An international research group recorded the acoustic signatures of gas bubbles rising from a hydrothermal vent field to gather clues about greenhouse gases escaping into the atmosphere.
greenhouse gases
Atlantic Circulation Consistently Tied to Carbon Dioxide
Past ocean surface conditions suggest that over the past 800,000 years, atmospheric carbon dioxide levels typically rose on millennial timescales when Atlantic overturning was weaker and vice versa.
Volcano in Iceland Is One of the Largest Sources of Volcanic CO2
High-precision airborne measurements, in combination with atmospheric modeling, suggest that the Katla subglacial caldera may be one of the planet’s biggest sources of volcanic carbon dioxide.
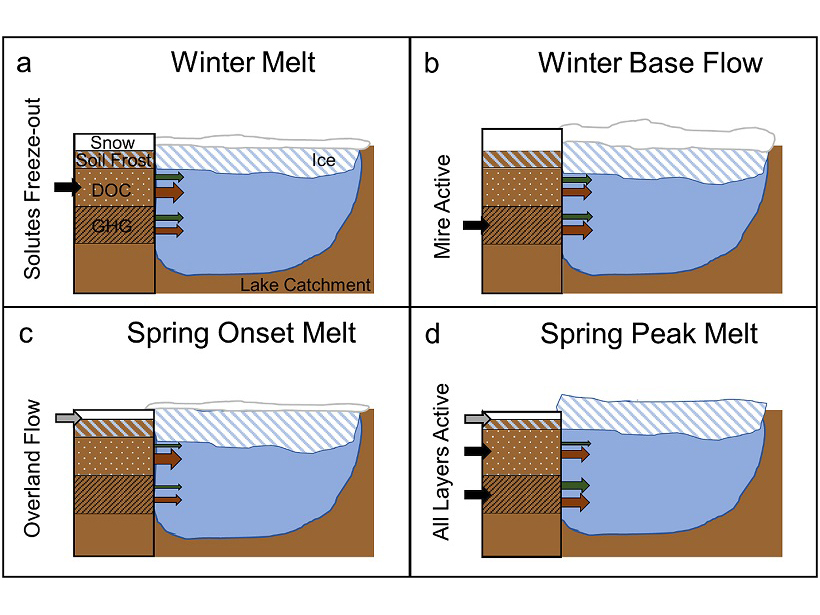
What Lies and Waits Beneath Lake Ice?
Rarely made detailed measurements of carbon dioxide and methane under lake ice reveal a story more complex than simple models of gas buildup, with surprising findings for climate change impacts.
Methane, Climate Change, and Our Uncertain Future
Methane is generally considered secondary to carbon dioxide in its importance to climate change, but what role might methane play in the future if global temperatures continue to rise?
A Benchmark for Trace Greenhouse Gases in the Arctic Ocean
Samples of seawater from the North American Arctic show that the region is neither a major source nor sink of methane and nitrous oxide to the overlying atmosphere.
New Technique Could Help Scientists Track Nitrous Oxide Sources
A long-term study in Switzerland reveals the promise of a new method to determine isotopic composition of the potent greenhouse gas.
High Arctic Emissions of a Strong Greenhouse Gas
Isotope data bring scientists one step closer to revealing the microbial processes behind nitrous oxide emission in the tundra.
EPA Reassesses Feasibility of Plan to Increase Fuel Efficiency
This January, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized mileage standards set in 2012. Now, at the push of the auto industry, EPA and other agencies are going back for another look.
Good Night Sunshine: Geoengineering Solutions to Climate Change?
In order to limit global warming to Paris Agreement goal levels, climate engineering should be considered as a viable solution.