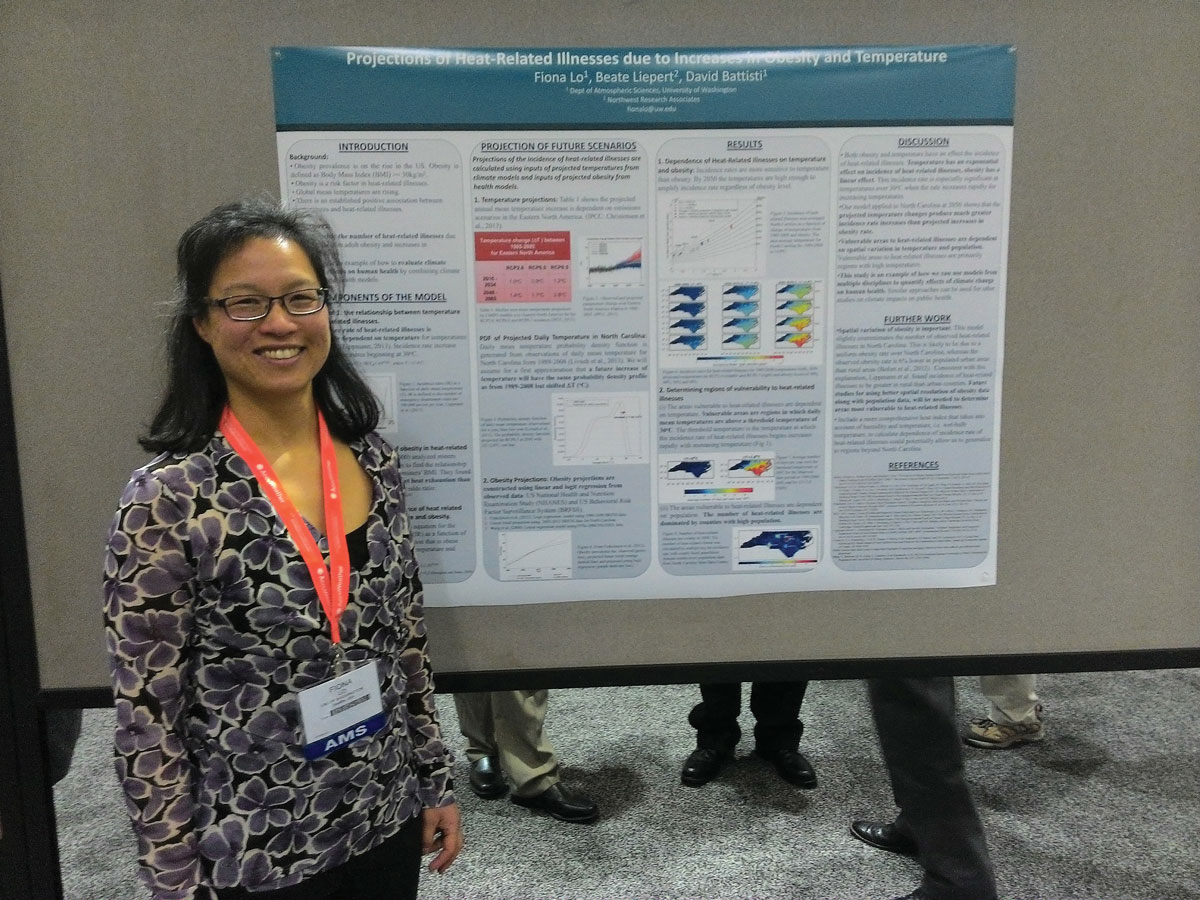
Lo uses her background in atmospheric sciences to forecast pollen concentrations.
machine learning & AI
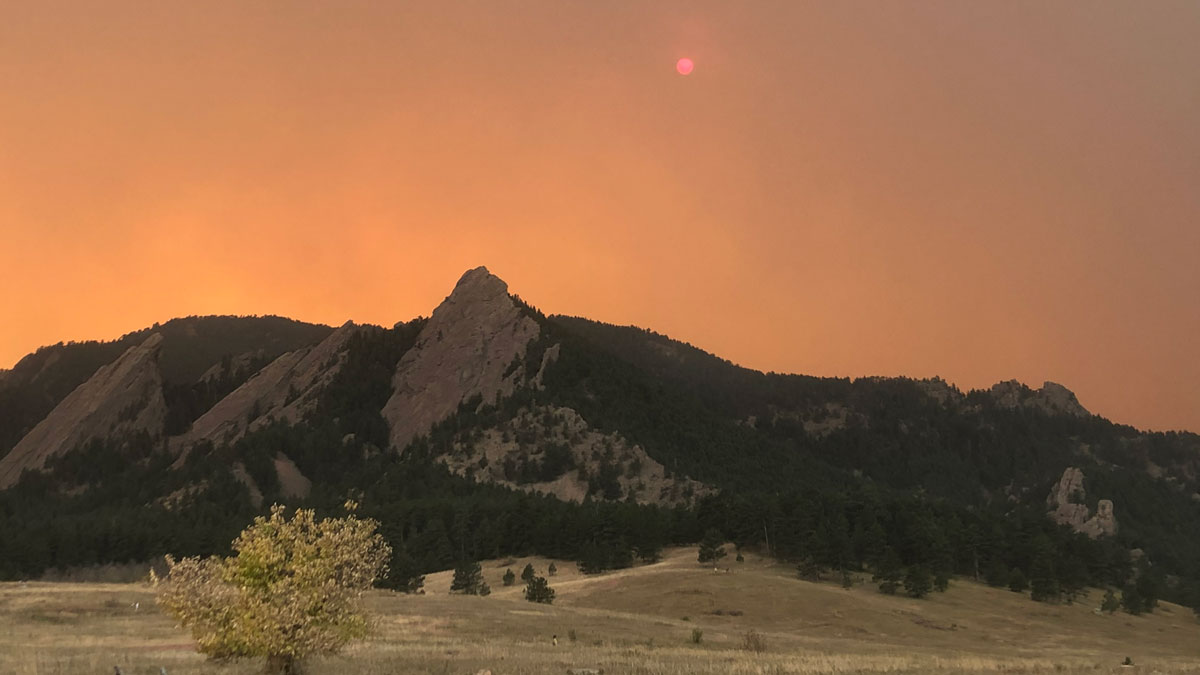
For Western Wildfires, the Immediate Past Is Prologue
A new machine learning approach trained on winter and spring climate conditions offers improved forecasts of summer fire activity across the western United States.
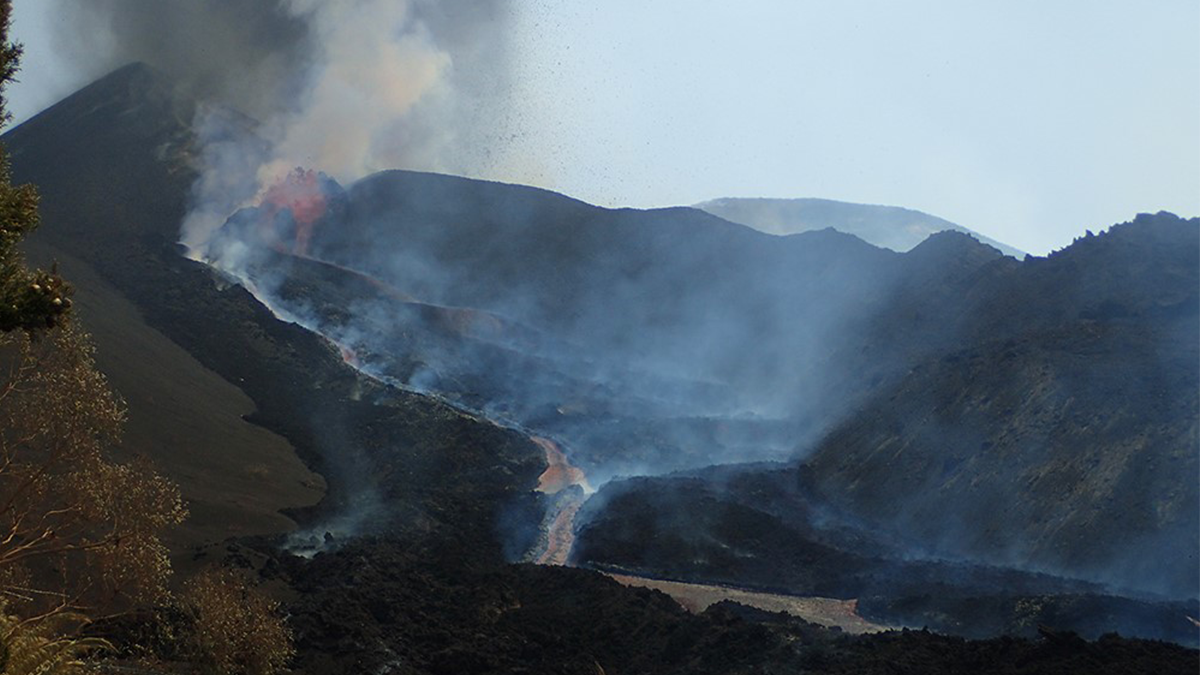
Dynamics of Volcanic Processes
A new cross-journal special collection invites contributions on modern approaches used to investigate dynamics of volcanic processes.
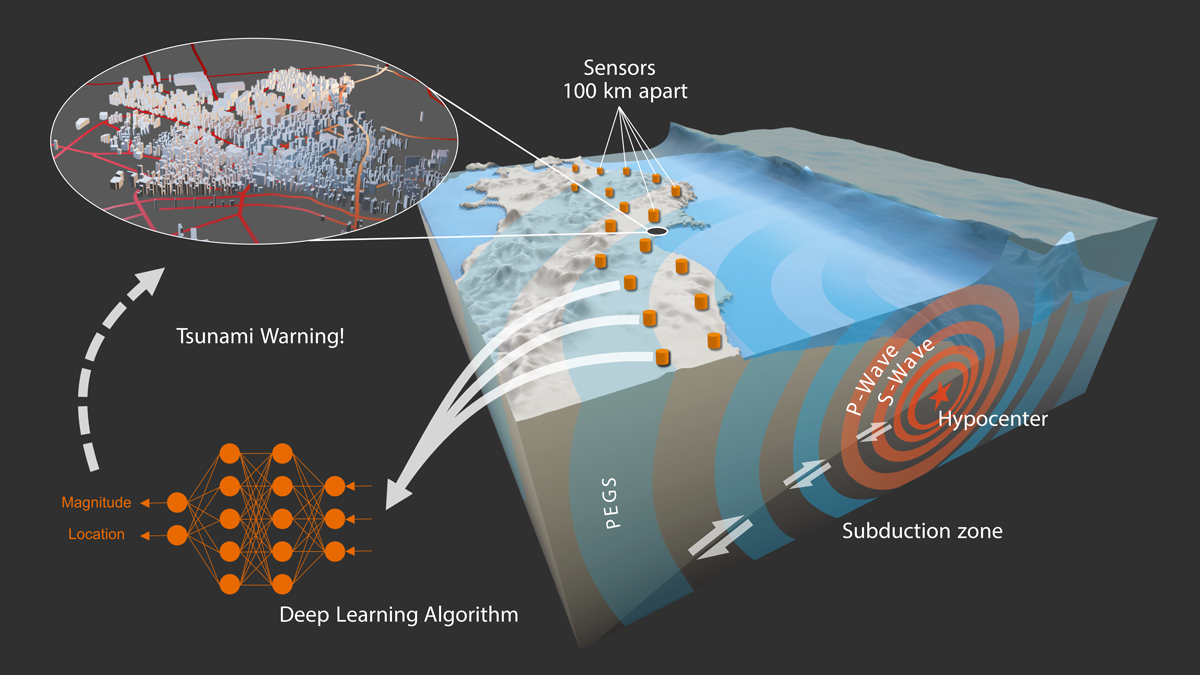
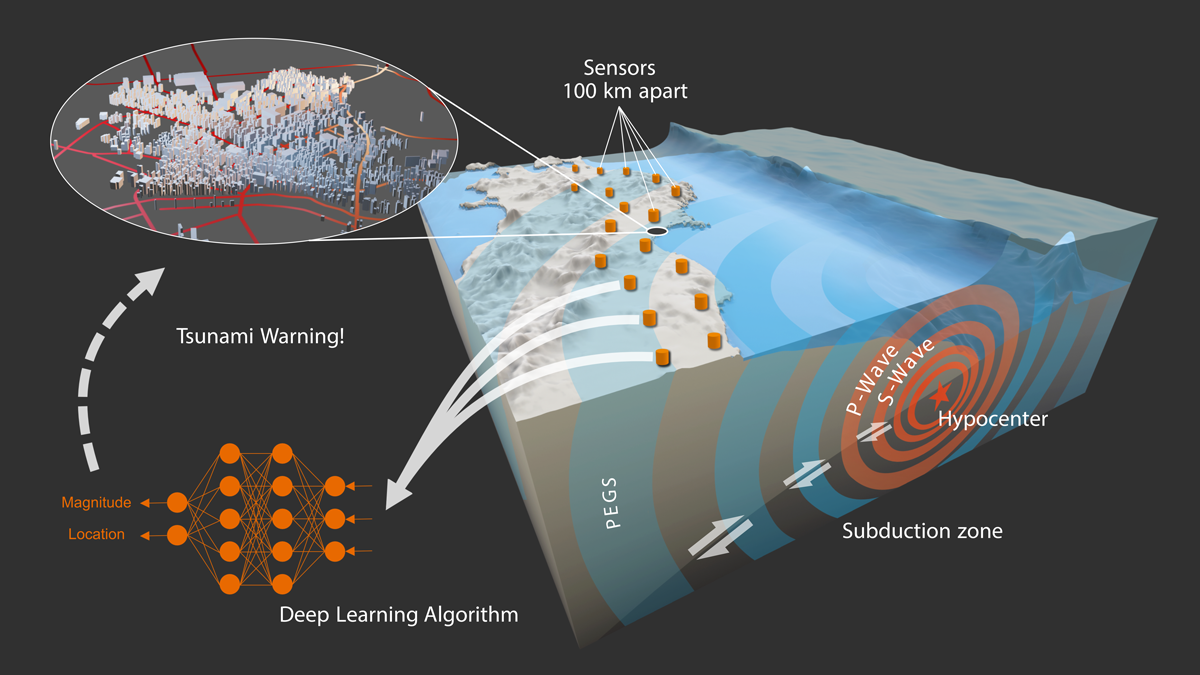
Monitoreando terremotos a la velocidad de la luz
Nueva investigación utiliza la gravedad y un modelo de aprendizaje automático para estimar instantáneamente la magnitud y ubicación de grandes terremotos.
Despite Improvements, China’s Air Remains Unsafe
Toxic particulate matter has decreased by about a third over the past decade, but levels are still above what’s considered healthy.
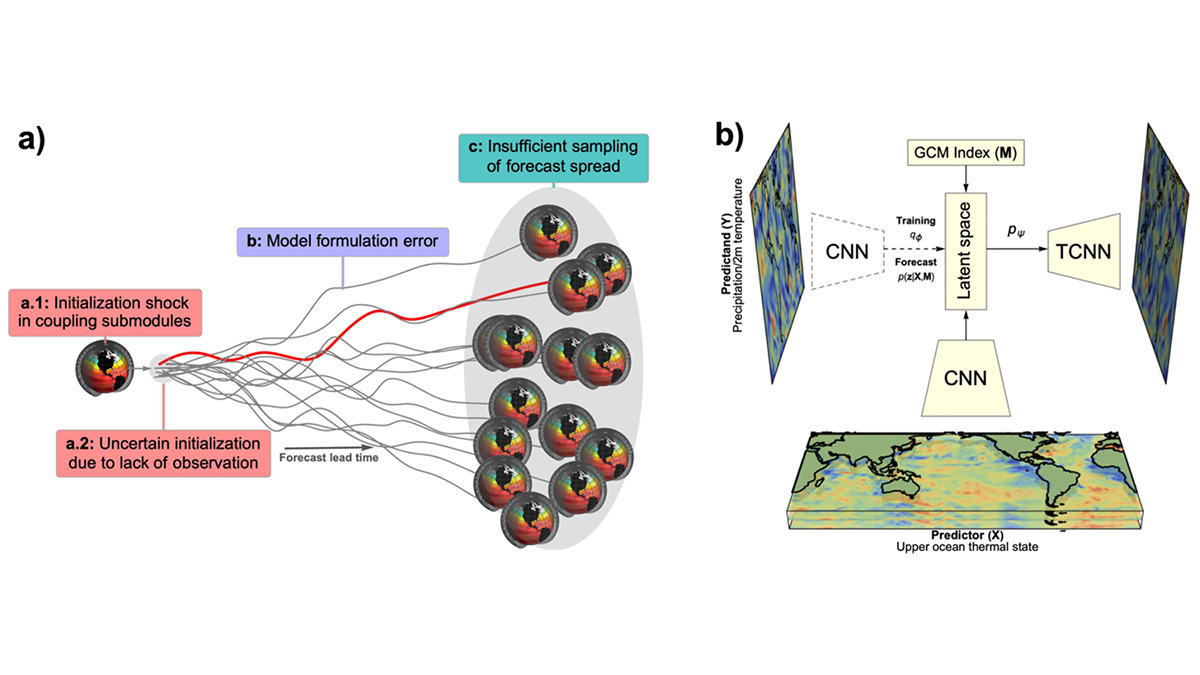
Learning from Climate Simulations for Global Seasonal Forecast
A probabilistic deep learning methodology that learns from climate simulation big data offers advantageous seasonal forecasting skill and crucial climate model diagnosis information at a global scale.
Algorithm Detects Thousands of Missing Levees from U.S. Database
An existing levee database accounts for just one fifth of the country’s actual total levee count, limiting the study of how these embankments affect riparian ecosystem health in the United States.
The Big Data Revolution Unlocks New Opportunities for Seismology
The field of seismology is entering a new era where our understanding of earthquakes and the solid earth is increasingly driven by new Big Data experiments and algorithms.
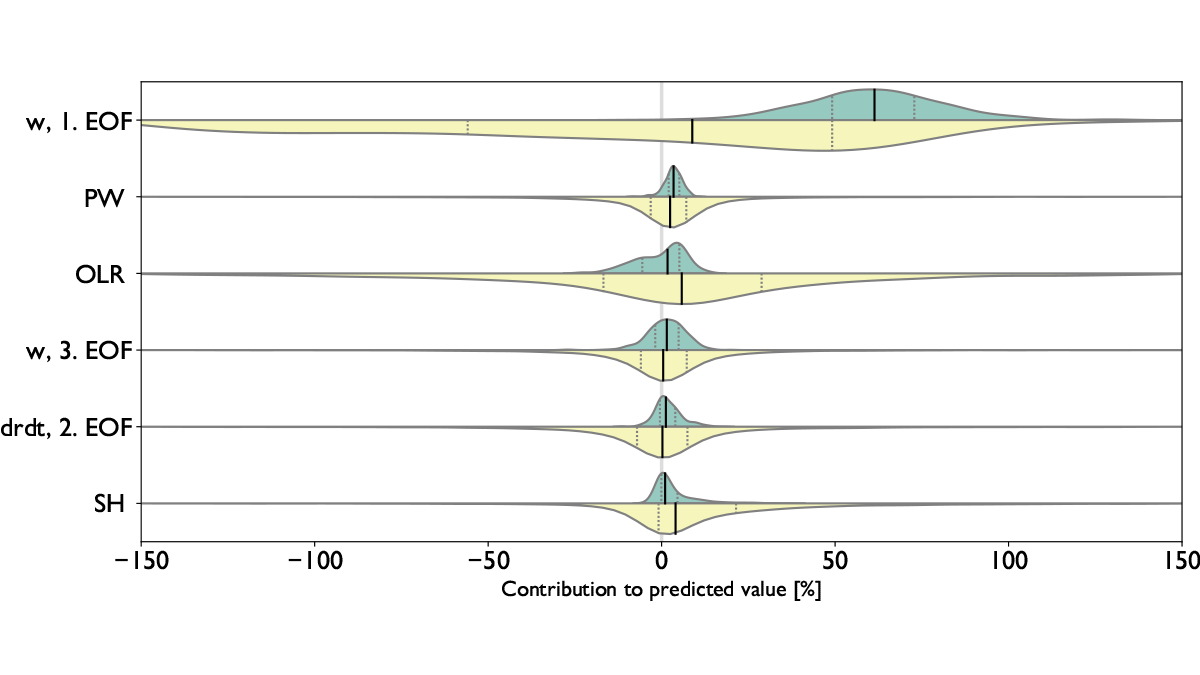
Using Artificial Intelligence to Study Convection
Machine learning techniques are used to examine relationships between the large-scale state of the atmosphere, the convection total area, and the degree of organization in northern Australia.
Monitoring Earthquakes at the Speed of Light
New research uses gravity and a machine learning model to instantaneously estimate the magnitude and location of large earthquakes.