A new special issue of JGR: Planets presents findings on sand motion, morphology, and mineralogy from the Curiosity rover’s traverse of the active Bagnold dune field in Gale crater.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
Choosing a Lunar Landing Site
A recent article in JGR: Planets described the geological characteristics of two candidate sites for the upcoming Chinese mission to the Moon.
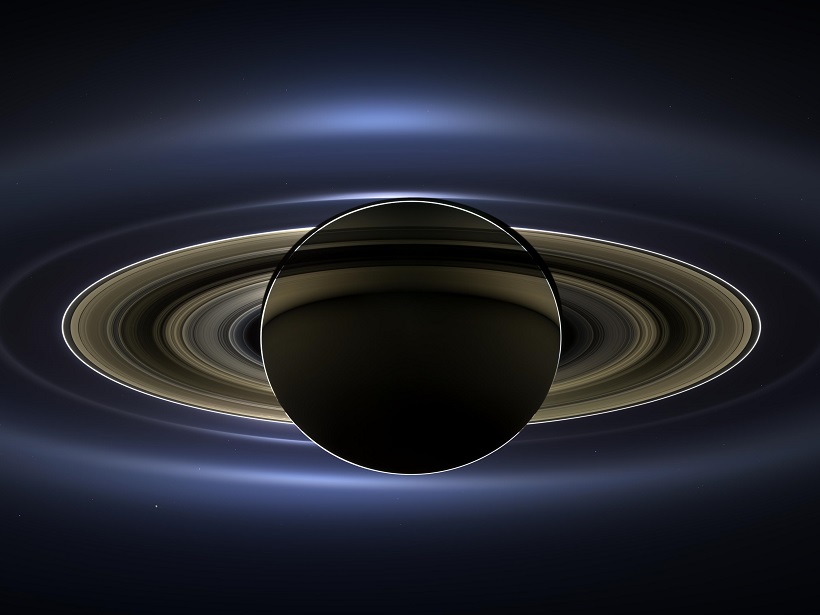
Cassini’s Legacy in Print
With over 750 papers published in AGU journals based on Cassini-Huygens mission data, three editors select some of the most noteworthy.
Where Are the Electrical Currents in the Enceladus Plume?
A plume of water ice that escapes Saturn’s moon Enceladus should be coursing with electrical currents, but data are mixed. Now simulations suggest that a sticky dust cloud may shield signals.
Time, Tides, and Wandering Poles
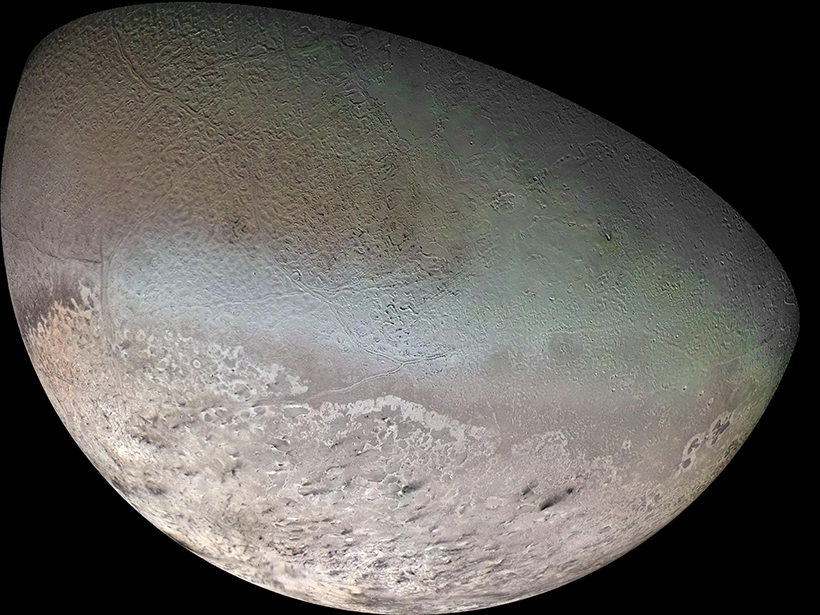
Models of Neptune’s moon Triton reveal curious behavior in how tidal forces and mass anomalies cause the poles to reorient their location.
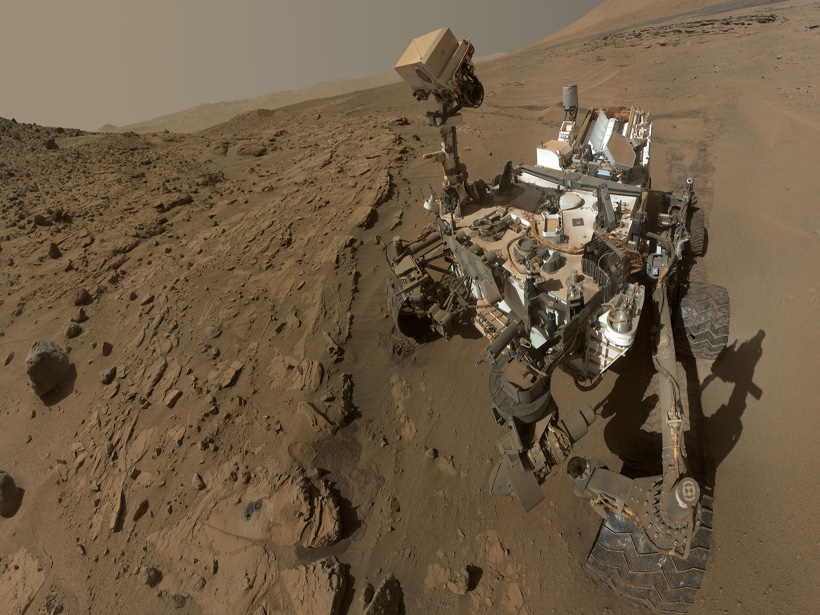
Curiosity Spies Shifting Sands on Mars
Images from the rover’s pioneering encounter with sand dunes on Mars constrain wind speeds required to move sand in the thin Martian atmosphere.
Lab Tests Probe Carbon Planets’ Inner Dynamics
Thermal convection in deep interiors could be more vigorous in carbide planets than in comparably sized silicate planets, according to new high-pressure measurements of silicon carbide.
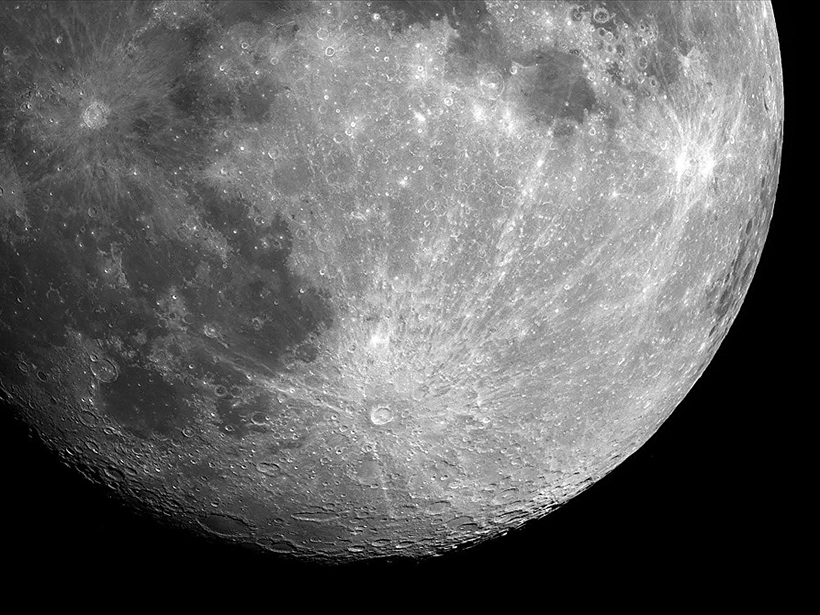
Meteorites Mix Moon’s Surface at Both Small and Large Scales
A three-dimensional model of material transport suggests that impact cratering can mix lunar soils across distances of more than 100 kilometers.
Ancient Impact May Have Triggered Long-Term Volcanic Eruptions
Scientists revisit Canada’s Sudbury crater in light of new evidence from other planets that suggests an alternative postimpact history.
Insights into the Habitability of Mars
NASA’s Curiosity rover explored the Kimberley region of Mars to search for signs that the planet was once habitable.