Extrapolation or not? Big data may help deep learning to go places where it has not been before by transferring learned hydrologic relationships.
machine learning & AI
How Quantum Computing Can Tackle Climate and Energy Challenges
The day is coming when quantum computers, once the stuff of science fiction, will help scientists solve complex, real-world problems that are proving intractable to classical computing.
Satellites Get First Full-Year View of Arctic Sea Ice Thickness
The AI-based monitoring method may unlock data that could improve shipping safety and climate predictions.
Tracking Climate Through Ship Exhaust
International regulations have reduced aerosol pollutants released from ships. Now, researchers want to use ship tracks to better understand the ambiguous effects that cleaner air has on climate.
Quantifying Changes in Midlatitude Subseasonal Prediction Skill
The differences between future and present subseasonal predictability in the Northern Hemisphere provided by the tropics are evaluated using neural networks.
Monitoring the Health of Our Planet using Earth Observations
A new book explores how Earth science knowledge addresses critical global challenges including sustainable development, disaster risk reduction, and climate change.
New Landslide Reporting Tool Uses Social Media and AI
The tool extracts landslide information in real time, which could advance landslide research as well as disaster response.
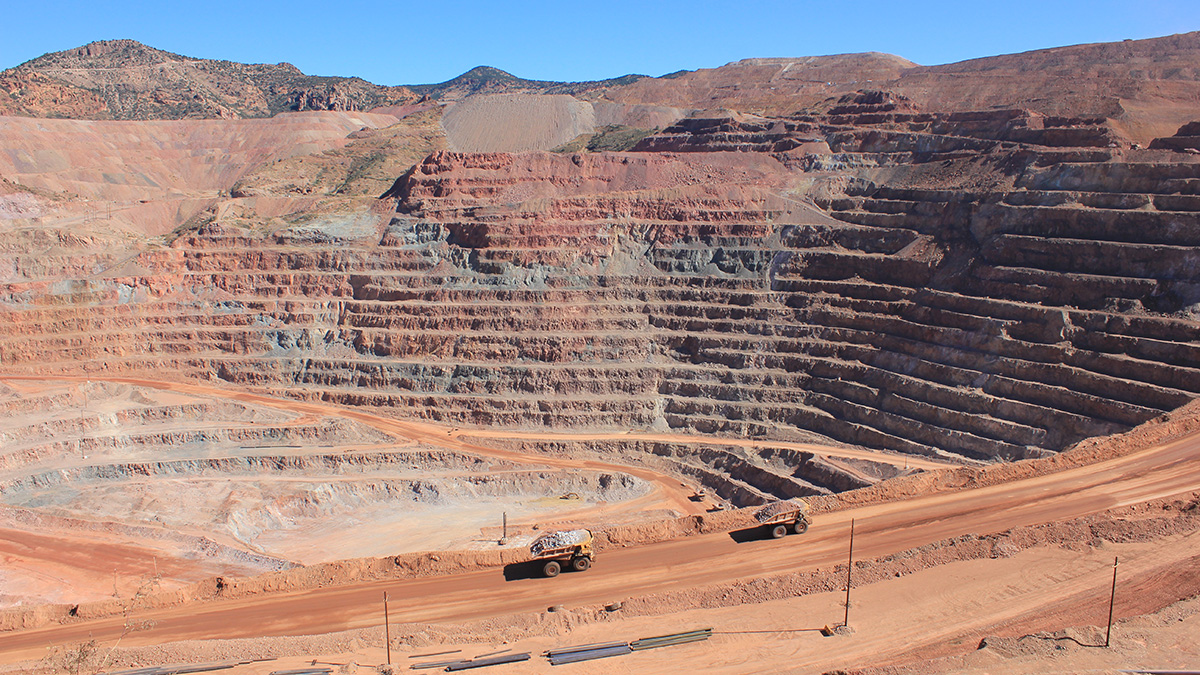
Machine Learning Could Revolutionize Mineral Exploration
Using a global data set of zircon trace elements, new research demonstrates the power of machine learning algorithms to accurately identify and locate porphyry copper deposits.
11 Discoveries Awaiting Us at Solar Max
Each solar cycle might seem like the same old story, but one thing has changed significantly since the previous solar maximum–our technology.
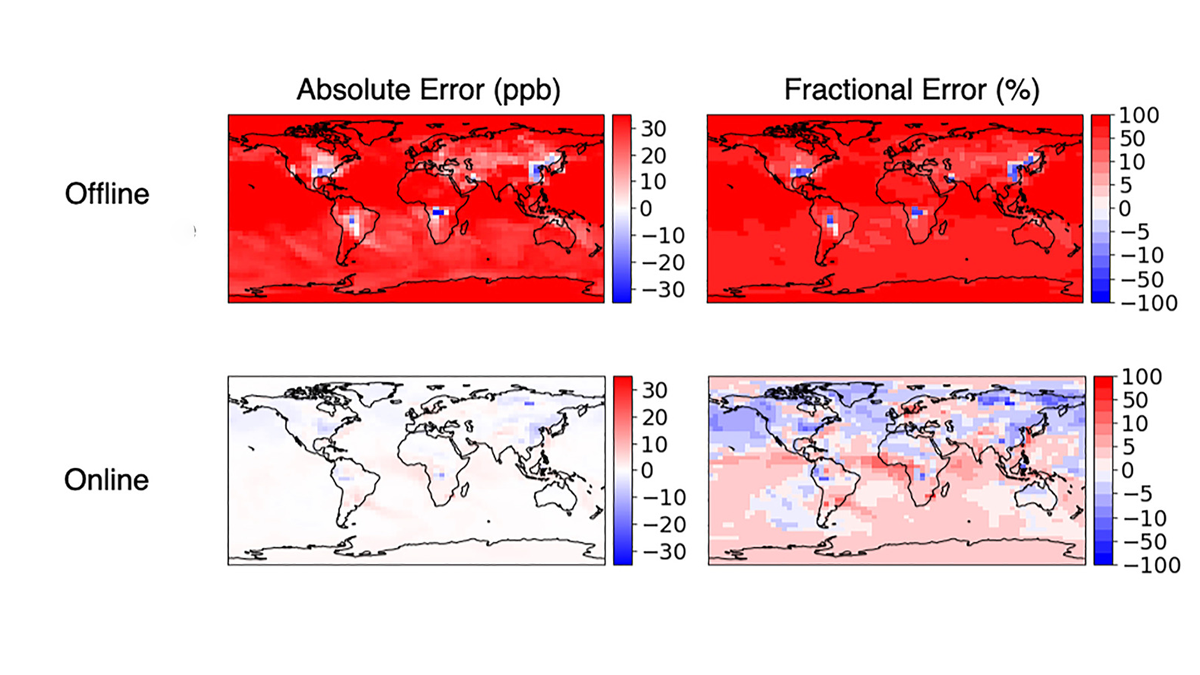
Accurate and Fast Emulation With Online Machine-Learning
Online training produces more accurate and stable machine-learned models than classic offline learning from big data sets.