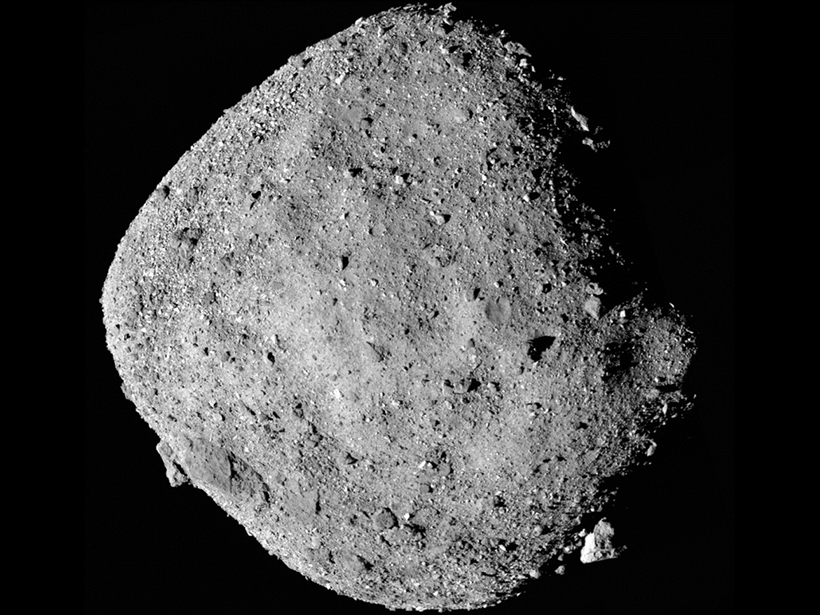
Hydrated minerals on near-Earth asteroids offer both scientific revelations and economic incentives for companies looking to refuel satellites with material from nearby space.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
How Long Can Celestial Bodies Retain Ice?
A new model suggests that many objects in the outer asteroid belt may still harbor deposits that formed around the time of their accretion.
New Hints About How Martian Moons Formed
A new study finds that Phobos includes chunks of Martian crust.
Researchers Bring Early Martian Water Chemistry to Life
Lab experiments constrain conditions necessary for a key mineral to have formed in ancient lagoons and a crater lake.
New Analysis Provides a Fresh View of the Atmosphere on Venus
Researchers apply a radio holographic method to standard Venusian atmospheric data, resulting in outputs with finer vertical resolution and revealing small-scale atmospheric structures.
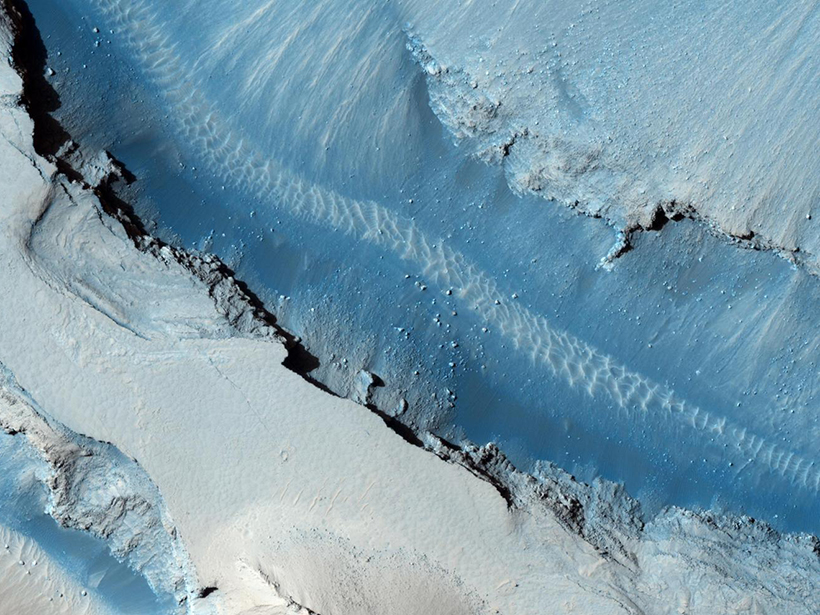
Searching for Signs of Marsquakes
Researchers use high-resolution images of Mars’s surface to look for signals of coseismic displacement.
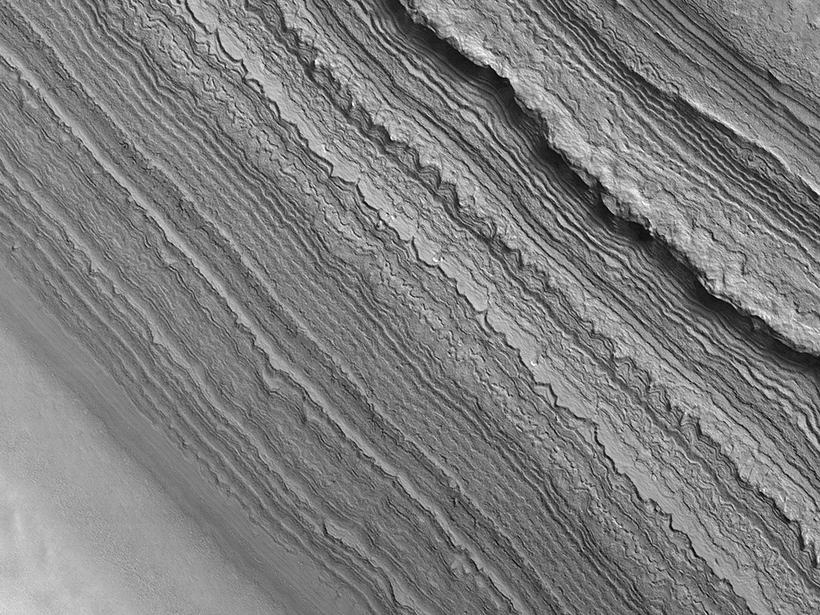
Evidence of Regional Deposition in Mars’s South Polar Deposits
Shallow Radar correlation of discrete units in one of the Red Planet’s largest ice reservoirs suggests that its material was emplaced as a single, regional deposit.
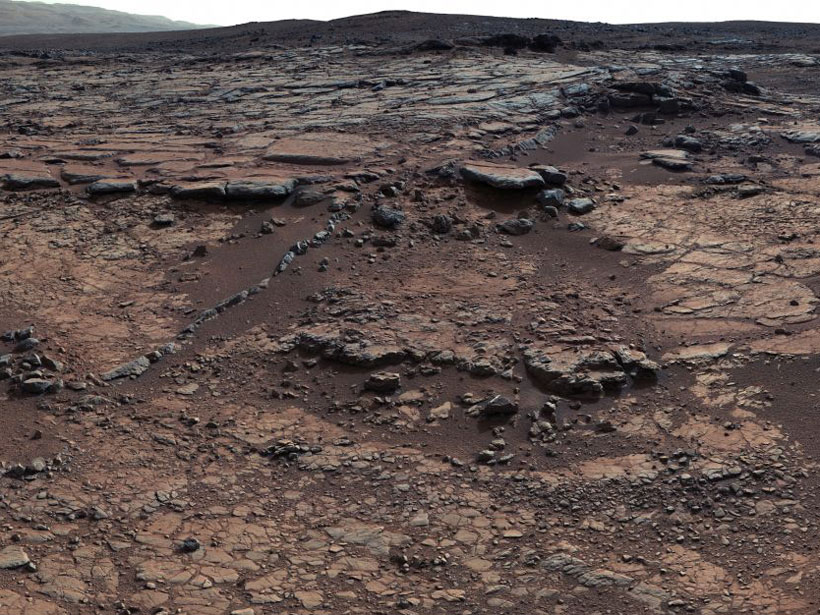
Is Mars Not So Earthlike After All?
Light-colored Gale crater rocks could have formed from intraplate volcanoes, not continental crust, new study finds.
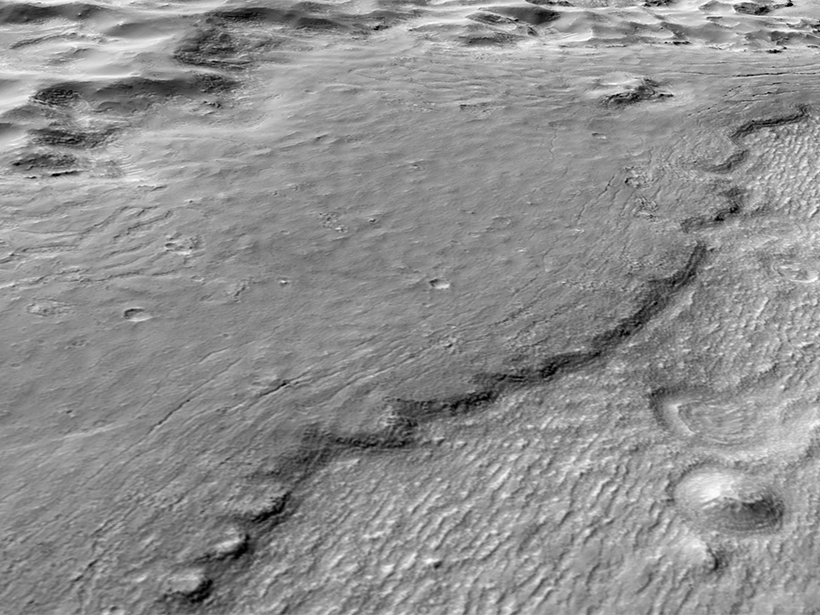
Tracing the Steps of Hydrothermal Activity in Hrad Vallis, Mars
Conditions that formed Amazonian age valleys may have been hospitable to microbial life.
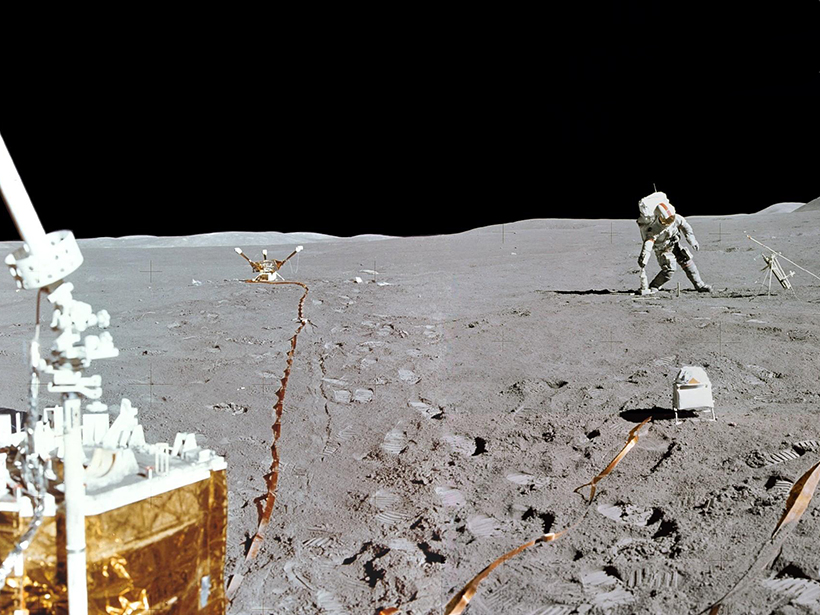
The Case of the Missing Lunar Heat Flow Data Is Finally Solved
Decades-old data analyzed for the first time suggest that astronauts’ disturbance of the Moon surface increased solar heat intake, warming the ground below.