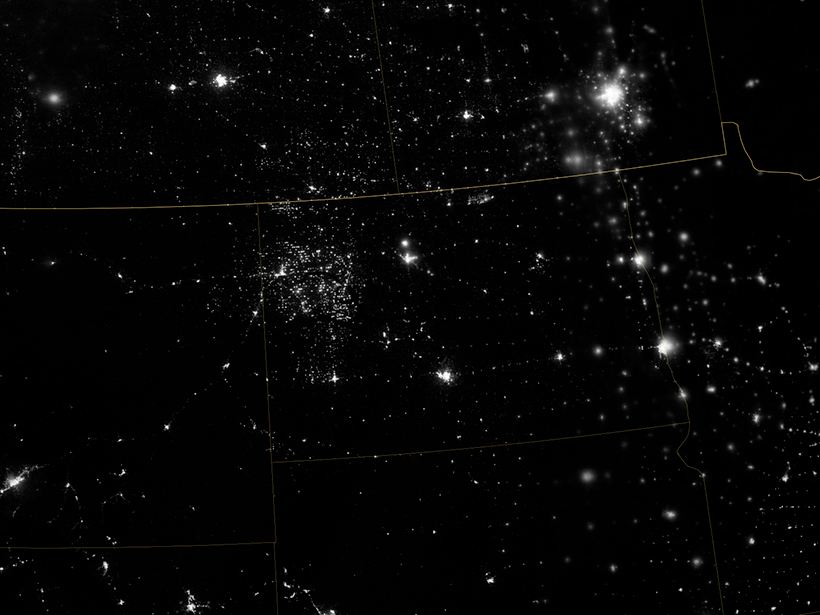
A new storm-following tool continually watches for lightning over the open ocean. Combined with satellite microwave data, the new real-time observations will improve forecasts of tropical cyclones.
Hazards & Disasters
The Challenges of Drought Prediction
Advances in dynamical modeling and the use of hybrid methods have improved drought prediction, but challenges still remain to improve the accuracy of drought forecasting.
California’s Water Savings Dwindle When Drought Fears Subside
Policy changes and media attention affect how much water Californians use, as well as how long these behaviors prevail. Could public awareness shift behaviors toward long-term conservation?
More Earthquakes May Be the Result of Fracking Than We Thought
Scientists show small earthquakes caused by fracking near Guy-Greenbrier, Ark., in 2010 that could have been early indicators of high stress levels on larger faults deeper underground.
Exploring How Space Weather Can Damage Power Grids
A new model of geomagnetically induced currents revisits how space weather damaged a New Zealand grid transformer in 2001, and shows how much worse it could be in a space weather superstorm.
Damage Assessment by Laser Could Focus Postearthquake Response
Airborne lidar surveys taken before and after a powerful 2016 earthquake in Japan revealed the potential for such surveys to identify hard-hit buildings quickly.
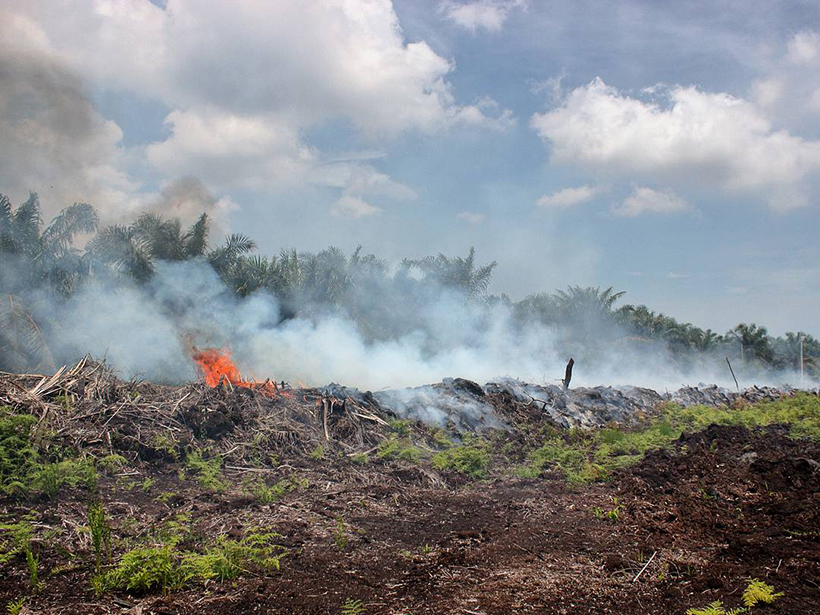
Measuring Emissions from Smoldering Peat Fires
A new study measures emission factors for tropical peatland fires in Malaysia.
A New Massive Open Online Course on Natural Disasters
Two professors put their college course online. Enrollment jumped more than 20-fold, and a forum for exchanging ideas with a multigenerational international community was born.
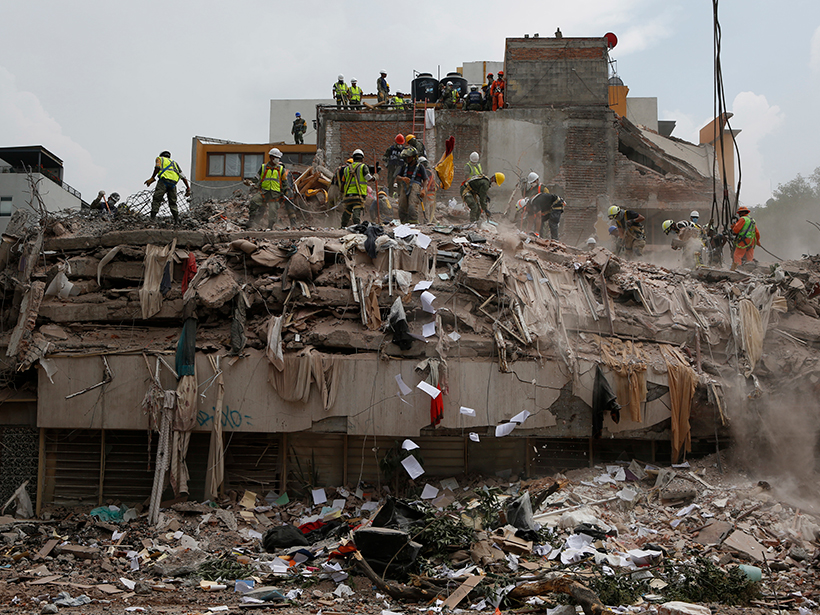
Were Mexico’s September Quakes Chance or a Chain Reaction?
Last year, two major earthquakes—one 12 days after the first—shook Mexico. New analysis blames this very unlikely event on chance. But one of the pair may have triggered a third large nearby temblor.
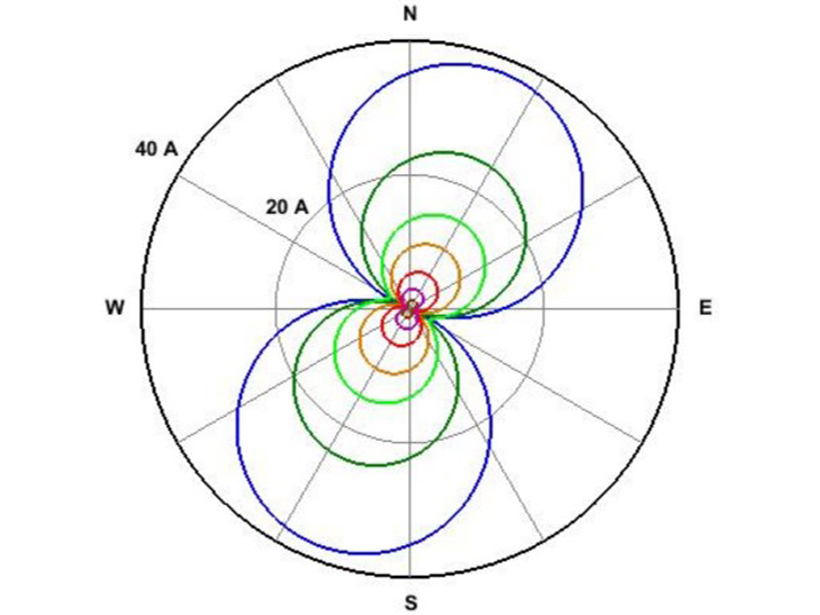
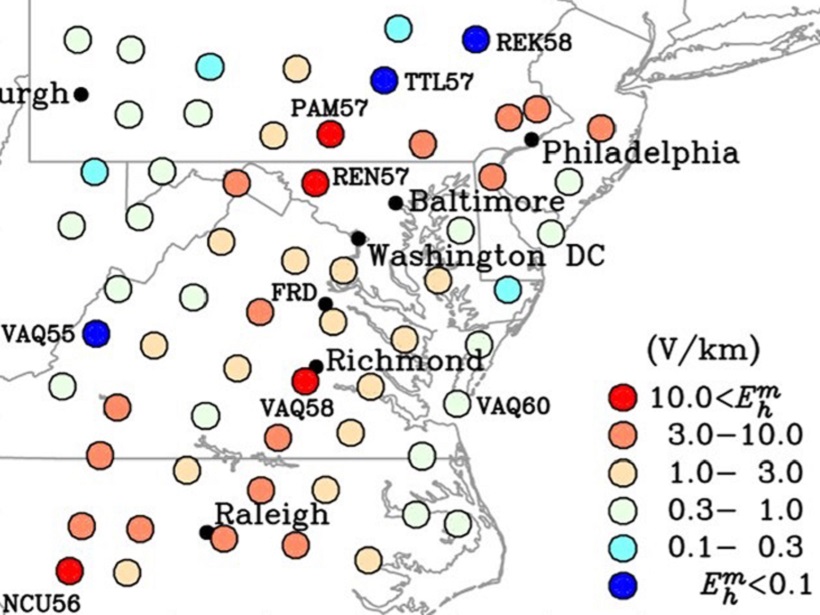
Mapping Extreme-Value Geoelectric Fields
To help mitigate magnetic storm interference on electric power grid operations, extreme-value geoelectric fields have been mapped across the mid-Atlantic United States.