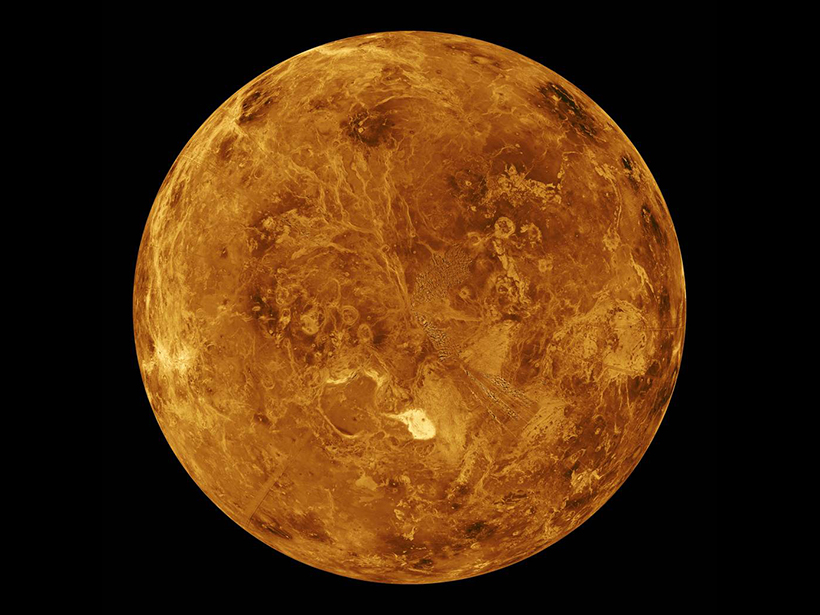
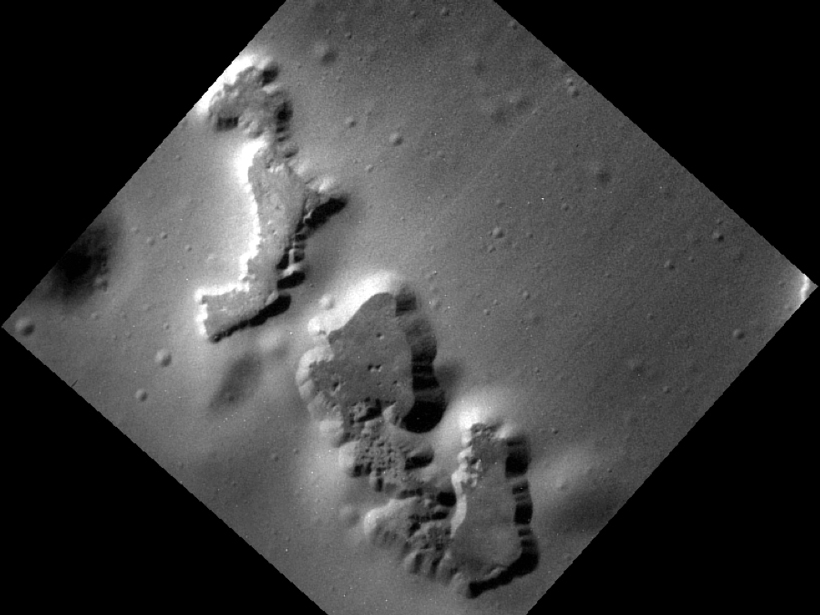
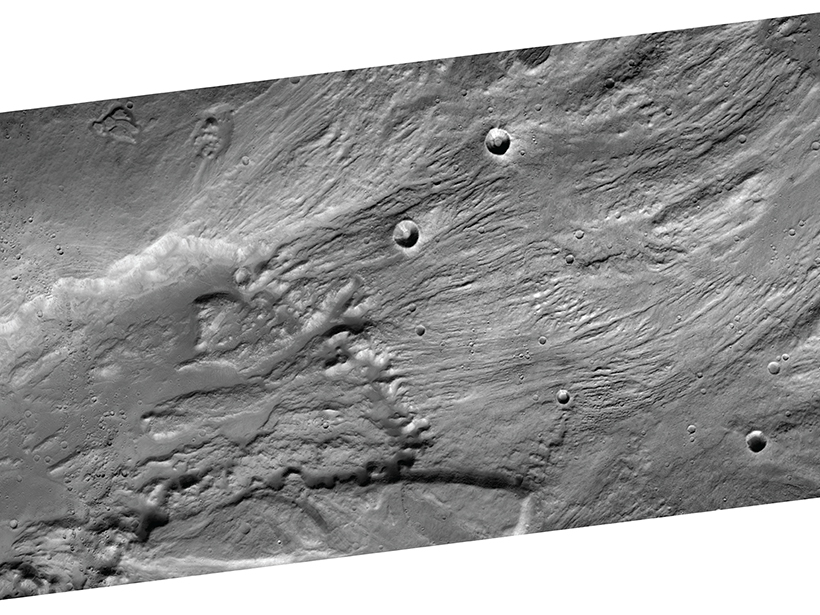
Matching Martian rock formations to those found on Earth can help researchers learn more about the Red Planet.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
Martian Mantle Models Pave the Way for NASA's InSight Lander
The most detailed simulations to date of how heat flows through Mars's interior are good news for the upcoming lander and will help scientists interpret its data.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets Celebrates 25 Years
Two editors look at the past, present, and future of the American Geophysical Union's planetary science journal.
Unprecedented Views of Mercury Constrain Hollow Formation
The consistently shallow depths of the depressions scattered across Mercury's surface suggest their morphology is not determined by the thickness of a volatile-rich outer layer.
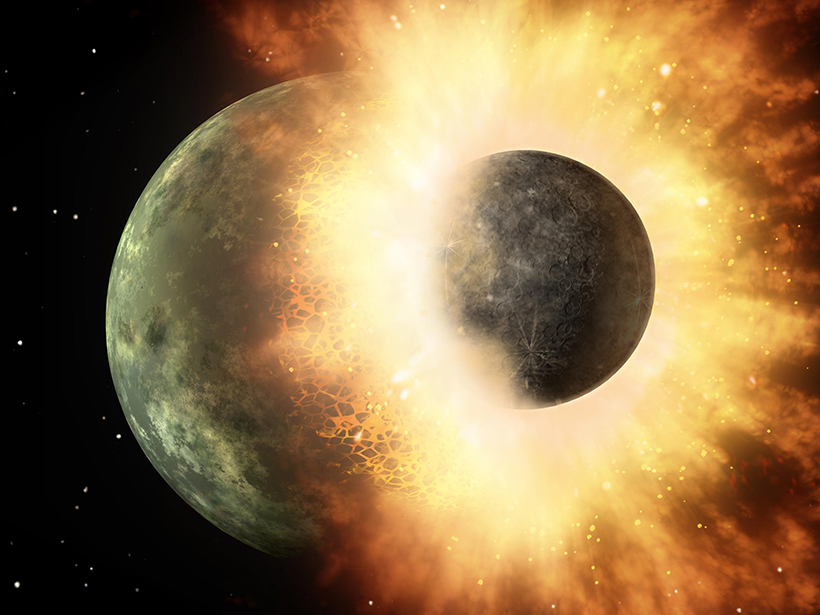
New Insight into Silica Explains Planetary Smashup
A better equation of state for silica will help planetary scientists accurately constrain the giant impacts that have shaped our solar system.
Mars’s Climate May Have Been Wet Much Later Than Thought
Water-carved valleys may be relatively young, challenging assumptions about the history of the Red Planet's climate.
Reconstructing Catastrophic Floods on Earth and Mars
A new theoretical model suggests that ancient floods that carved canyons on Earth and Mars may have been much smaller but lasted longer than previously thought.
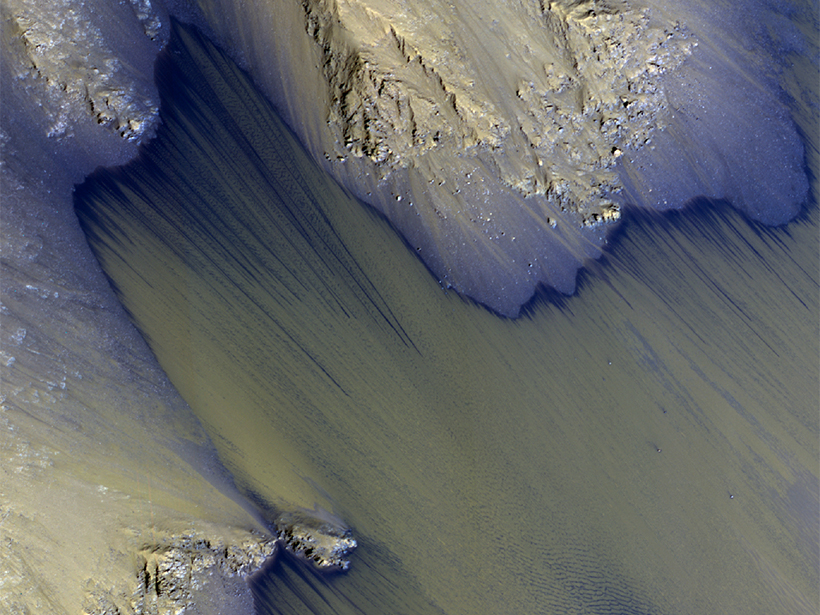
A Cluster of Water Seeps on Mars?
The discovery of dense concentrations of recurring flowlike features in two Valles Marineris chasms could aid in the search for life and influence future exploration of the Red Planet.
Carbon Dioxide Frost May Keep Martian Soil Dusty
Temperature readings acquired from orbit show that Mars's surface gets cold enough at night to allow layers of solid carbon dioxide frost up to several hundred micrometers thick to build up near the equator.
Curiosity Sends Curious Water Data from Mars
The rover's neutron spectroscopy instrument hints at an unexpected trend: The upper soil levels in the layers of Gale Crater's Kimberley formation seem to hold more water-associated hydrogen.