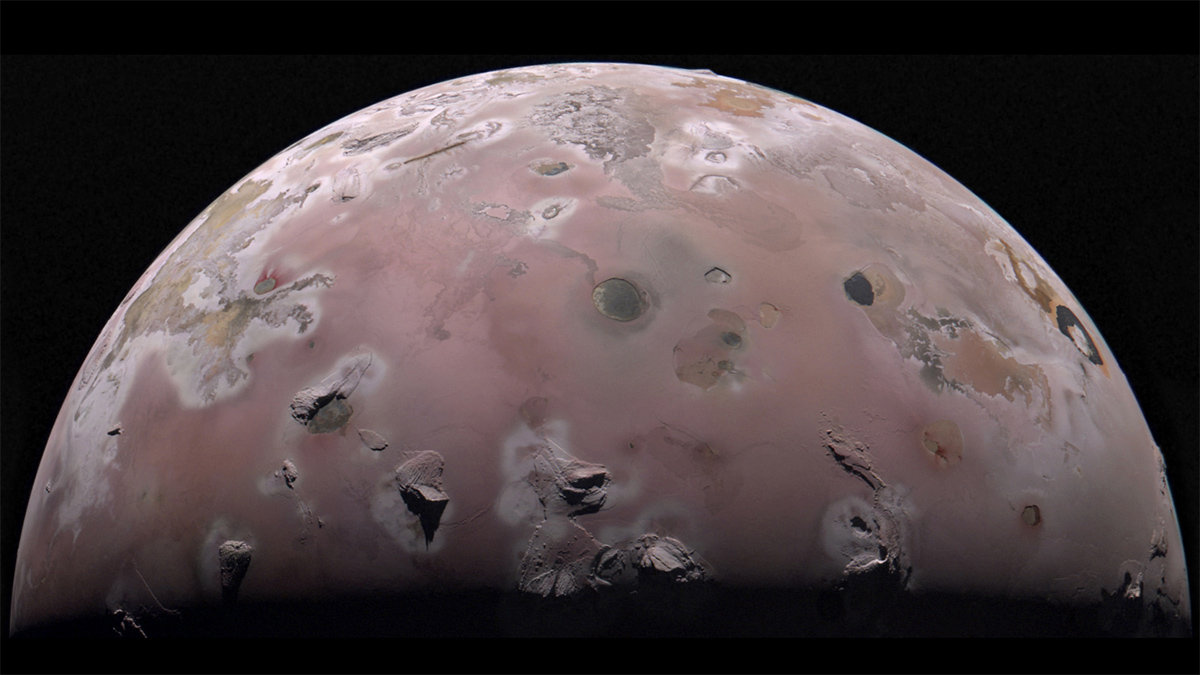
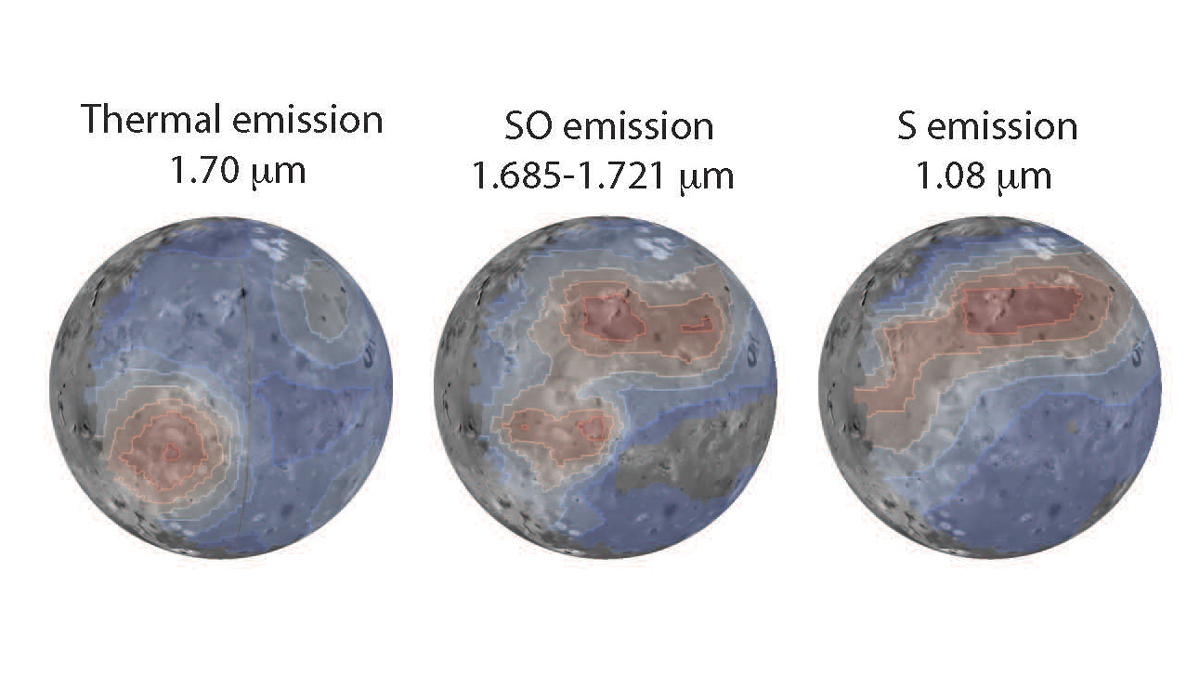
New James Webb Space Telescope images reveal cooling lava, volcanic sulfur monoxide gas, and sulfur gas emissions created by interactions between plasma and the moon’s atmosphere.
Jupiter
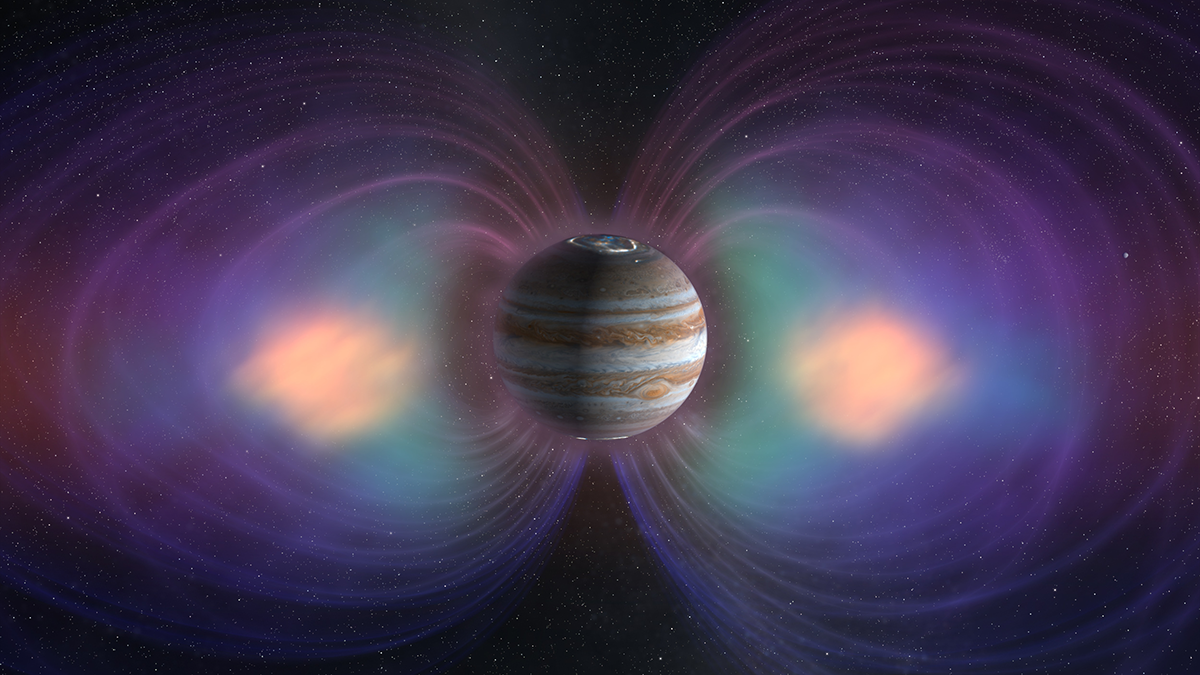
A Solar Wind Squeeze May Have Strengthened Jovian Aurorae
Juno spacecraft data suggest an extreme compression of the planet’s magnetosphere in December 2022, caused by the solar wind, briefly brightened the ultraviolet light displays.
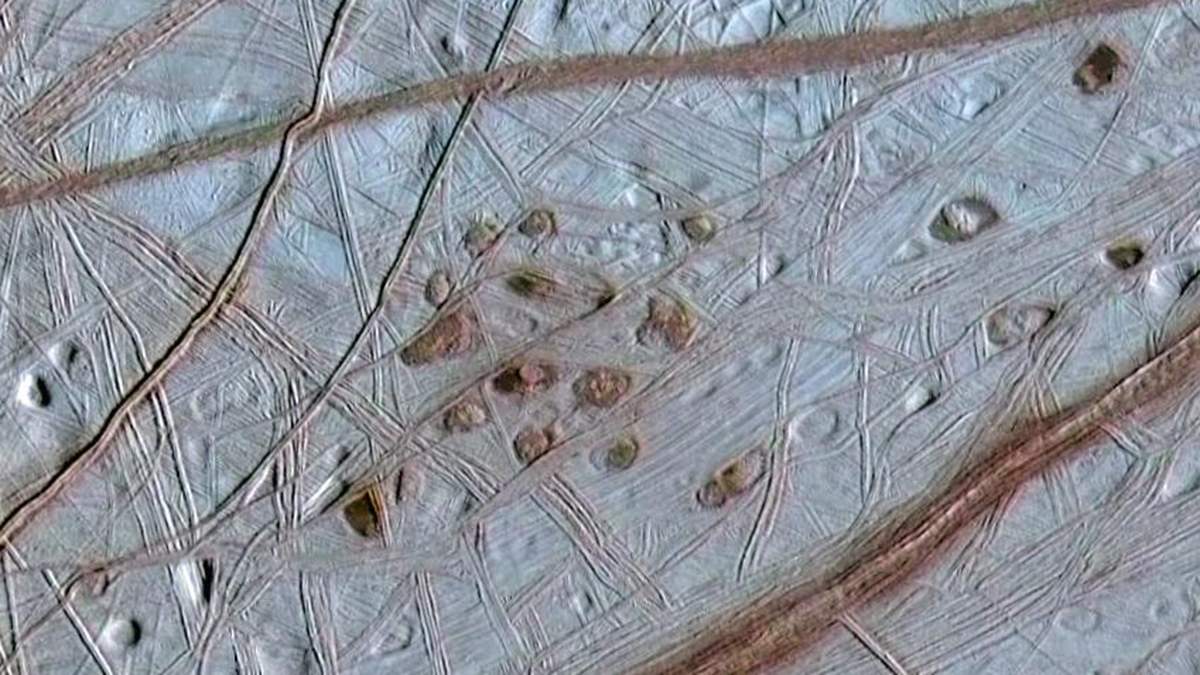
What Goes Up Must Come Down: Movement of Water in Europa’s Crust
Using Earth’s glaciers as an analog, a new study explores the possibility of downward propagation of fractures and melt in Europa’s icy crust.
Jupiter’s Moon Callisto Is Very Likely an Ocean World
A closer look at previously disregarded observations reveals stronger evidence that a deep ocean lies beneath Callisto’s icy surface.
Io Probably Doesn’t Have a Global Magma Ocean After All
Data from the Juno spacecraft may have answered a decades-old question about Jupiter’s moon.
Clipper Sets Sail for an Ocean Millions of Miles Away
Europa Clipper will assess whether Jupiter’s moon has the right ingredients to host life, and could illuminate the mysteries of icy worlds throughout the solar system.
All Eyes on Jupiter
Astronomers hope amateur enthusiasts will help them monitor Jovian weather.
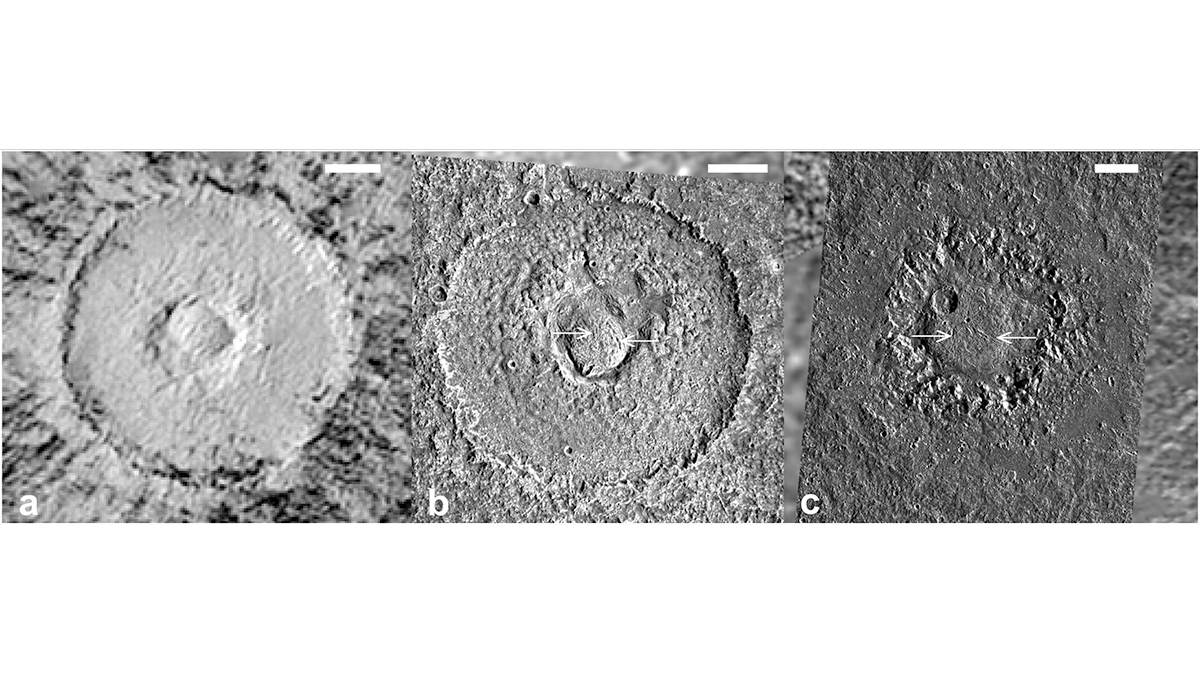
Unveiling the Origins of Dome Craters on Ganymede and Callisto
Large craters with broad central domes are a unique crater morphology on Jupiter’s largest icy moons: Ganymede and Callisto. A new study examines how remnant impact heat may lead to their formation.
Supersharp Images Reveal Scars of Major Eruption on Io
Jupiter’s volcanic moon is captured in exquisite detail by an instrument atop a mountain in Arizona.