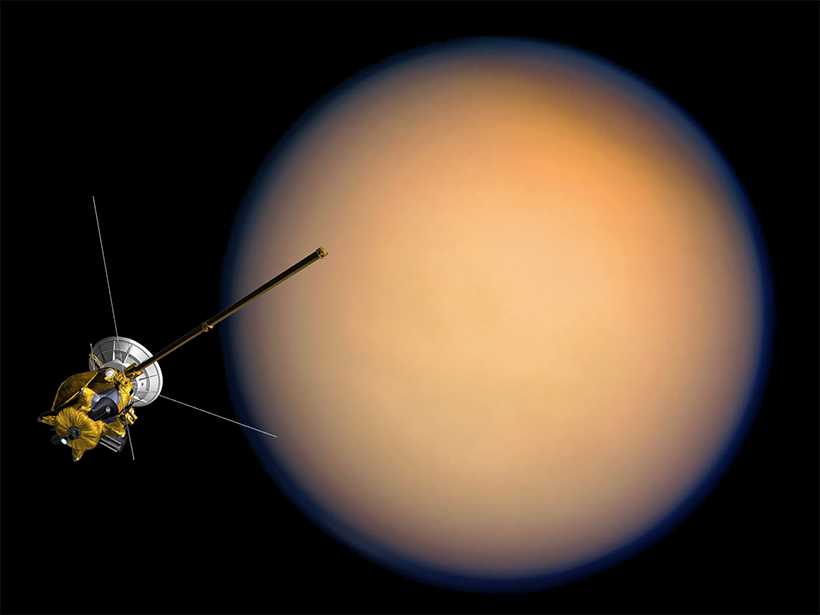
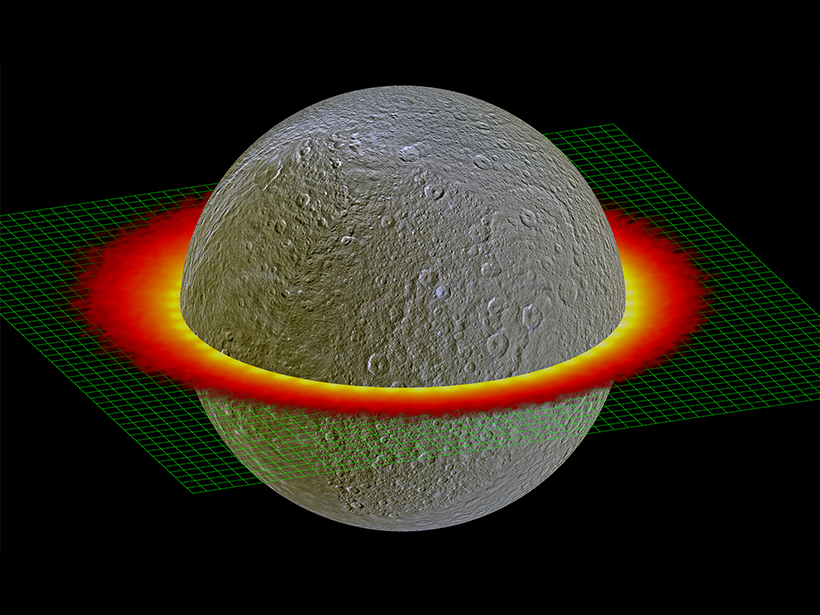
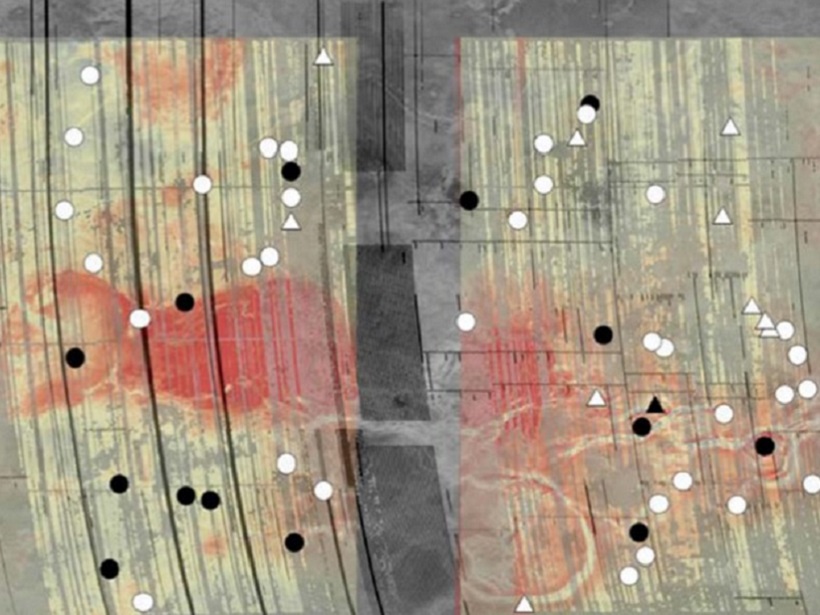
Variations in grain size and water ice content detected on Saturn’s largest moon offer evidence of geologically related units that resemble the mountain-to-desert transition on Earth.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
How Did Venus Get its Youthful Surface?
Catastrophic lithospheric recycling is unlikely to be the cause of Venus’s young surface from mantle convection models constrained by offset between the center of mass and center of shape of planet.
A Consistent Model of Ice Dissociation on Celestial Bodies
A model based on decades of experimental results can now quantify the products of water ice dissociation caused by radiation and predict the products expelled into an icy body’s outer atmosphere.
Evidence of Extensive Ice Deposits Near Mercury’s South Pole
New radar observations and refined illumination maps reveal uneven water ice deposits twice the size of those found around the planet’s north pole, suggesting the source may be a recent comet impact.
Elevated Heat Flow at Coronae on Venus
Enigmatic surface features on Venus called coronae are important for how Venus loses heat, and measurement of surface flexing around these features indicates higher heat flows than on Earth.
Moon’s Magnetic Field May Magnetize Iron That Hits Its Surface
Scientists are using satellite data to study large impact basins on the surface of the Moon that contain magnetic anomalies.
Earth-like Oscillations Detected in Saturn’s Stratosphere
By comparing Cassini observations spanning ten years, Saturn’s equatorial oscillation is shown to have similarities to Earth’s Quasi-Biennial Oscillation and Semi-Annual Oscillation.
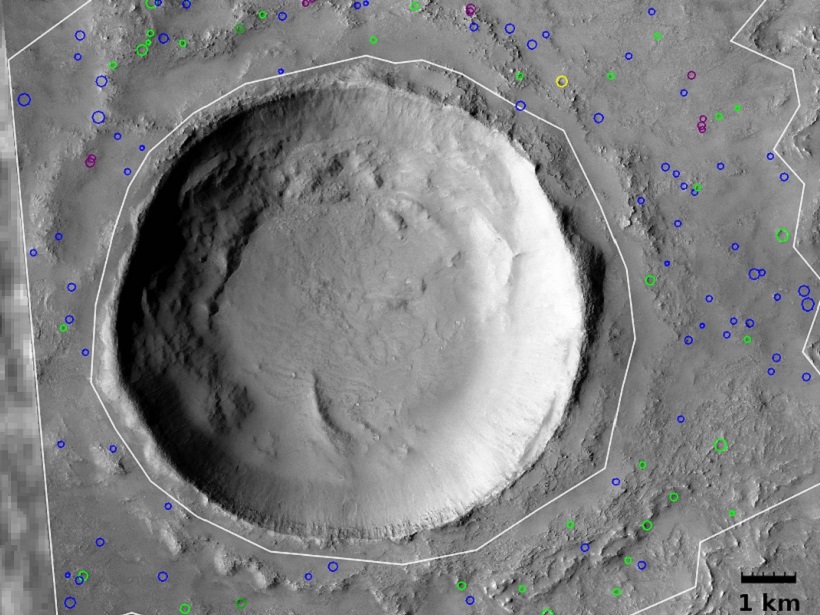
Long Term Preservation of Subsurface Ice on Mars
Layered-ejecta craters on Mars that are associated with impacts into rock mixed with volatiles have been formed throughout the planet’s history indicating the long-term preservation of subsurface ice.
History of Water on Mars’s Surface Is Longer Than We Thought
Curiosity’s two-step heating experiment of mudstone at Gale crater reveals minerals that formed in the presence of water less than 3 billion years ago.
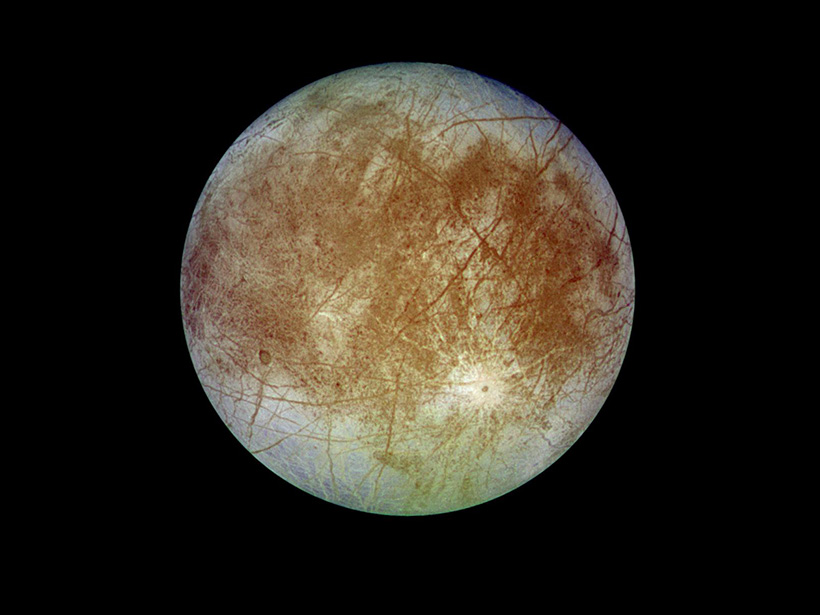
Seeking Salt That Surfaces from Europa’s Hidden Ocean
Irradiation-induced color changes in sodium chloride could reveal whether it came from ocean water mixing with surface water, a key component of the moon’s potential to support life.