Although the total surface area of Earth’s lakes emits less methane than previously believed, it is still among the largest natural methane sources.
greenhouse gases
Explaining Uncertainty in Estimates of Rain Response to Warming
Humidity increases with warming. Theory and observations about how increased humidity translates into more extreme rainfall can be reconciled if attention is paid to data and methods.
Cuantificando los beneficios para la salud de una transición a energías limpias en EE. UU.
Eliminar la contaminación del aire relacionada con la energía en los Estados Unidos podría evitar aproximadamente 50,000 muertes prematuras y ahorrar miles de millones de dólares al año.
Quantifying the Health Benefits of a U.S. Clean Energy Transition
Eliminating energy-related air pollution in the United States could prevent roughly 50,000 premature deaths and save billions of dollars per year.
Greenhouse Gases Must Begin to Fall by 2025, Says U.N. Climate Report
Emissions rates are still growing every year, though that growth has slowed. The world needs to reach negative growth soon to prevent a potential 3.2°C rise by the end of the century.
U.S. Businesses May Be Required to Report Emissions, Climate Risk
The proposed rules seek to give investors more complete and standardized climate risk information. The move would bring U.S. policy closer to international standards.
The Surprising Greenhouse Gas That Caused Volcanic Summer
Extended periods of volcanism known as flood basalt eruptions lead to volcanic winters, which are often followed by an extended period of warming. But it was more than just carbon dioxide that warmed the globe.
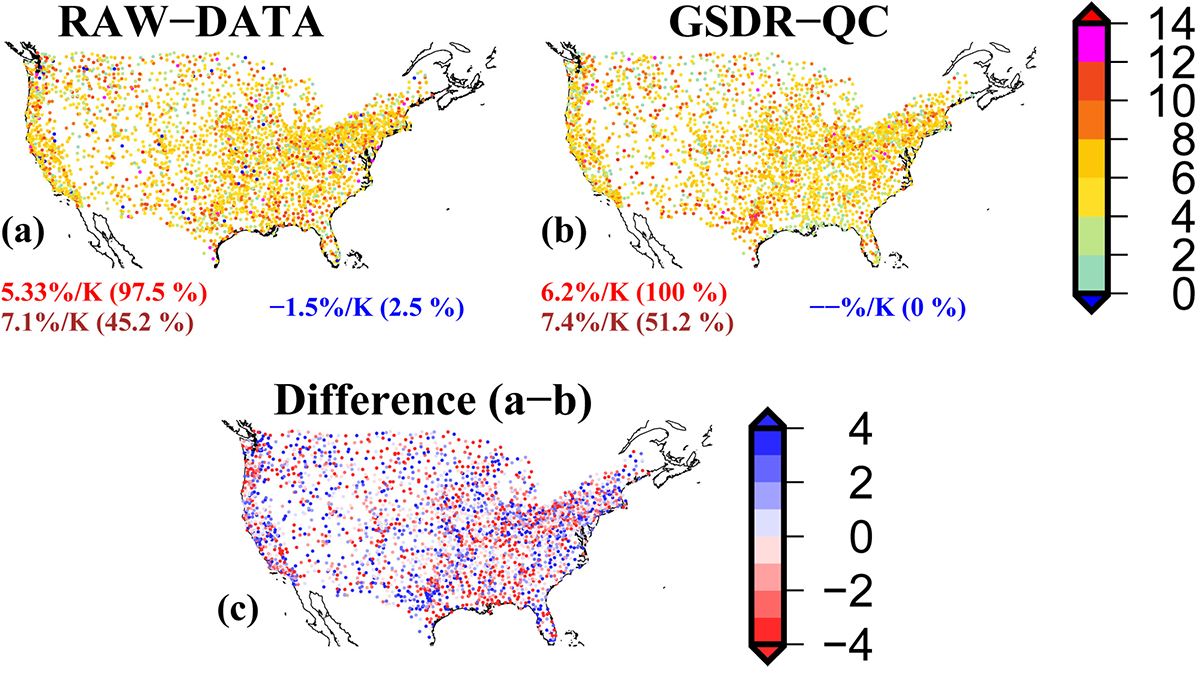
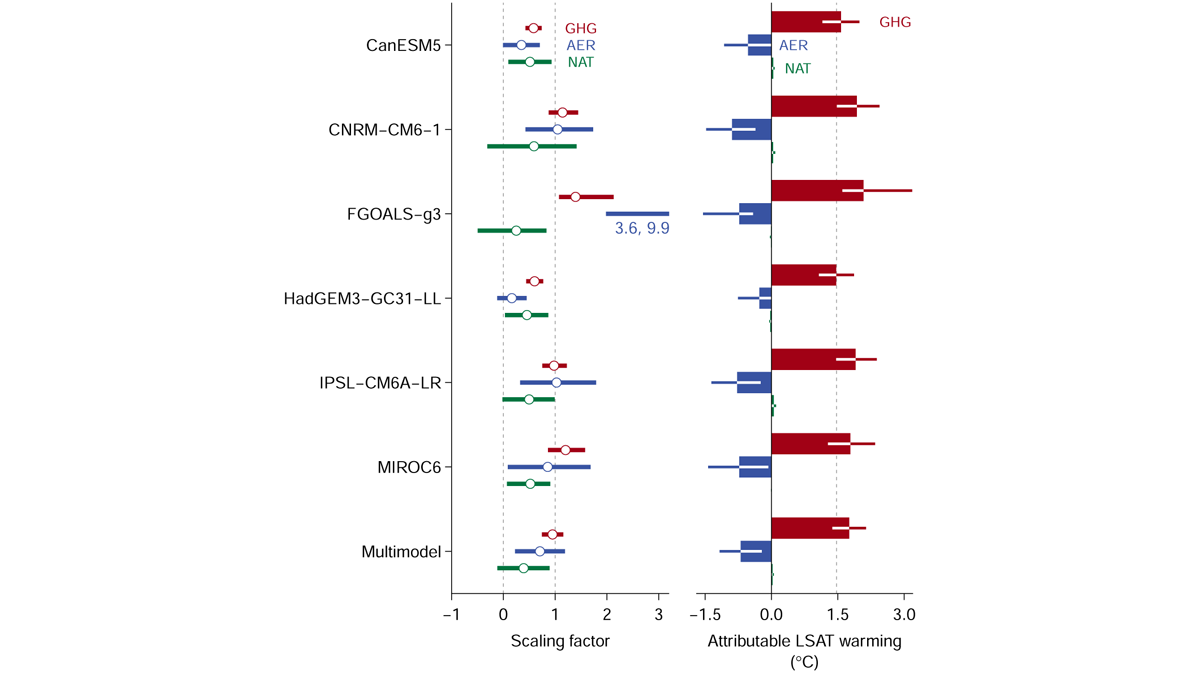
Framework for Fingerprinting Human Influence on Climate
An optimal approach for detection and attribution studies using the CMIP6 Detection and Attribution Model Intercomparison Project (DAMIP).
Inventorying Earth’s Land and Ocean Greenhouse Gases
A new special collection in AGU journals will present findings from the Second REgional Carbon Cycle Assessment and Processes (RECCAP2) study with a decade of data on greenhouse gas growth.
Termite Fumigation in California Is Fueling the Rise of a Rare Greenhouse Gas
The insecticide sulfuryl fluoride isn’t included in federal or state emissions reduction goals.