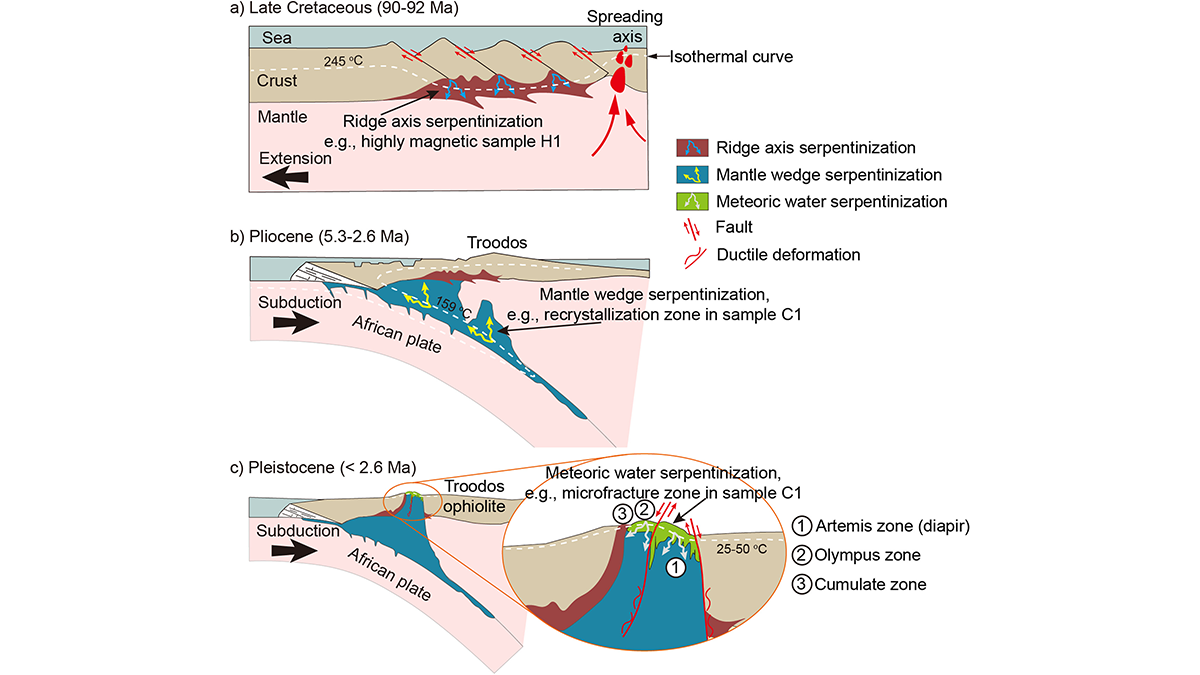
Scientists reconstruct the magnetization timeline of serpentinized rocks from the Troodos ophiolite by investigating remanent magnetization-carrying structures with a Quantum Diamond Microscope.
magnetic fields & magnetism
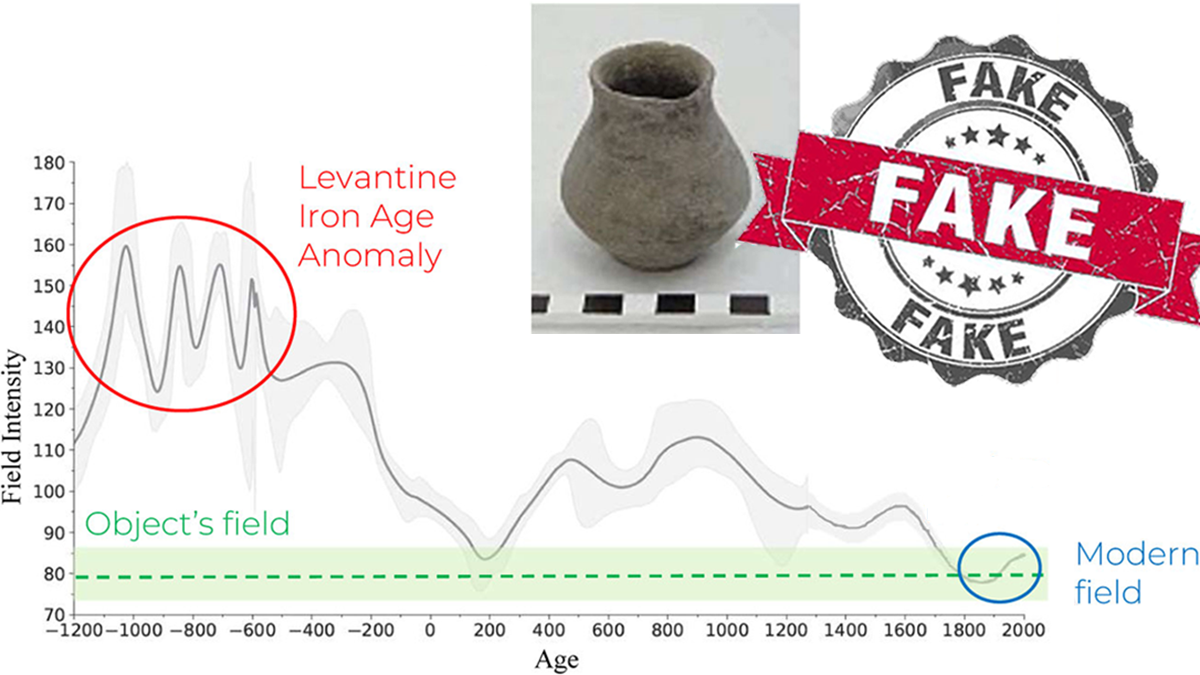
Credible or Counterfeit: How Paleomagnetism Can Help Archaeologists Find Frauds
Duplicating artifacts that preserve records from biblical times is a lucrative business. A method used for both dating artifacts and reconstructing Earth’s history could identify phony pieces.
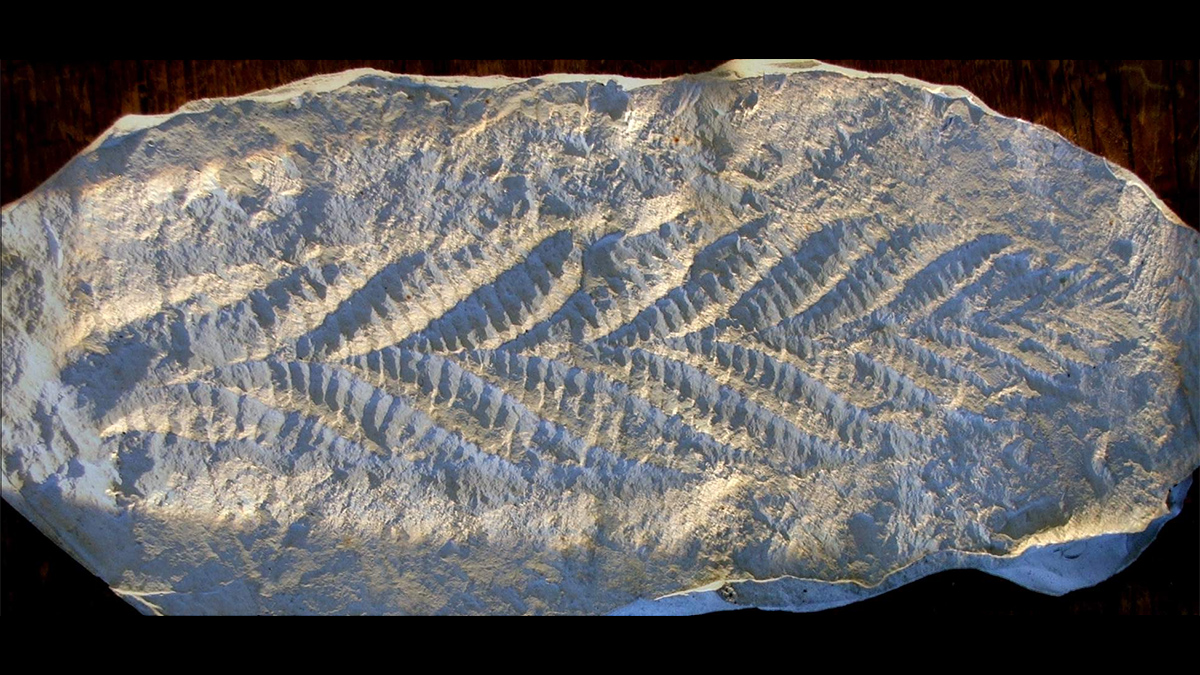
The Long and the Weak of It—The Ediacaran Magnetic Field
A roughly 70-million-year interval of anomalously weak magnetic field during the Ediacaran period could have triggered atmospheric changes that supported the rise of macroscopic life.
A Weak Spot in Earth’s Magnetic Field Is Going from Bad to Worse
This could be bad news for satellites and spacefarers.
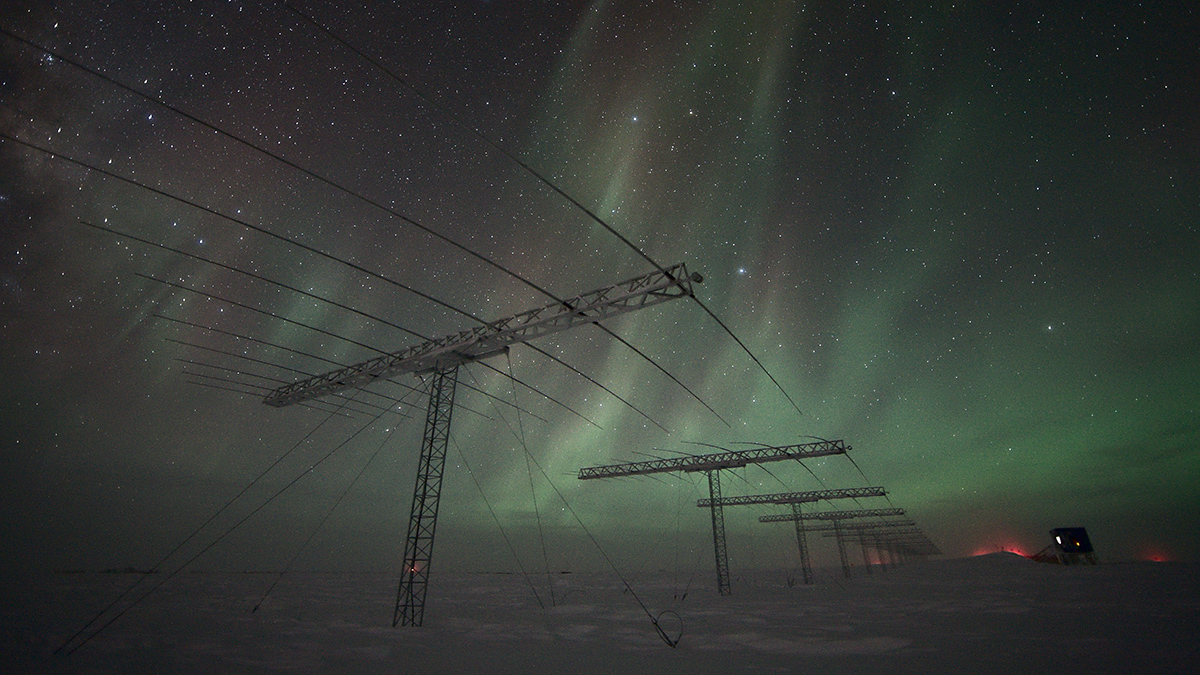
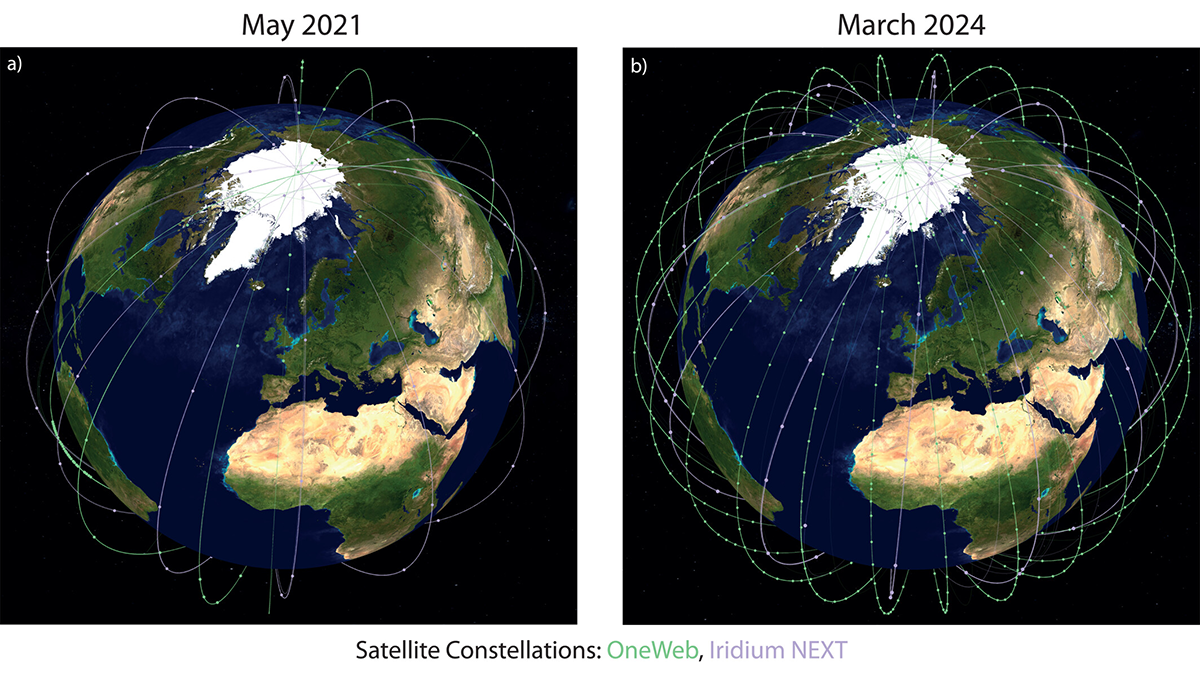
Space Weather Monitoring from Commercial Satellite Mega-Constellations
Enabling unprecedented monitoring of key electric current systems in low-Earth orbit using commercial satellite mega-constellations advances space weather monitoring.
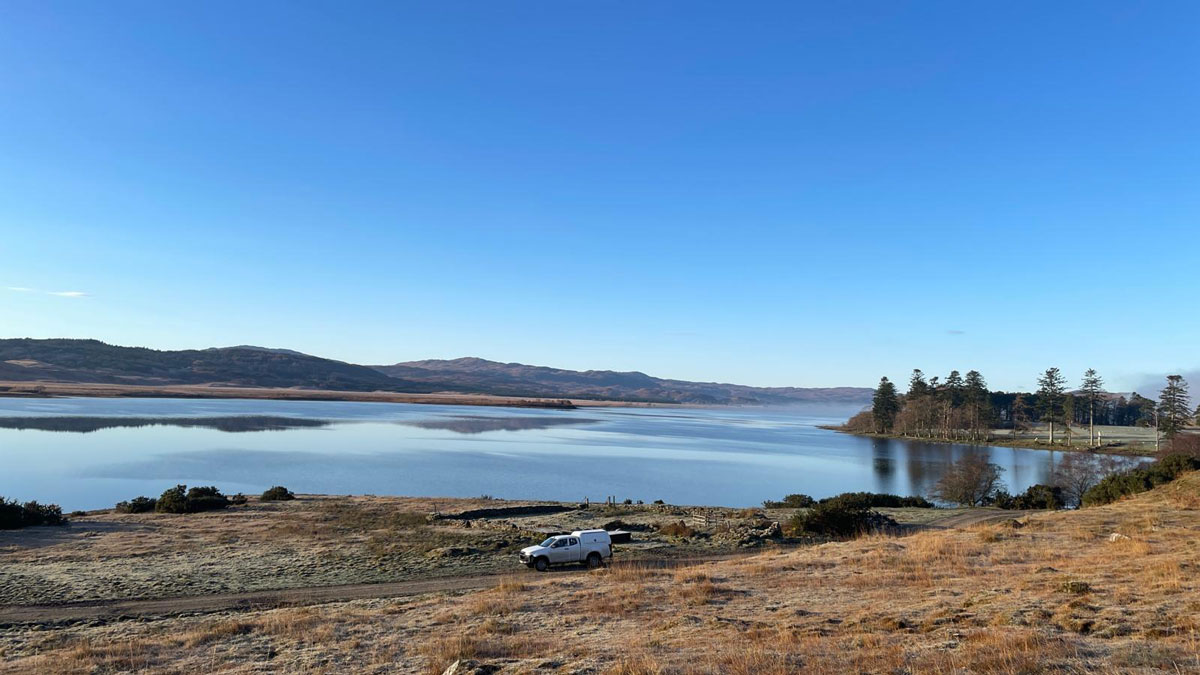
New 3D Model Reveals Geophysical Structures Beneath Britain
Using magnetotelluric data to identify subsurface electrically conductive and resistive areas, scientists can identify underground features and predict how space weather may affect infrastructure.
Magnetic “Switchback” Detected near Earth for First Time
Until recently, this type of zigzag shape—formed by energetic rearrangement of magnetic field lines—had been seen only near the Sun.
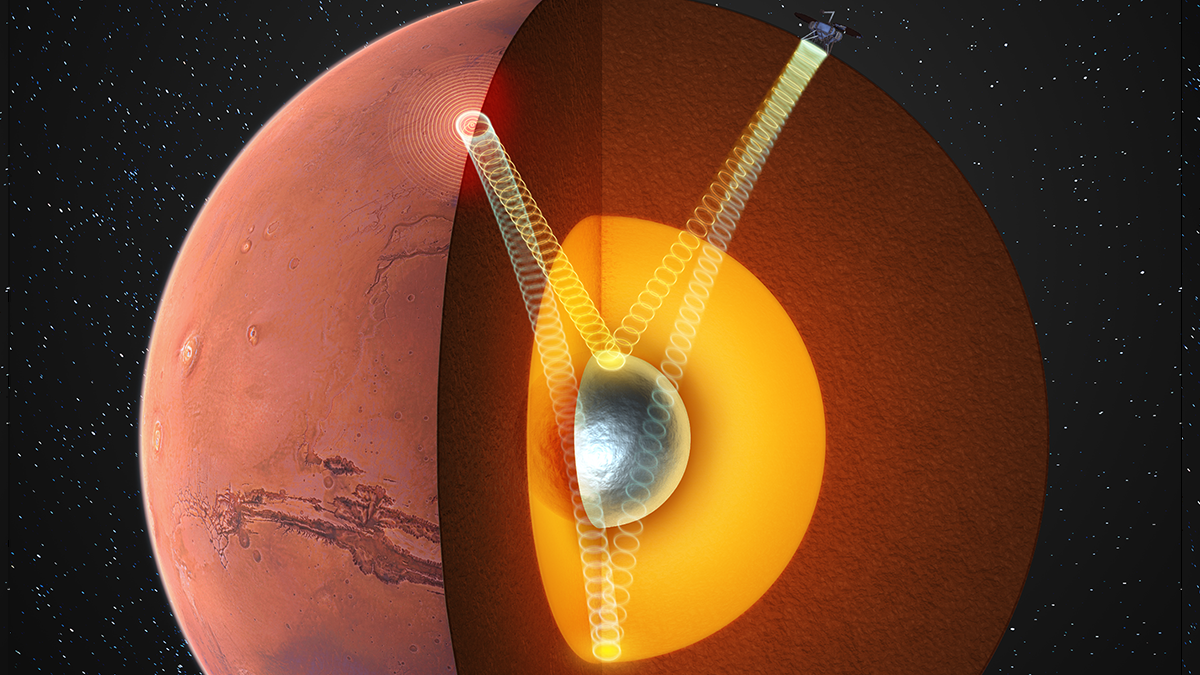
Scientists May Have Finally Detected a Solid Inner Core on Mars
Seismic clues from NASA’s InSight mission suggest that Mars hides a solid inner core, and raise new questions about why the planet’s magnetic field disappeared.
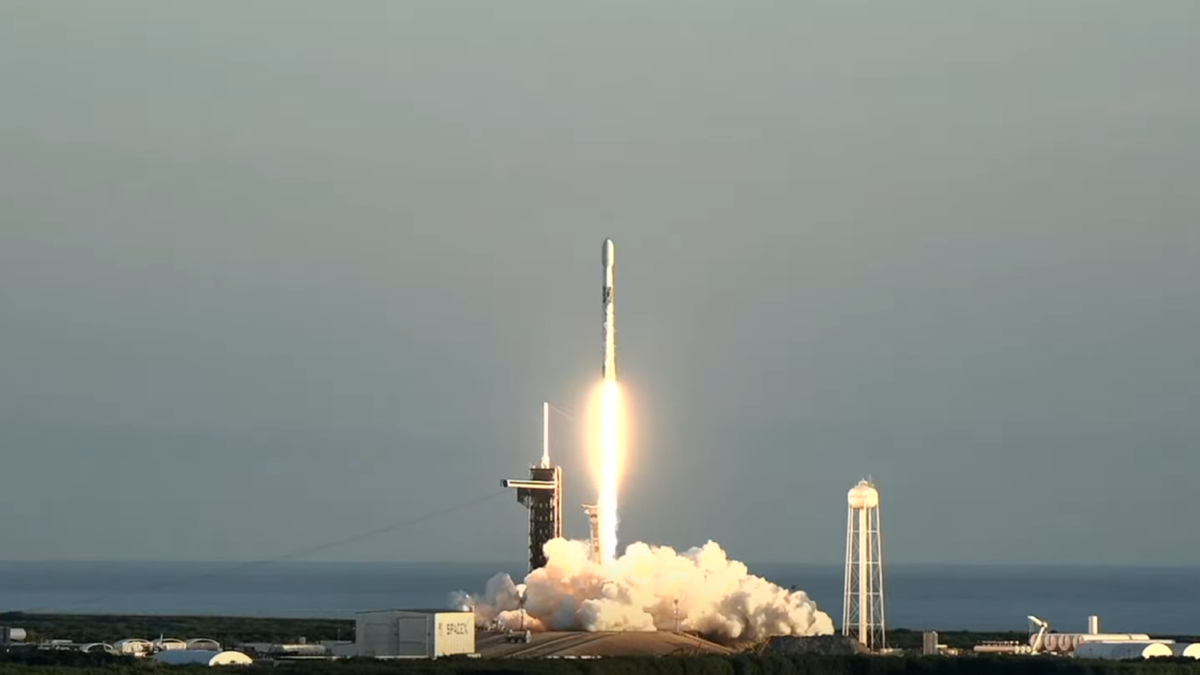
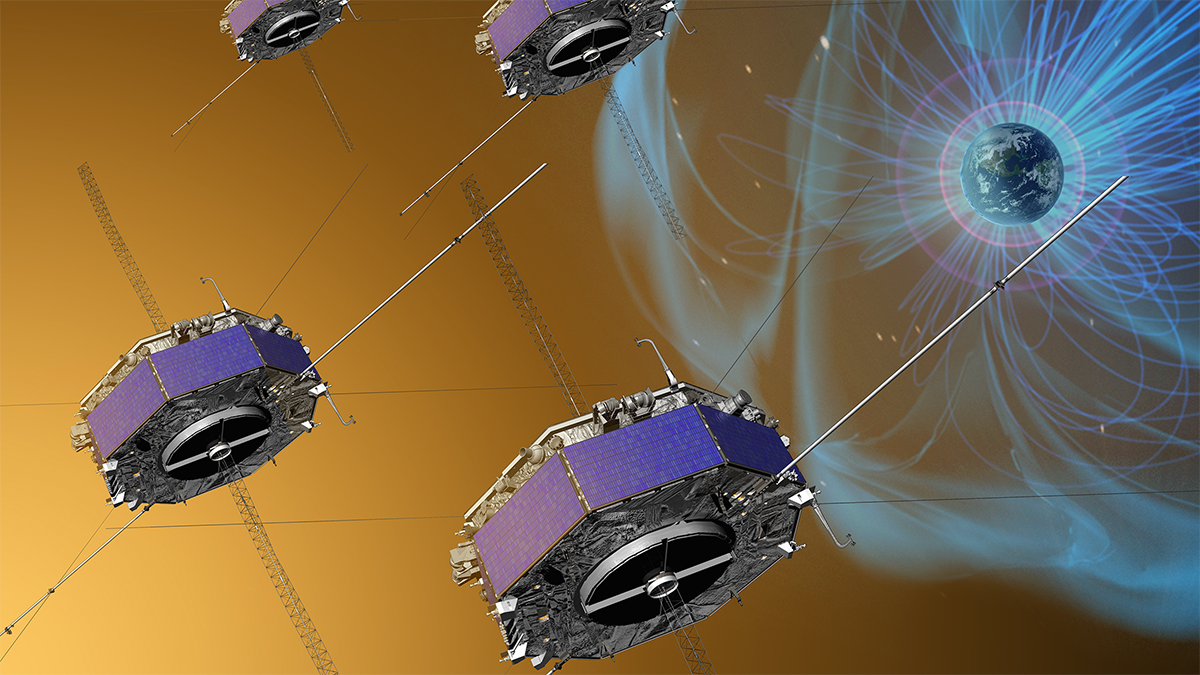
Trio of Space Weather Satellites Take Flight
These three satellites will that study the solar wind and its impacts.
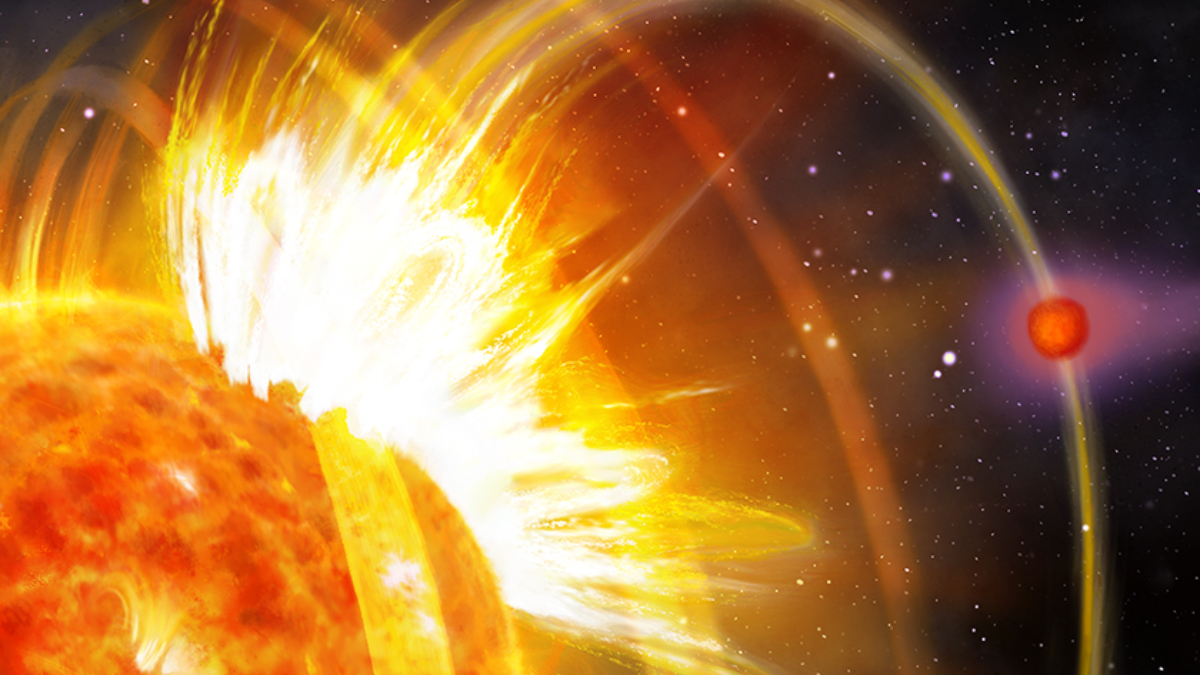
Exoplanet Triggers Stellar Flares and Hastens Its Demise
HIP 67522 b can’t stop blasting itself in the face with stellar flares, a type of magnetic interaction that scientists have spent decades looking for.