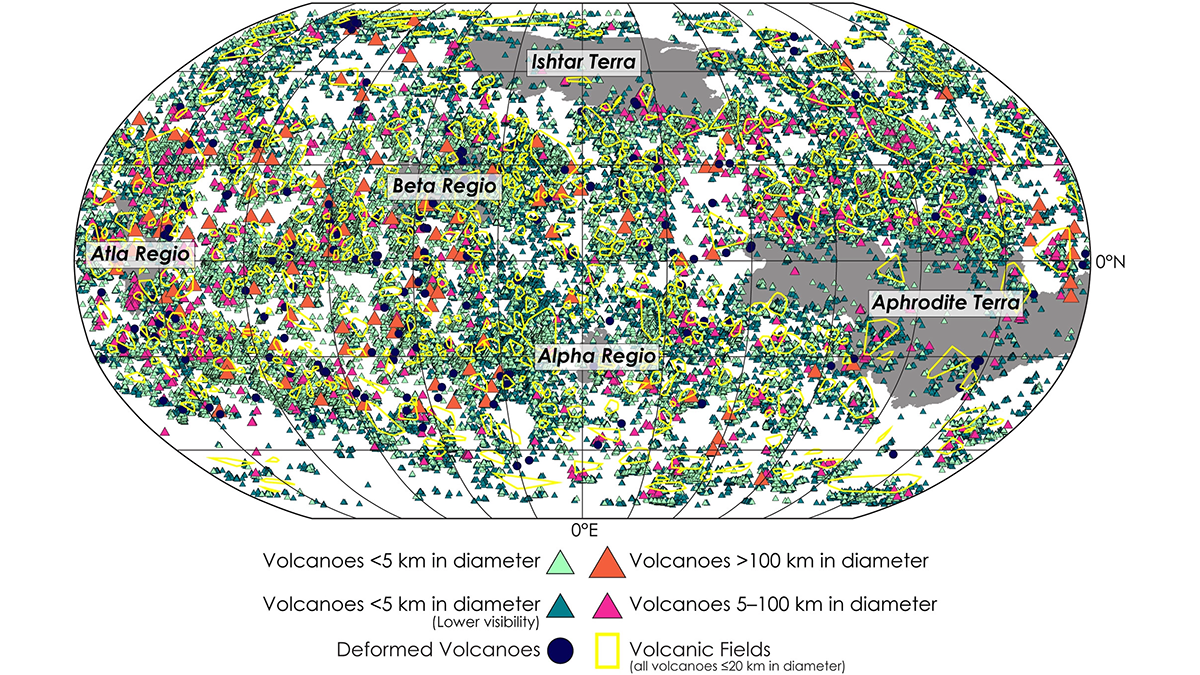
A New View of Volcanism on Venus
Researchers present the most comprehensive catalog of Venusian volcanic edifices to date, providing new knowledge of the geological evolution of a relatively understudied planet.
Machine Learning Helps Researchers Track Illegal Fishing
Using machine learning, researchers found that nearly 20% of high seas fishing could be unauthorized.
The International Reference Ionosphere – A Model Ionosphere
An accurate and reliable description of Earth’s ionosphere is of critical importance because of our increased reliance on satellite technology and the significant impact the ionosphere has on it.
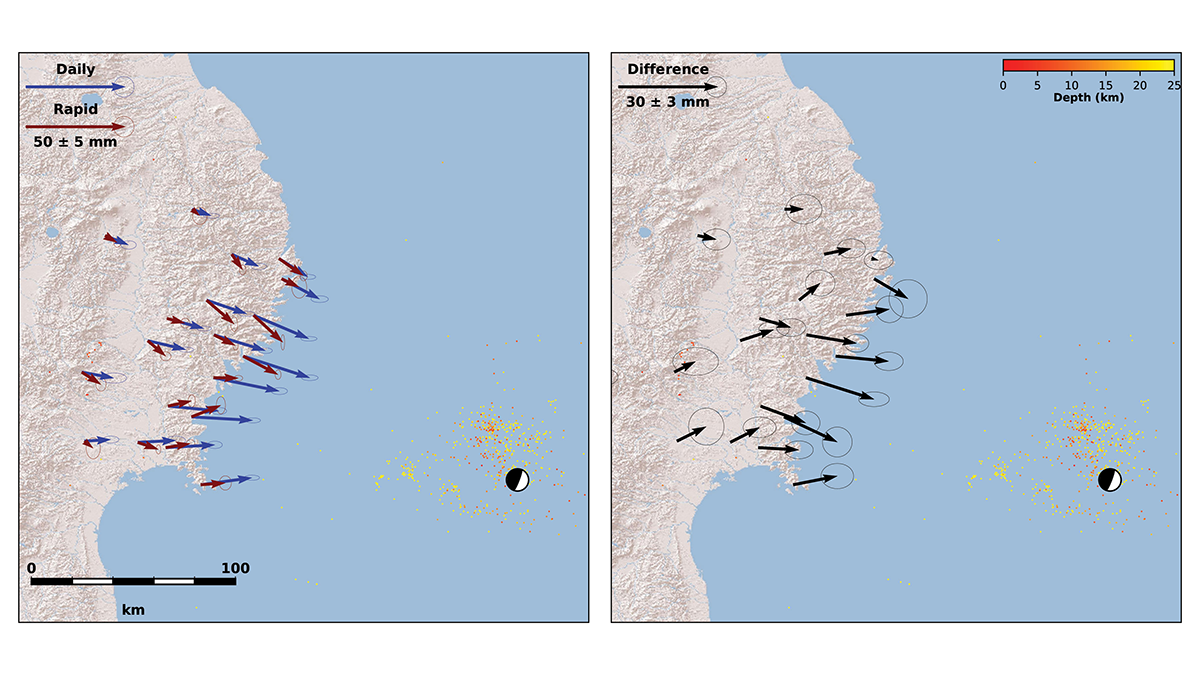
Improving Coseismic Slip Measurements
A physics-based method estimates the duration of earthquakes’ coseismic phase and can help improve the precision of coseismic slip models and magnitude estimates.
A Step Toward Making GPS More Resilient to Space Weather
Researchers have developed a new mathematical model to more accurately capture how irregularities in Earth’s atmosphere interrupt signals from Global Navigation Satellite Systems.
A New Method Produces Improved Surface Strain Rate Maps
The transdimensional Bayesian approach handles GPS data limitations better than existing methods and may assist future seismic hazard assessment studies.
Can Newspaper Reporting Uncover Flood Risk?
In areas of low or no flood monitoring, archival coverage of historical flooding can help scientists make better risk predictions.
Geodetic Data Pinpoint Earthquake-Prone Regions of the Himalayas
GPS measurements of the Indian and Eurasian plates reveal four locked segments most likely to produce large earthquakes.